A bacterial two-hybrid system based on a reconstituted signal transduction pathway
- PMID: 9576956
- PMCID: PMC20451
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.10.5752
A bacterial two-hybrid system based on a reconstituted signal transduction pathway
Abstract
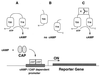
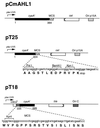
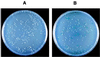
We describe a bacterial two-hybrid system that allows an easy in vivo screening and selection of functional interactions between two proteins. This genetic test is based on the reconstitution, in an Escherichia coli cya strain, of a signal transduction pathway that takes advantage of the positive control exerted by cAMP. Two putative interacting proteins are genetically fused to two complementary fragments, T25 and T18, that constitute the catalytic domain of Bordetella pertussis adenylate cyclase. Association of the two-hybrid proteins results in functional complementation between T25 and T18 fragments and leads to cAMP synthesis. Cyclic AMP then triggers transcriptional activation of catabolic operons, such as lactose or maltose, that yield a characteristic phenotype. In this genetic test, the involvement of a signaling cascade offers the unique property that association between the hybrid proteins can be spatially separated from the transcriptional activation readout. This permits a versatile design of screening procedures either for ligands that bind to a given "bait," as in the classical yeast two-hybrid system, or for molecules or mutations that block a given interaction between two proteins of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Analysis of Membrane Protein Interactions with a Bacterial Adenylate Cyclase-Based Two-Hybrid (BACTH) Technique.Curr Protoc Mol Biol. 2017 Apr 3;118:20.12.1-20.12.24. doi: 10.1002/cpmb.36. Curr Protoc Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28369675
-
A Bacterial Two-Hybrid System for In Vivo Assays of Protein-Protein Interactions and Drug Discovery.Methods Mol Biol. 2022;2548:145-167. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-2581-1_10. Methods Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 36151497
-
Structural flexibility of the calmodulin-binding locus in Bordetella pertussis adenylate cyclase. Reconstitution of catalytically active species from fragments or inactive forms of the enzyme.Eur J Biochem. 1993 Oct 15;217(2):581-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb18280.x. Eur J Biochem. 1993. PMID: 8223601
-
Invasive adenylate cyclase toxin of Bordetella pertussis.Trends Biochem Sci. 1989 Nov;14(11):459-63. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(89)90106-0. Trends Biochem Sci. 1989. PMID: 2560273 Review.
-
Bordetella pertussis adenylate cyclase toxin: a versatile screening tool.Toxicon. 2002 Oct;40(10):1383-7. doi: 10.1016/s0041-0101(02)00158-7. Toxicon. 2002. PMID: 12368108 Review.
Cited by
-
Allosteric activation of exopolysaccharide synthesis through cyclic di-GMP-stimulated protein-protein interaction.EMBO J. 2013 Feb 6;32(3):354-68. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2012.315. Epub 2012 Nov 30. EMBO J. 2013. PMID: 23202856 Free PMC article.
-
The TatC component of the twin-arginine protein translocase functions as an obligate oligomer.Mol Microbiol. 2015 Oct;98(1):111-29. doi: 10.1111/mmi.13106. Epub 2015 Jul 22. Mol Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 26112072 Free PMC article.
-
Control of Morphological Differentiation of Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) by Phosphorylation of MreC and PBP2.PLoS One. 2015 Apr 30;10(4):e0125425. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0125425. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25927987 Free PMC article.
-
Key role of two terminal domains in the bidirectional polymerization of FtsA protein.J Biol Chem. 2012 Mar 2;287(10):7756-65. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.311563. Epub 2012 Jan 14. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22247552 Free PMC article.
-
The pathogenicity island encoded PvrSR/RcsCB regulatory network controls biofilm formation and dispersal in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PA14.Mol Microbiol. 2013 Aug;89(3):450-63. doi: 10.1111/mmi.12287. Epub 2013 Jun 28. Mol Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23750818 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

