Sec35p, a novel peripheral membrane protein, is required for ER to Golgi vesicle docking
- PMID: 9606204
- PMCID: PMC2137178
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.141.5.1107
Sec35p, a novel peripheral membrane protein, is required for ER to Golgi vesicle docking
Abstract
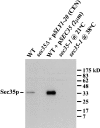
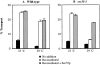
SEC35 was identified in a novel screen for temperature-sensitive mutants in the secretory pathway of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae (. Genetics. 142:393-406). At the restrictive temperature, the sec35-1 strain exhibits a transport block between the ER and the Golgi apparatus and accumulates numerous vesicles. SEC35 encodes a novel cytosolic protein of 32 kD, peripherally associated with membranes. The temperature-sensitive phenotype of sec35-1 is efficiently suppressed by YPT1, which encodes the rab-like GTPase required early in the secretory pathway, or by SLY1-20, which encodes a dominant form of the ER to Golgi target -SNARE-associated protein Sly1p. Weaker suppression is evident upon overexpression of genes encoding the vesicle-SNAREs SEC22, BET1, or YKT6. The cold-sensitive lethality that results from deleting SEC35 is suppressed by YPT1 or SLY1-20. These genetic relationships suggest that Sec35p acts upstream of, or in conjunction with, Ypt1p and Sly1p as was previously found for Uso1p. Using a cell-free assay that measures distinct steps in vesicle transport from the ER to the Golgi, we find Sec35p is required for a vesicle docking stage catalyzed by Uso1p. These genetic and biochemical results suggest Sec35p acts with Uso1p to dock ER-derived vesicles to the Golgi complex.
Figures



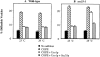
Similar articles
-
Sec34p, a protein required for vesicle tethering to the yeast Golgi apparatus, is in a complex with Sec35p.J Cell Biol. 1999 Nov 15;147(4):729-42. doi: 10.1083/jcb.147.4.729. J Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 10562277 Free PMC article.
-
Assembly of the ER to Golgi SNARE complex requires Uso1p.J Cell Biol. 1996 Mar;132(5):755-67. doi: 10.1083/jcb.132.5.755. J Cell Biol. 1996. PMID: 8603910 Free PMC article.
-
Initial docking of ER-derived vesicles requires Uso1p and Ypt1p but is independent of SNARE proteins.EMBO J. 1998 Apr 15;17(8):2156-65. doi: 10.1093/emboj/17.8.2156. EMBO J. 1998. PMID: 9545229 Free PMC article.
-
Small GTP-binding proteins and their role in transport.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;3(4):626-33. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(91)90033-u. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1991. PMID: 1663370 Review. No abstract available.
-
Proteins involved in vesicular transport and membrane fusion.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;3(4):615-20. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(91)90031-s. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1991. PMID: 1772655 Review.
Cited by
-
High-copy suppressor analysis reveals a physical interaction between Sec34p and Sec35p, a protein implicated in vesicle docking.Mol Biol Cell. 1999 Oct;10(10):3317-29. doi: 10.1091/mbc.10.10.3317. Mol Biol Cell. 1999. PMID: 10512869 Free PMC article.
-
Tethering molecules in membrane traffic.Protoplasma. 1999;209(1-2):38-45. doi: 10.1007/BF01415699. Protoplasma. 1999. PMID: 18987793
-
BPIFB6 Regulates Secretory Pathway Trafficking and Enterovirus Replication.J Virol. 2016 Apr 29;90(10):5098-107. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00170-16. Print 2016 May 15. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 26962226 Free PMC article.
-
Dsl1p, Tip20p, and the novel Dsl3(Sec39) protein are required for the stability of the Q/t-SNARE complex at the endoplasmic reticulum in yeast.Mol Biol Cell. 2005 Sep;16(9):3963-77. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e05-01-0056. Epub 2005 Jun 15. Mol Biol Cell. 2005. PMID: 15958492 Free PMC article.
-
Ric1p and the Ypt6p GTPase function in a common pathway required for localization of trans-Golgi network membrane proteins.Mol Biol Cell. 2001 Jan;12(1):13-26. doi: 10.1091/mbc.12.1.13. Mol Biol Cell. 2001. PMID: 11160819 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990;215:403–410. - PubMed
-
- Baker D, Hicke L, Rexach M, Schleyer M, Schekman R. Reconstitution of SECgene product-dependent intercompartmental protein transport. Cell. 1988;54:335–344. - PubMed
-
- Banfield DK, Lewis MJ, Pelham HRB. A SNARE-like protein required for traffic through the Golgi complex. Nature. 1995;375:806–809. - PubMed
-
- Barlowe C, Schekman R. SEC12encodes a guanine-nucleotide-exchange factor essential for transport vesicle budding from the ER. Nature. 1993;365:347–349. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

