Cleavage motifs of the yeast 20S proteasome beta subunits deduced from digests of enolase 1
- PMID: 9770515
- PMCID: PMC22860
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.21.12504
Cleavage motifs of the yeast 20S proteasome beta subunits deduced from digests of enolase 1
Abstract
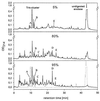
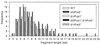
The 436-amino acid protein enolase 1 from yeast was degraded in vitro by purified wild-type and mutant yeast 20S proteasome particles. Analysis of the cleavage products at different times revealed a processive degradation mechanism and a length distribution of fragments ranging from 3 to 25 amino acids with an average length of 7 to 8 amino acids. Surprisingly, the average fragment length was very similar between wild-type and mutant 20S proteasomes with reduced numbers of active sites. This implies that the fragment length is not influenced by the distance between the active sites, as previously postulated. A detailed analysis of the cleavages also allowed the identification of certain amino acid characteristics in positions flanking the cleavage site that guide the selection of the P1 residues by the three active beta subunits. Because yeast and mammalian proteasomes are highly homologous, similar cleavage motifs might be used by mammalian proteasomes. Therefore, our data provide a basis for predicting proteasomal degradation products from which peptides are sampled by major histocompatibility complex class I molecules for presentation to cytotoxic T cells.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Discrete cleavage motifs of constitutive and immunoproteasomes revealed by quantitative analysis of cleavage products.J Exp Med. 2001 Jul 2;194(1):1-12. doi: 10.1084/jem.194.1.1. J Exp Med. 2001. PMID: 11435468 Free PMC article.
-
The 26S proteasome of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae.FEBS Lett. 1994 Nov 21;355(1):69-75. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)01177-x. FEBS Lett. 1994. PMID: 7957966
-
PAProC: a prediction algorithm for proteasomal cleavages available on the WWW.Immunogenetics. 2001 Mar;53(2):87-94. doi: 10.1007/s002510100300. Immunogenetics. 2001. PMID: 11345595
-
Studies on the yeast proteasome uncover its basic structural features and multiple in vivo functions.Enzyme Protein. 1993;47(4-6):189-201. doi: 10.1159/000468678. Enzyme Protein. 1993. PMID: 7697119 Review.
-
Structure and assembly of the 20S proteasome.Cell Mol Life Sci. 1998 Mar;54(3):253-62. doi: 10.1007/s000180050147. Cell Mol Life Sci. 1998. PMID: 9575337 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Crystal structure of suboptimal viral fragments of Epstein Barr Virus Rta peptide-HLA complex that stimulate CD8 T cell response.Sci Rep. 2019 Nov 13;9(1):16660. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-53201-6. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31723204 Free PMC article.
-
Computational prediction of cleavage using proteasomal in vitro digestion and MHC I ligand data.J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2013 Sep;14(9):816-28. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B1200299. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2013. PMID: 24009202 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Protein Kinase G to Treat Cardiac Proteotoxicity.Front Physiol. 2020 Jul 28;11:858. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.00858. eCollection 2020. Front Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32848832 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tumors escape immunosurveillance by overexpressing the proteasome activator PSME3.Oncoimmunology. 2020 May 21;9(1):1761205. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2020.1761205. Oncoimmunology. 2020. PMID: 32923122 Free PMC article.
-
Proline- and Arginine-Rich Peptides as Flexible Allosteric Modulators of Human Proteasome Activity.J Med Chem. 2019 Jan 10;62(1):359-370. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.8b01025. Epub 2018 Dec 3. J Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 30452262 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Groll M, Ditzel L, Lowe J, Stock D, Bochtler M, Bartunik H D, Huber R. Nature (London) 1997;386:463–471. - PubMed
-
- Kisselev A F, Akopian T N, Goldberg A L. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:1982–1989. - PubMed
-
- Orlowski M, Michaud C. Biochemistry. 1989;28:9270–9278. - PubMed
-
- Cardozo C, Vinitsky A, Hidalgo M C, Michaud C, Orlowski M. Biochemistry. 1992;31:7373–7380. - PubMed
-
- Heinemeyer W, Fischer M, Krimmer T, Stachon U, Wolf D H. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:25200–25209. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

