Morphine-activated opioid receptors elude desensitization by beta-arrestin
- PMID: 9707575
- PMCID: PMC21436
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.17.9914
Morphine-activated opioid receptors elude desensitization by beta-arrestin
Abstract
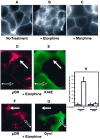
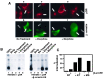
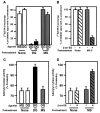
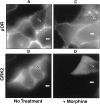
mu opioid receptors are targets of native opioid peptides and addictive analgesic drugs. A major clinical liability of opiate drugs is their ability to cause physiological tolerance. Individual opiates, such as morphine and etorphine, differ both in their ability to promote physiological tolerance and in their effects on receptor regulation by endocytosis. Here, we demonstrate that arrestins play a fundamental role in mediating this agonist-selective regulation and that morphine-activated mu receptors fail to undergo arrestin-dependent uncoupling from cognate G proteins. Thus, highly addictive opiate drugs elude a fundamental mode of physiological regulation that is mediated by agonist-specific interaction of opioid receptors with arrestins.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Functional dissociation of mu opioid receptor signaling and endocytosis: implications for the biology of opiate tolerance and addiction.Neuron. 1999 Aug;23(4):737-46. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(01)80032-5. Neuron. 1999. PMID: 10482240
-
Mu-opioid receptor desensitization by beta-arrestin-2 determines morphine tolerance but not dependence.Nature. 2000 Dec 7;408(6813):720-3. doi: 10.1038/35047086. Nature. 2000. PMID: 11130073
-
Enhanced morphine analgesia in mice lacking beta-arrestin 2.Science. 1999 Dec 24;286(5449):2495-8. doi: 10.1126/science.286.5449.2495. Science. 1999. PMID: 10617462
-
Neurokinin 1 receptors regulate morphine-induced endocytosis and desensitization of mu-opioid receptors in CNS neurons.J Neurosci. 2009 Jan 7;29(1):222-33. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4315-08.2009. J Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19129399 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of rapid opioid receptor desensitization, resensitization and tolerance in brain neurons.Br J Pharmacol. 2012 Mar;165(6):1704-1716. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01482.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 21564086 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Respiratory effects of low and high doses of fentanyl in control and β-arrestin 2-deficient mice.J Neurophysiol. 2021 Apr 1;125(4):1396-1407. doi: 10.1152/jn.00711.2020. Epub 2021 Mar 3. J Neurophysiol. 2021. PMID: 33656934 Free PMC article.
-
Somatosensory scaffolding structures.Front Mol Neurosci. 2012 Jan 23;5:2. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2012.00002. eCollection 2012. Front Mol Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22291616 Free PMC article.
-
Mu-opioid receptor desensitization: is morphine different?Br J Pharmacol. 2004 Nov;143(6):685-96. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705938. Epub 2004 Oct 25. Br J Pharmacol. 2004. PMID: 15504746 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional selectivity at the μ-opioid receptor: implications for understanding opioid analgesia and tolerance.Pharmacol Rev. 2011 Dec;63(4):1001-19. doi: 10.1124/pr.111.004598. Epub 2011 Aug 26. Pharmacol Rev. 2011. PMID: 21873412 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cellular neuroadaptations to chronic opioids: tolerance, withdrawal and addiction.Br J Pharmacol. 2008 May;154(2):384-96. doi: 10.1038/bjp.2008.100. Epub 2008 Apr 14. Br J Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18414400 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Evans C J. In: Diversity Among the Opioid Receptors. Korenman S G, Barchas J D, editors. New York: Oxford University Press; 1993. pp. 31–48.
-
- Grudt T J, Williams J T. Rev Neurosci. 1995;6:279–286. - PubMed
-
- Matthes H W, Maldonado R, Simonin F, Valverde O, Slowe S, Kitchen I, Befort K, Dierich A, Le M M, Dolle P, et al. Nature (London) 1996;383:819–823. - PubMed
-
- Yu Y, Zhang L, Yin X, Sun H, Uhl G R, Wang J B. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:28869–28874. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

