Differential roles for bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) receptor type IB and IA in differentiation and specification of mesenchymal precursor cells to osteoblast and adipocyte lineages
- PMID: 9660882
- PMCID: PMC2133031
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.142.1.295
Differential roles for bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) receptor type IB and IA in differentiation and specification of mesenchymal precursor cells to osteoblast and adipocyte lineages
Abstract
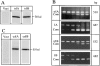
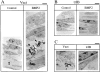
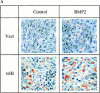
Cumulative evidence indicates that osteoblasts and adipocytes share a common mesenchymal precursor and that bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs) can induce both osteoblast and adipocyte differentiation of this precursor. In the present study, we investigated the roles of BMP receptors in differentiation along these separate lineages using a well-characterized clonal cell line, 2T3, derived from the mouse calvariae. BMP-2 induced 2T3 cells to differentiate into mature osteoblasts or adipocytes depending upon culture conditions. To test the specific roles of the type IA and IB BMP receptor components, truncated and constitutively active type IA and IB BMP receptor cDNAs were stably expressed in these cells. Overexpression of truncated type IB BMP receptor (trBMPR-IB) in 2T3 cells completely blocked BMP-2-induced osteoblast differentiation and mineralized bone matrix formation. Expression of trBMPR-IB also blocked mRNA expression of the osteoblast specific transcription factor, Osf2/ Cbfa1, and the osteoblast differentiation-related genes, alkaline phosphatase (ALP) and osteocalcin (OC). BMP-2-induced ALP activity could be rescued by transfection of wild-type (wt) BMPR-IB into 2T3 clones containing trBMPR-IB. Expression of a constitutively active BMPR-IB (caBMPR-IB) induced formation of mineralized bone matrix by 2T3 cells without addition of BMP-2. In contrast, overexpression of trBMPR-IA blocked adipocyte differentiation and expression of caBMPR-IA induced adipocyte formation in 2T3 cells. Expression of the adipocyte differentiation-related genes, adipsin and PPARgamma, correlated with the distinct phenotypic changes found after overexpression of the appropriate mutant receptors. These results demonstrate that type IB and IA BMP receptors transmit different signals to bone-derived mesenchymal progenitors and play critical roles in both the specification and differentiation of osteoblasts and adipocytes.
Figures






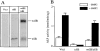



Similar articles
-
Collagen integrin receptors regulate early osteoblast differentiation induced by BMP-2.J Bone Miner Res. 1999 Jul;14(7):1075-83. doi: 10.1359/jbmr.1999.14.7.1075. J Bone Miner Res. 1999. PMID: 10404007
-
Differentiation of human marrow stromal precursor cells: bone morphogenetic protein-2 increases OSF2/CBFA1, enhances osteoblast commitment, and inhibits late adipocyte maturation.J Bone Miner Res. 1999 Sep;14(9):1522-35. doi: 10.1359/jbmr.1999.14.9.1522. J Bone Miner Res. 1999. PMID: 10469280
-
Hedgehog stimulates only osteoblastic differentiation of undifferentiated KS483 cells.Bone. 2003 Dec;33(6):899-910. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2003.07.004. Bone. 2003. PMID: 14678849
-
Bone morphogenetic proteins.Growth Factors. 2004 Dec;22(4):233-41. doi: 10.1080/08977190412331279890. Growth Factors. 2004. PMID: 15621726 Review.
-
The developmental control of osteoblast-specific gene expression: role of specific transcription factors and the extracellular matrix environment.Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 1999;10(1):40-57. doi: 10.1177/10454411990100010201. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 1999. PMID: 10759426 Review.
Cited by
-
Bone morphogenetic protein 2-induced human dental pulp cell differentiation involves p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase-activated canonical WNT pathway.Int J Oral Sci. 2015 Jun 26;7(2):95-102. doi: 10.1038/ijos.2015.7. Int J Oral Sci. 2015. PMID: 26047580 Free PMC article.
-
Removal of serum factors by charcoal treatment promotes adipogenesis via a MAPK-dependent pathway.Mol Cell Biochem. 2005 Jan;268(1-2):159-67. doi: 10.1007/s11010-005-3857-7. Mol Cell Biochem. 2005. PMID: 15724449
-
The BMP signaling and in vivo bone formation.Gene. 2005 Aug 29;357(1):1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2005.06.017. Gene. 2005. PMID: 16125875 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bone morphogenetic protein 2 is a depot-specific regulator of human adipogenesis.Int J Obes (Lond). 2019 Dec;43(12):2458-2468. doi: 10.1038/s41366-019-0421-1. Epub 2019 Jul 19. Int J Obes (Lond). 2019. PMID: 31324879 Free PMC article.
-
BMP-2 modulates beta-catenin signaling through stimulation of Lrp5 expression and inhibition of beta-TrCP expression in osteoblasts.J Cell Biochem. 2009 Nov 1;108(4):896-905. doi: 10.1002/jcb.22319. J Cell Biochem. 2009. PMID: 19795382 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahrens M, Ankenbauer T, Schroder D, Hollnagel A, Mayer H, Gross G. Expression of human bone morphogenetic protein-2 or -4 in murine mesenchymal progenitor C3H10T1/2 cells induces differentiation into distinct mesenchymal cell lineages. DNA Cell Biol. 1993;12:871–880. - PubMed
-
- Asahina I, Sampath TK, Hauschka PV. Human osteogenic protein-1 induces chondroblastics, osteoblastics and/or adipocyte differentiation of clonal murine target cells. Exp Cell Res. 1996;222:38–47. - PubMed
-
- Aubin JE, Liu F, Malaval L, Gupta AK. Osteoblast and chondroblast differentiation. Bone. 1995;17:77S–83S. - PubMed
-
- Bennett JH, Joyner CJ, Triffitt JT, Owen ME. Adipocytic cells cultured from marrow have osteogenic potential. J Cell Sci. 1991;99:131–139. - PubMed
-
- Beresford JN, Bennett JH, Delving C, Leboy PS, Owen ME. Evidence for an inverse relationship between the differentiation of adipocytic and osteogenic cells in rat marrow stromal cell cultures. J Cell Sci. 1992;102:341–351. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

