Integrin alpha1beta1 mediates a unique collagen-dependent proliferation pathway in vivo
- PMID: 9679154
- PMCID: PMC2133043
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.142.2.587
Integrin alpha1beta1 mediates a unique collagen-dependent proliferation pathway in vivo
Abstract
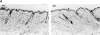
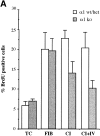
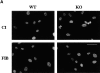
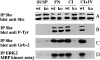
Activation of integrins upon binding to extracellular matrix proteins is believed to be a crucial step for the regulation of cell survival and proliferation. We have used integrin alpha1-null mice to investigate the role of this collagen receptor in the regulation of cell growth and survival in vivo. alpha1-deficient animals, which are viable and fertile, have a hypocellular dermis and a deficiency in dermal fibroblast proliferation as embryos. In vitro analysis of alpha1-null embryonic fibroblasts has revealed that their proliferation rate is markedly reduced when plated on collagenous substrata, despite normal attachment and spreading. Moreover, on the same collagenous matrices, alpha1-null fibroblasts fail to recruit and activate the adaptor protein Shc. The failure to activate Shc is accompanied by a downstream deficiency in recruitment of Grb2 and subsequent mitogen-activated protein kinase activation. Taken together with the growth deficiency observed on collagens, this finding indicates that the alpha1beta1 is the sole collagen receptor which can activate the Shc mediated growth pathway. Thus, integrin alpha1 has a unique role among the collagen receptors in regulating both in vivo and in vitro cell proliferation in collagenous matrices.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Multiple Grb2-mediated integrin-stimulated signaling pathways to ERK2/mitogen-activated protein kinase: summation of both c-Src- and focal adhesion kinase-initiated tyrosine phosphorylation events.Mol Cell Biol. 1998 May;18(5):2571-85. doi: 10.1128/MCB.18.5.2571. Mol Cell Biol. 1998. PMID: 9566877 Free PMC article.
-
The coupling of alpha6beta4 integrin to Ras-MAP kinase pathways mediated by Shc controls keratinocyte proliferation.EMBO J. 1997 May 1;16(9):2365-75. doi: 10.1093/emboj/16.9.2365. EMBO J. 1997. PMID: 9171350 Free PMC article.
-
Signal transduction by beta1 integrin receptors in human chondrocytes in vitro: collaboration with the insulin-like growth factor-I receptor.Biochem J. 1999 Sep 15;342 Pt 3(Pt 3):615-23. Biochem J. 1999. PMID: 10477272 Free PMC article.
-
The adaptor protein Shc couples a class of integrins to the control of cell cycle progression.Cell. 1996 Nov 15;87(4):733-43. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81392-6. Cell. 1996. PMID: 8929541
-
Tumor suppressor PTEN inhibits integrin- and growth factor-mediated mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase signaling pathways.J Cell Biol. 1998 Nov 30;143(5):1375-83. doi: 10.1083/jcb.143.5.1375. J Cell Biol. 1998. PMID: 9832564 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Interplay between integrins and cadherins to control bone differentiation upon BMP-2 stimulation.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Jan 4;10:1027334. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.1027334. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 36684447 Free PMC article.
-
Integrin signaling in fibrosis and scleroderma.Curr Rheumatol Rep. 1999 Oct;1(1):28-33. doi: 10.1007/s11926-999-0021-5. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 1999. PMID: 11123011 Review.
-
Impact of type-1 collagen hydrogel density on integrin-linked morphogenic response of SH-SY5Y neuronal cells.RSC Adv. 2021 Oct 7;11(52):33124-33135. doi: 10.1039/d1ra05257h. eCollection 2021 Oct 4. RSC Adv. 2021. PMID: 35493559 Free PMC article.
-
Differential modulation of cellular phenotype and drug sensitivity by extracellular matrix proteins in primary and metastatic pancreatic cancer cells.Mol Biol Cell. 2023 Dec 1;34(13):ar130. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E23-02-0075. Epub 2023 Oct 30. Mol Biol Cell. 2023. PMID: 37903222 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancing integrin α1 inserted (I) domain affinity to ligand potentiates integrin α1β1-mediated down-regulation of collagen synthesis.J Biol Chem. 2012 Oct 12;287(42):35139-35152. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.358648. Epub 2012 Aug 10. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22888006 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams JC, Watt FM. Regulation of development and differentiation by the extracellular matrix. Development (Camb) 1993;117:1183–1198. - PubMed
-
- Broberg A, Heino J. Integrin α2β1-dependent contraction of floating collagen gels and induction of collagenase are inhibited by tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Exp Cell Res. 1996;228:29–35. - PubMed
-
- Clark EA, Brugge JS. Integrins and signal transduction pathways: the road taken. Science. 1995;268:233–239. - PubMed
-
- Clark EA, Hynes RO. 1997 Keystone symposium on signal transduction by cell adhesion receptors. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1997;1333:9–16. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

