The muscle regulatory factors MyoD and myf-5 undergo distinct cell cycle-specific expression in muscle cells
- PMID: 9744876
- PMCID: PMC2141770
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.142.6.1447
The muscle regulatory factors MyoD and myf-5 undergo distinct cell cycle-specific expression in muscle cells
Abstract
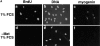
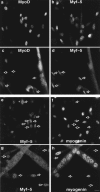
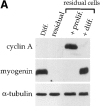
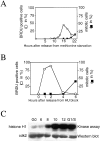
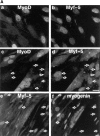
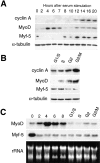
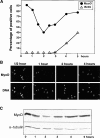
The muscle regulators MyoD and Myf-5 control cell cycle withdrawal and induction of differentiation in skeletal muscle cells. By immunofluorescence analysis, we show that MyoD and Myf-5 expression patterns become mutually exclusive when C2 cells are induced to differentiate with Myf-5 staining present in cells which fail to differentiate. Isolation of these undifferentiated cells reveals that upon serum stimulation they reenter the cell cycle, express MyoD and downregulate Myf-5. Similar regulations of MyoD and Myf-5 were observed using cultured primary myoblasts derived from satellite cells. To further analyze these regulations of MyoD and Myf-5 expression, we synchronized proliferating myoblasts. Analysis of MyoD and Myf-5 expression during cell cycle progression revealed distinct and contrasting profiles of expression. MyoD is absent in G0, peaks in mid-G1, falls to its minimum level at G1/S and reaugments from S to M. In contrast, Myf-5 protein is high in G0, decreases during G1 and reappears at the end of G1 to remain stable until mitosis. These data demonstrate that the two myogenic factors MyoD and Myf-5 undergo specific and distinct cell cycle-dependent regulation, thus establishing a correlation between the cell cycle-specific ratios of MyoD and Myf-5 and the capacity of cells to differentiate: (a) in G1, when cells express high levels of MyoD and enter differentiation; (b) in G0, when cells express high levels of Myf-5 and fail to differentiate.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Myogenin's functions do not overlap with those of MyoD or Myf-5 during mouse embryogenesis.Dev Biol. 1995 Nov;172(1):37-50. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1995.0004. Dev Biol. 1995. PMID: 7589813
-
Cultured myf5 null and myoD null muscle precursor cells display distinct growth defects.Biol Cell. 2000 Dec;92(8-9):565-72. doi: 10.1016/s0248-4900(00)01110-2. Biol Cell. 2000. PMID: 11374435
-
Activation of different myogenic pathways: myf-5 is induced by the neural tube and MyoD by the dorsal ectoderm in mouse paraxial mesoderm.Development. 1996 Feb;122(2):429-37. doi: 10.1242/dev.122.2.429. Development. 1996. PMID: 8625794
-
Targeted inactivation of myogenic factor genes reveals their role during mouse myogenesis: a review.Int J Dev Biol. 1996 Feb;40(1):345-53. Int J Dev Biol. 1996. PMID: 8735947 Review.
-
Transcriptional mechanisms regulating MyoD expression in the mouse.Cell Tissue Res. 1999 Apr;296(1):213-9. doi: 10.1007/s004410051282. Cell Tissue Res. 1999. PMID: 10199981 Review.
Cited by
-
Modulation of cell cycle progression by 5-azacytidine is associated with early myogenesis induction in murine myoblasts.Int J Biol Sci. 2013 Apr 27;9(4):391-402. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.4729. Print 2013. Int J Biol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23678289 Free PMC article.
-
DUX4c is up-regulated in FSHD. It induces the MYF5 protein and human myoblast proliferation.PLoS One. 2009 Oct 15;4(10):e7482. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0007482. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19829708 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of the role of the AMP-activated protein kinase in the stimulation of glucose transport in skeletal muscle cells.Biochem J. 2002 Apr 1;363(Pt 1):167-74. doi: 10.1042/0264-6021:3630167. Biochem J. 2002. PMID: 11903059 Free PMC article.
-
Apoptosis in differentiating C2C12 muscle cells selectively targets Bcl-2-deficient myotubes.Apoptosis. 2014 Jan;19(1):42-57. doi: 10.1007/s10495-013-0922-7. Apoptosis. 2014. PMID: 24129924 Free PMC article.
-
Maternal inflammation at midgestation impairs subsequent fetal myoblast function and skeletal muscle growth in rats, resulting in intrauterine growth restriction at term.Transl Anim Sci. 2019 Mar;3(2):txz037. doi: 10.1093/tas/txz037. Epub 2019 Apr 3. Transl Anim Sci. 2019. PMID: 31032478 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Albagli-Curiel O, Carnac G, Vandromme M, Vincent S, Crepieux P, Bonnieu A. Serum-induced inhibition of myogenesis is differentially relieved by retinoic acid and triiodothyronine in C2 murine muscle cells. Differentiation. 1993;52:201–210. - PubMed
-
- Alterio J, Courtois Y, Robelin J, Bechet D, Martelly I. Acidic and basic fibroblast growth factor mRNAs are expressed by skeletal muscle satellite cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990;166:1205–1212. - PubMed
-
- Auradé F, Pinset C, Chaffey P, Gros F, Montarras D. Myf-5, MyoD, Myogenin and MRF4myogenic derivatives of the embryonic mesenchymal cell line 10T1/2 exhibit the same adult phenotype. Differentiation. 1994;55:185–192. - PubMed
-
- Auradé F, Pfarr CM, Lindon C, Garcia A, Primig M, Montarras D, Pinset C. The glucocorticoid receptor and AP-1 are involved in a positive regulation of the muscle regulatory gene Myf-5 in cultured myoblasts. J Cell Sci. 1997;110:2771–2779. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

