Gating modifier toxins reveal a conserved structural motif in voltage-gated Ca2+ and K+ channels
- PMID: 9671721
- PMCID: PMC21119
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.15.8585
Gating modifier toxins reveal a conserved structural motif in voltage-gated Ca2+ and K+ channels
Abstract
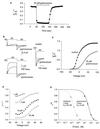
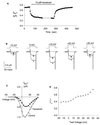
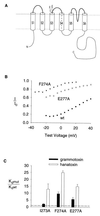
Protein toxins from venomous animals exhibit remarkably specific and selective interactions with a wide variety of ion channels. Hanatoxin and grammotoxin are two related protein toxins found in the venom of the Chilean Rose Tarantula, Phrixotrichus spatulata. Hanatoxin inhibits voltage-gated K+ channels and grammotoxin inhibits voltage-gated Ca2+ channels. Both toxins inhibit their respective channels by interfering with normal operation of the voltage-dependent gating mechanism. The sequence homology of hanatoxin and grammotoxin, as well as their similar mechanism of action, raises the possibility that they interact with the same region of voltage-gated Ca2+ and K+ channels. Here, we show that each toxin can interact with both voltage-gated Ca2+ and K+ channels and modify channel gating. Moreover, mutagenesis of voltage-gated K+ channels suggests that hanatoxin and grammotoxin recognize the same structural motif. We propose that these toxins recognize a voltage-sensing domain or module present in voltage-gated ion channels and that this domain has a highly conserved three-dimensional structure.
Figures
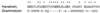

Similar articles
-
Solution structure of hanatoxin1, a gating modifier of voltage-dependent K(+) channels: common surface features of gating modifier toxins.J Mol Biol. 2000 Mar 31;297(3):771-80. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.2000.3609. J Mol Biol. 2000. PMID: 10731427
-
Solution structure of omega-grammotoxin SIA, a gating modifier of P/Q and N-type Ca(2+) channel.J Mol Biol. 2002 Aug 16;321(3):517-26. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(02)00595-8. J Mol Biol. 2002. PMID: 12162963
-
Localization and molecular determinants of the Hanatoxin receptors on the voltage-sensing domains of a K(+) channel.J Gen Physiol. 2000 Jun;115(6):673-84. doi: 10.1085/jgp.115.6.673. J Gen Physiol. 2000. PMID: 10828242 Free PMC article.
-
Tarantula toxins interacting with voltage sensors in potassium channels.Toxicon. 2007 Feb;49(2):213-30. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2006.09.024. Epub 2006 Sep 29. Toxicon. 2007. PMID: 17097703 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gating modifier toxins of voltage-gated calcium channels.Toxicon. 2007 Feb;49(2):202-12. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2006.09.018. Epub 2006 Sep 27. Toxicon. 2007. PMID: 17097124 Review.
Cited by
-
Semaphorin 3A growth cone collapse requires a sequence homologous to tarantula hanatoxin.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999 Nov 9;96(23):13501-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.23.13501. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999. PMID: 10557350 Free PMC article.
-
Constitutive activation of the Shaker Kv channel.J Gen Physiol. 2003 Nov;122(5):541-56. doi: 10.1085/jgp.200308905. Epub 2003 Oct 13. J Gen Physiol. 2003. PMID: 14557403 Free PMC article.
-
Helical structure of the COOH terminus of S3 and its contribution to the gating modifier toxin receptor in voltage-gated ion channels.J Gen Physiol. 2001 Mar;117(3):205-18. doi: 10.1085/jgp.117.3.205. J Gen Physiol. 2001. PMID: 11222625 Free PMC article.
-
Kurtoxin, a gating modifier of neuronal high- and low-threshold ca channels.J Neurosci. 2002 Mar 15;22(6):2023-34. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-06-02023.2002. J Neurosci. 2002. PMID: 11896142 Free PMC article.
-
Pain-related toxins in scorpion and spider venoms: a face to face with ion channels.J Venom Anim Toxins Incl Trop Dis. 2021 Dec 6;27:e20210026. doi: 10.1590/1678-9199-JVATITD-2021-0026. eCollection 2021. J Venom Anim Toxins Incl Trop Dis. 2021. PMID: 34925480 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

