Fgf-10 is required for both limb and lung development and exhibits striking functional similarity to Drosophila branchless
- PMID: 9784490
- PMCID: PMC317210
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.12.20.3156
Fgf-10 is required for both limb and lung development and exhibits striking functional similarity to Drosophila branchless
Abstract
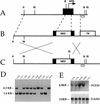
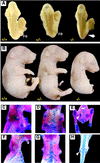
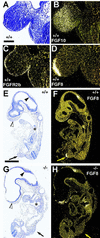
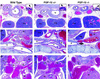
Fgf-10-deficient mice (Fgf-10(-/-)) were generated to determine the role(s) of Fgf-10 in vertebrate development. Limb bud initiation was abolished in Fgf-10(-/-) mice. Strikingly, Fgf-10(-/-) fetuses continued to develop until birth, despite the complete absence of both fore- and hindlimbs. Fgf-10 is necessary for apical ectodermal ridge (AER) formation and acts epistatically upstream of Fgf-8, the earliest known AER marker in mice. Fgf-10(-/-) mice exhibited perinatal lethality associated with complete absence of lungs. Although tracheal development was normal, main-stem bronchial formation, as well as all subsequent pulmonary branching morphogenesis, was completely disrupted. The pulmonary phenotype of Fgf-10(-/-) mice is strikingly similar to that of the Drosophila mutant branchless, an Fgf homolog.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Fgf8 signalling from the AER is essential for normal limb development.Nat Genet. 2000 Dec;26(4):460-3. doi: 10.1038/82609. Nat Genet. 2000. PMID: 11101846
-
Fgf10 is essential for limb and lung formation.Nat Genet. 1999 Jan;21(1):138-41. doi: 10.1038/5096. Nat Genet. 1999. PMID: 9916808
-
Formin isoforms are differentially expressed in the mouse embryo and are required for normal expression of fgf-4 and shh in the limb bud.Development. 1995 Oct;121(10):3151-62. doi: 10.1242/dev.121.10.3151. Development. 1995. PMID: 7588050
-
Function of FGF-4 in limb development.Mol Reprod Dev. 1994 Sep;39(1):83-8; discussion 88-9. doi: 10.1002/mrd.1080390113. Mol Reprod Dev. 1994. PMID: 7999365 Review.
-
FGF-FGFR signaling in vertebrate organogenesis.Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 1999 Jul;45(5):631-8. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 1999. PMID: 10512194 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular crosstalk in tracheal development and its recurrence in adult tissue regeneration.Dev Dyn. 2021 Nov;250(11):1552-1567. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.345. Epub 2021 May 6. Dev Dyn. 2021. PMID: 33840142 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fgf10 gene expression is delayed in the embryonic lung mesenchyme in the adriamycin mouse model.Pediatr Surg Int. 2010 Jan;26(1):23-7. doi: 10.1007/s00383-009-2519-3. Pediatr Surg Int. 2010. PMID: 19855977
-
Systems analysis of salivary gland development and disease.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med. 2010 Nov-Dec;2(6):670-82. doi: 10.1002/wsbm.94. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med. 2010. PMID: 20890964 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Specific sides to multifaceted glycosaminoglycans are observed in embryonic development.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2010 Aug;21(6):631-7. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2010.06.002. Epub 2010 Jul 3. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2010. PMID: 20599516 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dual functions of ASCIZ in the DNA base damage response and pulmonary organogenesis.PLoS Genet. 2010 Oct 21;6(10):e1001170. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1001170. PLoS Genet. 2010. PMID: 20975950 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bellusci S, Grindley J, Emoto H, Itoh N, Hogan BLM. Fibroblast growth factor 10 (FGF10) and branching morphogenesis in the embryonic mouse lung. Development. 1997;124:4867–4878. - PubMed
-
- Cardoso WV, Itoh A, Nogawa H, Mason I, Brody JS. FGF1 and FGF7 induce distinct patterns of growth and differentiation in embryonic lung epithelium. Dev Dyn. 1997;208:398–405. - PubMed
-
- Chang DT, López A, von Kessler DP, Chiang C, Simandl BK, Zhao R, Seldin MF, Fallon JF, Beachy PA. Products, genetic linkage and limb patterning activity of a murine hedgehog gene. Development. 1994;120:3339–3353. - PubMed
-
- Chiang C, Litingtung Y, Lee E, Young KE, Cordoen JL, Westphal H, Beachy PA. Cyclopia and defective axial patterning in mice lacking Sonic hedgehog gene function. Nature. 1996;383:407–413. - PubMed
-
- Cohn MJ, Izpiseúa-Belmonte J-C, Abud H, Heath JK, Tickle C. Fibroblast growth factors induce additional limb development from the flank of chick embryos. Cell. 1995;80:739–746. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
