Inhibition of major histocompatibility complex class I antigen presentation in pig and primate cells by herpes simplex virus type 1 and 2 ICP47
- PMID: 9573278
- PMCID: PMC110071
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.72.6.5076-5084.1998
Inhibition of major histocompatibility complex class I antigen presentation in pig and primate cells by herpes simplex virus type 1 and 2 ICP47
Abstract
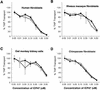
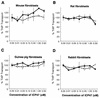
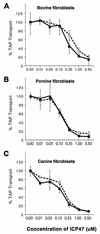
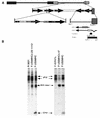
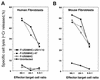
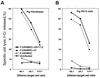
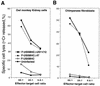
Herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2 (HSV-1 and HSV-2) express an immediate-early protein, ICP47, that effectively inhibits the human transporter associated with antigen presentation (TAP), blocking major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I antigen presentation to CD8+ T cells. Previous work indicated that the mouse TAP is relatively resistant to inhibition by the HSV-1 and HSV-2 ICP47 proteins (ICP47-1 and ICP47-2) and that mouse cells infected with HSV-1 are lysed by anti-HSV CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL). Therefore, mice are apparently not suitable animals in which to study the in vivo effects of ICP47. In order to find an animal model, we introduced ICP47-1 and ICP47-2 into cells from various animal species-mice, rats, guinea pigs, rabbits, dogs, pigs, cows, monkeys, and humans-and measured TAP activity in the cells. Both proteins were unable to inhibit TAP in mouse, rat, guinea pig, and rabbit cells. In contrast, ICP47-1 and ICP47-2 inhibited TAP in pig, dog, cow, and monkey cells, and the TAP in pig and dog fibroblasts was often more sensitive to both proteins than TAP in human fibroblasts. These results were extended by measuring CD8+-T-cell recognition (CTL lysis) of cells from various species. Cells were infected with recombinant HSV-1 constructed to express murine MHC class I proteins so that the cells would be recognized and lysed by well-characterized murine anti-HSV CTL unless antigen presentation was blocked by ICP47. Anti-HSV CD8+ CTL effectively lysed pig and primate cells infected with a recombinant HSV-1 ICP47- mutant but were unable to lyse pig or primate cells infected with a recombinant HSV-1 that expressed ICP47. Therefore, pigs, dogs, and monkeys may be useful animal models in which to test the effects of ICP47 on HSV pathogenesis or the use of ICP47 as a selective immunosuppressive agent.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Human herpes simplex virus (HSV)-specific CD8+ CTL clones recognize HSV-2-infected fibroblasts after treatment with IFN-gamma or when virion host shutoff functions are disabled.J Immunol. 1996 May 15;156(10):3901-10. J Immunol. 1996. PMID: 8621929
-
Effective suppression of class I major histocompatibility complex expression by the US11 or ICP47 genes can be limited by cell type or interferon-gamma exposure.Hum Gene Ther. 2003 Dec 10;14(18):1765-75. doi: 10.1089/104303403322611773. Hum Gene Ther. 2003. PMID: 14670127
-
Herpes simplex virus type 2 ICP47 inhibits human TAP but not mouse TAP.J Virol. 1998 Mar;72(3):2560-3. doi: 10.1128/JVI.72.3.2560-2563.1998. J Virol. 1998. PMID: 9499125 Free PMC article.
-
Of mice and not humans: how reliable are animal models for evaluation of herpes CD8(+)-T cell-epitopes-based immunotherapeutic vaccine candidates?Vaccine. 2011 Aug 11;29(35):5824-36. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2011.06.083. Epub 2011 Jun 28. Vaccine. 2011. PMID: 21718746 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[The immune escape mechanism of herpes simplex virus type 1--suppression of transporter associated with antigen processing (TAP) by ICP47].Bing Du Xue Bao. 2007 Jan;23(1):72-5. Bing Du Xue Bao. 2007. PMID: 17886726 Review. Chinese. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Immunovirotherapy: The role of antibody based therapeutics combination with oncolytic viruses.Front Immunol. 2022 Oct 13;13:1012806. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1012806. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36311790 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of MHC class I is a virulence factor in herpes simplex virus infection of mice.PLoS Pathog. 2005 Sep;1(1):e7. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.0010007. Epub 2005 Sep 30. PLoS Pathog. 2005. PMID: 16201019 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of porcine TAP genes: alternative splicing of TAP1.Immunogenetics. 2006 Jun;58(5-6):374-82. doi: 10.1007/s00251-006-0103-8. Epub 2006 Mar 23. Immunogenetics. 2006. PMID: 16555068
-
Virus and host genomic, molecular, and cellular interactions during Marek's disease pathogenesis and oncogenesis.Poult Sci. 2016 Feb;95(2):412-29. doi: 10.3382/ps/pev369. Epub 2016 Jan 11. Poult Sci. 2016. PMID: 26755654 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Herpes virus fusion and entry: a story with many characters.Viruses. 2012 May;4(5):800-32. doi: 10.3390/v4050800. Epub 2012 May 10. Viruses. 2012. PMID: 22754650 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ahn K, Gruhler A, Galocha B, Jones T R, Wiertz E J, Ploegh H L, Peterson P, Yang Y, Fruh K. The ER-luminal domain of the HCMV glycoprotein US6 inhibits peptide translocation by TAP. Immunity. 1997;6:613–621. - PubMed
-
- Fruh K, Ahn K, Djaballah H, Sempe P, van Endert P, Tampe R, Peterson P, Yang Y. A viral inhibitor of peptide transporters for antigen presentation. Nature. 1995;375:415–418. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

