The Epstein-Barr virus lytic transactivator Zta interacts with the helicase-primase replication proteins
- PMID: 9765394
- PMCID: PMC110266
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.72.11.8559-8567.1998
The Epstein-Barr virus lytic transactivator Zta interacts with the helicase-primase replication proteins
Abstract
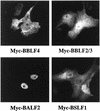
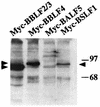
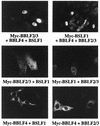
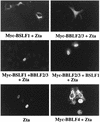
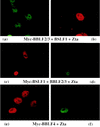
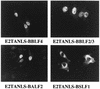
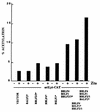
The Epstein-Barr virus transactivator Zta triggers lytic gene expression and is essential for replication of the lytic origin, oriLyt. Previous analysis indicated that the Zta activation domain contributed a replication-specific function. We now show that the Zta activation domain interacts with components of the EBV helicase-primase complex. The three helicase-primase proteins BBLF4 (helicase), BSLF1 (primase), and BBLF2/3 (primase-associated factor) were expressed fused to the Myc epitope. When expression plasmids for BBLF4 or BBLF2/3 plus BSLF1 (primase subcomplex) were separately transfected, the proteins localized to the cytoplasm. Interaction between Zta and the components of the helicase-primase complex was tested by examining the ability of Zta to alter the intracellular localization of these proteins. Cotransfection of Zta with Myc-BBLF4 resulted in nuclear translocation of Myc-BBLF4; similarly, cotransfection of Zta with the primase subcomplex led to nuclear translocation of the Myc-BSLF1 and Myc-BBLF2/3 proteins. This relocalization provides evidence for an interaction between Zta and the helicase and Zta and the primase subcomplex. An affinity assay using glutathione S-transferase-Zta fusion proteins demonstrated that Myc-BBLF4 and Myc-BBLF2/3 plus BSLF1 bound to the Zta activation domain (amino acids 1 to 133). In the nuclear relocalization assay, the amino-terminal 25 amino acids of Zta were required for efficient interaction with the primase subcomplex but not for interaction with BBLF4. Evidence for interaction between oriLyt bound Zta and the helicase-primase complex was obtained in a superactivation assay using an oriLyt-chloramphenicol acetyltransferase (CAT) reporter. Zta activated expression from a CAT reporter containing the complete oriLyt region and regulated by the oriLyt BHLF1 promoter. Cotransfection of the helicase-primase proteins, one of which was fused to a heterologous activation domain, led to Zta-dependent superactivation of CAT expression. This assay also provided evidence for an interaction between the single-stranded DNA binding protein, BALF2, and the Zta-tethered helicase-primase complex. The helicase-primase interaction is consistent with a role for Zta in stabilizing the formation of an origin-bound replication complex.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Interaction with the Epstein-Barr virus helicase targets Zta to DNA replication compartments.J Virol. 2001 Sep;75(18):8792-802. doi: 10.1128/jvi.75.18.8792-8802.2001. J Virol. 2001. PMID: 11507224 Free PMC article.
-
The Epstein-Barr virus pol catalytic subunit physically interacts with the BBLF4-BSLF1-BBLF2/3 complex.J Virol. 2000 Mar;74(6):2550-7. doi: 10.1128/jvi.74.6.2550-2557.2000. J Virol. 2000. PMID: 10684269 Free PMC article.
-
trans-acting requirements for replication of Epstein-Barr virus ori-Lyt.J Virol. 1992 Aug;66(8):5030-9. doi: 10.1128/JVI.66.8.5030-5039.1992. J Virol. 1992. PMID: 1321285 Free PMC article.
-
Replication of Epstein-Barr virus oriLyt: lack of a dedicated virally encoded origin-binding protein and dependence on Zta in cotransfection assays.J Virol. 1995 May;69(5):2998-3006. doi: 10.1128/JVI.69.5.2998-3006.1995. J Virol. 1995. PMID: 7707526 Free PMC article.
-
EBV replication enzymes.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2001;258:65-87. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-56515-1_5. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11443868 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Interaction with the Epstein-Barr virus helicase targets Zta to DNA replication compartments.J Virol. 2001 Sep;75(18):8792-802. doi: 10.1128/jvi.75.18.8792-8802.2001. J Virol. 2001. PMID: 11507224 Free PMC article.
-
Oncogenic Properties of the EBV ZEBRA Protein.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Jun 5;12(6):1479. doi: 10.3390/cancers12061479. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32517128 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The CBP bromodomain and nucleosome targeting are required for Zta-directed nucleosome acetylation and transcription activation.Mol Cell Biol. 2003 Apr;23(8):2633-44. doi: 10.1128/MCB.23.8.2633-2644.2003. Mol Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 12665567 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear localization of CBF1 is regulated by interactions with the SMRT corepressor complex.Mol Cell Biol. 2001 Sep;21(18):6222-32. doi: 10.1128/MCB.21.18.6222-6232.2001. Mol Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11509665 Free PMC article.
-
A subset of replication proteins enhances origin recognition and lytic replication by the Epstein-Barr virus ZEBRA protein.PLoS Pathog. 2010 Aug 19;6(8):e1001054. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1001054. PLoS Pathog. 2010. PMID: 20808903 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Borowiec J A, Dean F B, Bullock P A, Hurwitz J. Binding and unwinding—how T antigen engages the SV40 origin of DNA replication. Cell. 1990;60:181–184. - PubMed
-
- Bruckner R C, Crute J J, Dodson M S, Lehman I R. The herpes simplex virus 1 origin binding protein: a DNA helicase. J Biol Chem. 1991;266:2669–2674. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

