Disruption of PML subnuclear domains by the acidic IE1 protein of human cytomegalovirus is mediated through interaction with PML and may modulate a RING finger-dependent cryptic transactivator function of PML
- PMID: 9671498
- PMCID: PMC109074
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.18.8.4899
Disruption of PML subnuclear domains by the acidic IE1 protein of human cytomegalovirus is mediated through interaction with PML and may modulate a RING finger-dependent cryptic transactivator function of PML
Abstract
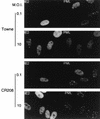
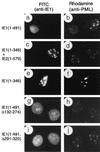
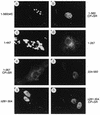
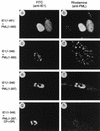
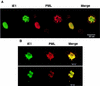
Both of the major immediate-early (IE) proteins IE1 and IE2 of human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) as well as input viral DNA and sites of viral IE transcription colocalize with or adjacent to punctate PML domains (PML oncogenic domains [PODs] or nuclear domain 10) in the nucleus within the first few hours after infection of permissive human fibroblasts. However, colocalization of IE1 and PML in PODs is only transient, with both proteins subsequently redistributing into a nuclear diffuse form. These processes are believed to promote efficient viral IE transcription and initiation of DNA synthesis especially at low multiplicities of infection. To examine the mechanism of PML displacement by IE1, we carried out indirect immunofluorescence assay experiments with plasmids expressing intact or deleted forms of PML and IE1 in DNA-transfected cells. The results demonstrated that deletion of the C-terminal acidic region of IE1 uncouples the requirements for displacement of both endogenous and coexpressed PML from those needed to target to the PODs. Mutant PML proteins containing either a Cys point mutation within the N-terminal RING finger domain or a small deletion (of positions 281 to 304) within the coiled-coil region did not localize to the PODs but instead gave a nuclear diffuse distribution, similar to that produced by intact PML in the presence of IE1. Endogenous PML also colocalized with IE1 in metaphase chromosomes in HCMV or recombinant adenovirus type 5-IE1-infected HF cells undergoing mitosis, implying that there may be a direct physical interaction between IE1 and PML. Indeed, a specific interaction between IE1 and PML was observed in a yeast two-hybrid assay, and the strength of this interaction was comparable to that of IE2 with the retinoblastoma protein. The RING finger mutant form of PML showed a threefold-lower interaction with IE1 in the yeast system, and deletion of the N-terminal RING finger domain of PML abolished the interaction. Consistent with the IFA results, a mutant IE1 protein that lacks the C-terminal acidic region was sufficient for interaction with PML in the yeast system. The two-hybrid interaction assay also showed that both the N-terminal RING finger domain and the intact coiled-coil region of PML are required cooperatively for efficient self-interactions involving dimerization or oligomerization. Furthermore, truncated or deleted GAL4/PML fusion proteins that retained the RING finger domain but lacked the intact coiled-coil region displayed an unmasked cryptic transactivator function in both yeast and mammalian cells, and the RING finger mutation abolished this transactivation property of PML. Therefore, we suggest that a direct interaction between IE1 and the N-terminal RING finger domain of PML may inhibit oligomerization and protein-protein complex formation by PML, leading to displacement of PML and IE1 from the PODs, and that this interaction may also modulate a putative conditional transactivator function of PML.
Figures


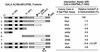

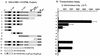

Similar articles
-
The major immediate-early proteins IE1 and IE2 of human cytomegalovirus colocalize with and disrupt PML-associated nuclear bodies at very early times in infected permissive cells.J Virol. 1997 Jun;71(6):4599-613. doi: 10.1128/JVI.71.6.4599-4613.1997. J Virol. 1997. PMID: 9151854 Free PMC article.
-
Disruption of PML-associated nuclear bodies by IE1 correlates with efficient early stages of viral gene expression and DNA replication in human cytomegalovirus infection.Virology. 2000 Aug 15;274(1):39-55. doi: 10.1006/viro.2000.0448. Virology. 2000. PMID: 10936087
-
The human cytomegalovirus IE2 and UL112-113 proteins accumulate in viral DNA replication compartments that initiate from the periphery of promyelocytic leukemia protein-associated nuclear bodies (PODs or ND10).J Virol. 1999 Dec;73(12):10458-71. doi: 10.1128/JVI.73.12.10458-10471.1999. J Virol. 1999. PMID: 10559364 Free PMC article.
-
Proteasome-independent disruption of PML oncogenic domains (PODs), but not covalent modification by SUMO-1, is required for human cytomegalovirus immediate-early protein IE1 to inhibit PML-mediated transcriptional repression.J Virol. 2001 Nov;75(22):10683-95. doi: 10.1128/JVI.75.22.10683-10695.2001. J Virol. 2001. PMID: 11602710 Free PMC article.
-
Characterisation of the PML/RAR alpha rearrangement associated with t(15;17) acute promyelocytic leukaemia.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1997;220:81-112. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-60479-9_6. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1997. PMID: 9103677 Review.
Cited by
-
PML Degradation: Multiple Ways to Eliminate PML.Front Oncol. 2013 Mar 22;3:60. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2013.00060. eCollection 2013. Front Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23526763 Free PMC article.
-
Virus-host protein interactions as footprints of human cytomegalovirus replication.Curr Opin Virol. 2022 Feb;52:135-147. doi: 10.1016/j.coviro.2021.11.016. Epub 2021 Dec 16. Curr Opin Virol. 2022. PMID: 34923282 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Revisiting promyelocytic leukemia protein targeting by human cytomegalovirus immediate-early protein 1.PLoS Pathog. 2020 May 4;16(5):e1008537. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1008537. eCollection 2020 May. PLoS Pathog. 2020. PMID: 32365141 Free PMC article.
-
A Tale of Usurpation and Subversion: SUMO-Dependent Integrity of Promyelocytic Leukemia Nuclear Bodies at the Crossroad of Infection and Immunity.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Aug 27;9:696234. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.696234. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34513832 Free PMC article. Review.
-
As(2)O(3) enhances retroviral reverse transcription and counteracts Ref1 antiviral activity.J Virol. 2003 Mar;77(5):3167-80. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.5.3167-3180.2003. J Virol. 2003. PMID: 12584341 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahn J-H, Chiou C-J, Hayward G S. Evaluation and mapping of the DNA binding and oligomerization domains of the IE2 regulatory protein of human cytomegalovirus using yeast one and two hybrid interaction assays. Gene. 1998;210:25–36. - PubMed
-
- Ahn, J.-H. Unpublished data.
-
- Barlow P N, Luisi B, Milner A, Elliott M, Everett R D. Structure of the C3HC4 domain by 1H-nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J Mol Biol. 1994;237:201–211. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
