Ligand-independent activation of platelet-derived growth factor receptor is a necessary intermediate in lysophosphatidic, acid-stimulated mitogenic activity in L cells
- PMID: 9671791
- PMCID: PMC21189
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.15.8985
Ligand-independent activation of platelet-derived growth factor receptor is a necessary intermediate in lysophosphatidic, acid-stimulated mitogenic activity in L cells
Abstract
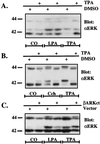
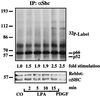
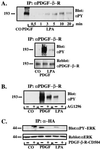
Growth factor-derived mitogenic signals from the cell surface are transmitted to the nucleus via receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs), the adaptor proteins Shc and Grb2, and a Ras-dependent protein kinase cascade that activates the extracellular signal regulated kinase (ERK) subfamily of mitogen-activated protein kinases. ERKs also are activated by hormones that stimulate G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs). We report here that, in agreement with previous data, the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is a signaling intermediate in ERK activation by GPCRs. Of import, we show that cross-talk between two classes of surface receptors, RTKs and GPCRs, is a general feature. Lysophosphatidic acid not only induces ligand-independent tyrosine autophosphorylation of EGFR but also of platelet-derived growth factor beta receptor (PDGF-beta-R) as shown by detection of tyrosine phosphorylation and by the use of specific inhibitors of RTKs. The cross-talk appears to be cell type-specific: In L cells that lack EGFR, lysophosphatidic acid-induced Shc and ERK activation is prevented completely by specific inhibition of PDGFR, whereas in COS-7 cells expressing only EGFR, the pathway via EGFR is chosen. In Rat-1 cells, however, that express both EGFR and PDGFR, the EGFR pathway dominates.
Figures
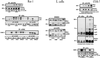

Similar articles
-
Epidermal growth factor-receptor mutant lacking the autophosphorylation sites induces phosphorylation of Shc protein and Shc-Grb2/ASH association and retains mitogenic activity.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jan 4;91(1):167-71. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.1.167. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994. PMID: 7506413 Free PMC article.
-
Optimal lysophosphatidic acid-induced DNA synthesis and cell migration but not survival require intact autophosphorylation sites of the epidermal growth factor receptor.J Biol Chem. 2004 Nov 12;279(46):47871-80. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M405443200. Epub 2004 Sep 10. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15364923
-
Synergism among lysophosphatidic acid, beta1A integrins, and epidermal growth factor or platelet-derived growth factor in mediation of cell migration.J Biol Chem. 1999 May 28;274(22):15480-6. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.22.15480. J Biol Chem. 1999. PMID: 10336439
-
EGF and PDGF receptor tyrosine kinases as therapeutic targets for chronic lung diseases.Curr Mol Med. 2006 Jun;6(4):409-21. doi: 10.2174/156652406777435426. Curr Mol Med. 2006. PMID: 16900664 Review.
-
EGFR signal transactivation in cancer cells.Biochem Soc Trans. 2003 Dec;31(Pt 6):1203-8. doi: 10.1042/bst0311203. Biochem Soc Trans. 2003. PMID: 14641026 Review.
Cited by
-
Pericyte-fibroblast transition promotes tumor growth and metastasis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Sep 20;113(38):E5618-27. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1608384113. Epub 2016 Sep 7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 27608497 Free PMC article.
-
Cross-talk between receptors with intrinsic tyrosine kinase activity and alpha1b-adrenoceptors.Biochem J. 2000 Sep 1;350 Pt 2(Pt 2):413-9. doi: 10.1042/0264-6021:3500413. Biochem J. 2000. PMID: 10947955 Free PMC article.
-
Role of proneuregulin 1 cleavage and human epidermal growth factor receptor activation in hypertonic aquaporin induction.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Nov 2;101(44):15799-804. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0406853101. Epub 2004 Oct 21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004. PMID: 15498868 Free PMC article.
-
Growth factors outside the PDGF family drive experimental PVR.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2009 Jul;50(7):3394-403. doi: 10.1167/iovs.08-3042. Epub 2009 Mar 25. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2009. PMID: 19324843 Free PMC article.
-
GPCR-mediated EGFR transactivation ameliorates skin toxicities induced by afatinib.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2022 Jun;43(6):1534-1543. doi: 10.1038/s41401-021-00774-6. Epub 2021 Sep 22. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2022. PMID: 34552215 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Treisman R. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1996;8:205–215. - PubMed
-
- Weiss F U, Daub H, Ullrich A. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1997;7:80–86. - PubMed
-
- Heldin C H. Cancer Surv. 1996;27:7–24. - PubMed
-
- Dhanasekaran N, Heasley L E, Johnson G L. Endocr Rev. 1995;16:259–270. - PubMed
-
- Shenker A, Laue L, Kosugi S, Merendino J J, Jr, Minegishi T, Cutler G B., Jr Nature (London) 1993;365:652–654. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

