Induction of microsatellite instability by oxidative DNA damage
- PMID: 9770509
- PMCID: PMC22854
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.21.12468
Induction of microsatellite instability by oxidative DNA damage
Abstract
Instability of repetitive sequences, both in intronic sequences and within coding regions, has been demonstrated to be a hallmark of genomic instability in human cancer. Understanding how these mutational events arise may provide an opportunity for prevention or early intervention in cancer development. To study the source of this instability, we have identified a region of the beta-lactamase gene that is tolerant to the insertion of fragments of exogenous DNA as large as 1,614 bp with minimal loss of enzyme activity, as determined by antibiotic resistance. Fragments inserted out-of-frame render Escherichia coli sensitive to antibiotic, and compensatory frameshift mutations that restore the reading frame of beta-lactamase can be selected on the basis of antibiotic resistance. We have utilized this site to insert a synthetic microsatellite sequence within the beta-lactamase gene and selected for mutations yielding frameshifts. This assay provides for detection of one frameshift mutation in a background of 10(6) wild-type sequences. Mismatch repair deficiency increased the observed frameshift frequency approximately 300-fold. Exposure of plasmid containing microsatellite sequences to hydrogen peroxide resulted in frameshift mutations that were localized exclusively to the microsatellite sequences, whereas DNA damage by UV or N-methyl-N'-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine did not result in enhanced mutagenesis. We postulate that in tumor cells, endogenous production of oxygen free radicals may be a major factor in promoting instability of microsatellite sequences. This beta-lactamase assay may provide a sensitive methodology for the detection and quantitation of mutations associated with the development of cancer.
Figures
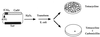
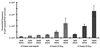

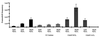
Similar articles
-
Mutation frequency analysis of mononucleotide and dinucleotide repeats after oxidative stress.Environ Mol Mutagen. 2003;42(2):75-84. doi: 10.1002/em.10179. Environ Mol Mutagen. 2003. PMID: 12929119
-
Microsatellite instability induced by hydrogen peroxide in Escherichia coli.Mutat Res. 2000 Feb 14;447(2):187-98. doi: 10.1016/s0027-5107(99)00206-7. Mutat Res. 2000. PMID: 10751602
-
Hydrogen peroxide-induced microsatellite instability in the Escherichia coli K-12 endogenous tonB gene.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2003 Jun 27;306(2):570-6. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(03)01027-1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2003. PMID: 12804603
-
Selection for genome instability by DNA damage in human cells: unstable microsatellites and their consequences for tumourigenesis.Radiat Oncol Investig. 1997;5(3):111-4. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1520-6823(1997)5:3<111::AID-ROI5>3.0.CO;2-0. Radiat Oncol Investig. 1997. PMID: 9303066 Review.
-
Frameshift mutation, microsatellites and mismatch repair.Mutat Res. 1999 Nov;437(3):195-203. doi: 10.1016/s1383-5742(99)00066-6. Mutat Res. 1999. PMID: 10592327 Review.
Cited by
-
Common mitochondrial DNA mutations generated through DNA-mediated charge transport.Biochemistry. 2009 Feb 3;48(4):660-6. doi: 10.1021/bi801570j. Biochemistry. 2009. PMID: 19128037 Free PMC article.
-
Astaxanthin protects oxidative stress mediated DNA damage and enhances longevity in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Biogerontology. 2021 Feb;22(1):81-100. doi: 10.1007/s10522-020-09904-9. Epub 2020 Oct 27. Biogerontology. 2021. PMID: 33108581
-
Induction of frameshift and base pair substitution mutations by the major DNA adduct of the endogenous carcinogen malondialdehyde.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Nov 25;100(24):14247-52. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2332176100. Epub 2003 Nov 5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003. PMID: 14603032 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic changes of p53, K-ras, and microsatellite instability in gallbladder carcinoma in high-incidence areas of Japan and Hungary.World J Gastroenterol. 2008 Jan 7;14(1):70-5. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.70. World J Gastroenterol. 2008. PMID: 18176964 Free PMC article.
-
Biological Aging and the Cellular Pathogenesis of Huntington's Disease.J Huntingtons Dis. 2020;9(2):115-128. doi: 10.3233/JHD-200395. J Huntingtons Dis. 2020. PMID: 32417788 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

