The interaction of Arp2/3 complex with actin: nucleation, high affinity pointed end capping, and formation of branching networks of filaments
- PMID: 9600938
- PMCID: PMC27619
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.11.6181
The interaction of Arp2/3 complex with actin: nucleation, high affinity pointed end capping, and formation of branching networks of filaments
Abstract
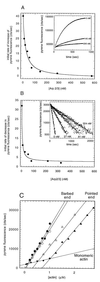
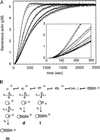
The Arp2/3 complex is a stable assembly of seven protein subunits including two actin-related proteins (Arp2 and Arp3) and five novel proteins. Previous work showed that this complex binds to the sides of actin filaments and is concentrated at the leading edges of motile cells. Here, we show that Arp2/3 complex purified from Acanthamoeba caps the pointed ends of actin filaments with high affinity. Arp2/3 complex inhibits both monomer addition and dissociation at the pointed ends of actin filaments with apparent nanomolar affinity and increases the critical concentration for polymerization at the pointed end from 0.6 to 1.0 microM. The high affinity of Arp2/3 complex for pointed ends and its abundance in amoebae suggest that in vivo all actin filament pointed ends are capped by Arp2/3 complex. Arp2/3 complex also nucleates formation of actin filaments that elongate only from their barbed ends. From kinetic analysis, the nucleation mechanism appears to involve stabilization of polymerization intermediates (probably actin dimers). In electron micrographs of quick-frozen, deep-etched samples, we see Arp2/3 bound to sides and pointed ends of actin filaments and examples of Arp2/3 complex attaching pointed ends of filaments to sides of other filaments. In these cases, the angle of attachment is a remarkably constant 70 +/- 7 degrees. From these in vitro biochemical properties, we propose a model for how Arp2/3 complex controls the assembly of a branching network of actin filaments at the leading edge of motile cells.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Interactions of ADF/cofilin, Arp2/3 complex, capping protein and profilin in remodeling of branched actin filament networks.Curr Biol. 2000 Oct 19;10(20):1273-82. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(00)00749-1. Curr Biol. 2000. PMID: 11069108
-
Direct observation of dendritic actin filament networks nucleated by Arp2/3 complex and WASP/Scar proteins.Nature. 2000 Apr 27;404(6781):1007-11. doi: 10.1038/35010008. Nature. 2000. PMID: 10801131
-
Rho-family GTPases require the Arp2/3 complex to stimulate actin polymerization in Acanthamoeba extracts.Curr Biol. 1999 Apr 22;9(8):405-15. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(99)80187-0. Curr Biol. 1999. PMID: 10226024
-
Control of actin assembly and disassembly at filament ends.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2000 Feb;12(1):97-103. doi: 10.1016/s0955-0674(99)00062-9. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 10679358 Review.
-
Structure and function of the Arp2/3 complex.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 1999 Apr;9(2):244-9. doi: 10.1016/s0959-440x(99)80034-7. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 1999. PMID: 10322212 Review.
Cited by
-
Under lock and key: spatiotemporal regulation of WASP family proteins coordinates separate dynamic cellular processes.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2013 Apr;24(4):258-66. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2012.12.005. Epub 2013 Jan 3. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2013. PMID: 23291261 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unravelling the Actin Cytoskeleton: A New Competitive Edge?Trends Cell Biol. 2016 Aug;26(8):569-576. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2016.04.001. Epub 2016 Apr 25. Trends Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 27133808 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A meta-analysis indicates that the regulation of cell motility is a non-intrinsic function of chemoattractant receptors that is governed independently of directional sensing.Front Immunol. 2022 Oct 20;13:1001086. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1001086. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36341452 Free PMC article.
-
Myosin 1b flattens and prunes branched actin filaments.J Cell Sci. 2020 Sep 24;133(18):jcs247403. doi: 10.1242/jcs.247403. J Cell Sci. 2020. PMID: 32895245 Free PMC article.
-
Brillouin microscopy: an emerging tool for mechanobiology.Nat Methods. 2019 Oct;16(10):969-977. doi: 10.1038/s41592-019-0543-3. Epub 2019 Sep 23. Nat Methods. 2019. PMID: 31548707 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

