Polarized secretion of IL-6 and IL-8 by human retinal pigment epithelial cells
- PMID: 9566787
- PMCID: PMC1904947
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.1998.00560.x
Polarized secretion of IL-6 and IL-8 by human retinal pigment epithelial cells
Abstract
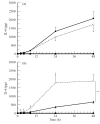
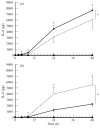
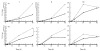
A number of cell types situated along interfaces of various tissues and organs such as the peritoneum and the intestine have been shown to secrete inflammatory cytokines in a polarized fashion. Retinal pigment epithelial (RPE) cells are positioned at the interface between the vascularized choroid and the avascular retina, forming part of the blood-retina barrier. These cells are potent producers of inflammatory cytokines and are therefore considered to play an important role in the pathogenesis of ocular inflammation. Whether cytokine secretion by these cells also follows a vectorial pattern is not yet known, and was therefore the subject of this study. Monolayers of human RPE cells (primary cultures and the ARPE-19 cell line) cultured on transwell filters were stimulated to produce IL-6 and IL-8 by adding IL-1beta (100 U/ml) to either the upper or the lower compartment. After stimulation, the human RPE cell lines showed polarized secretion of IL-6 and IL-8 towards the basal side, irrespective of the side of stimulation. The ARPE- 19 cell line also secreted IL-6 and IL-8 in a polarized fashion towards the basal side after basal stimulation; polarized secretion was, however, not apparent after apical stimulation. The observation that human RPE cells secrete IL-6 and IL-8 in a polarized fashion towards the choroid may represent a mechanism to prevent damage to the adjacent fragile retinal tissue.
Figures

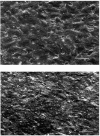
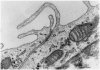
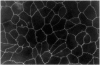
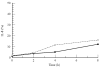
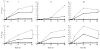
Similar articles
-
Analysis of the secretion pattern of monocyte chemotactic protein-1 (MCP-1) and transforming growth factor-beta 2 (TGF-beta2) by human retinal pigment epithelial cells.Clin Exp Immunol. 1999 Oct;118(1):35-40. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.1999.01016.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 1999. PMID: 10540157 Free PMC article.
-
Stimulation of apical and basolateral VEGF-A and VEGF-C secretion by oxidative stress in polarized retinal pigment epithelial cells.Mol Vis. 2006 Dec 22;12:1649-59. Mol Vis. 2006. PMID: 17200665
-
Interleukin-6 (IL-6) gene expression and secretion by cytokine-stimulated human retinal pigment epithelial cells.Exp Eye Res. 1992 Mar;54(3):361-8. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(92)90048-w. Exp Eye Res. 1992. PMID: 1381679
-
Deletion mutants in human cytomegalovirus glycoprotein US9 are impaired in cell-cell transmission and in altering tight junctions of polarized human retinal pigment epithelial cells.Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1995;99:82-7. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1995. PMID: 8668948 Review.
-
Retinal pigment epithelium-immune system interactions: cytokine production and cytokine-induced changes.Prog Retin Eye Res. 2001 Jan;20(1):29-48. doi: 10.1016/s1350-9462(00)00017-3. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2001. PMID: 11070367 Review.
Cited by
-
A2E induces IL-1ß production in retinal pigment epithelial cells via the NLRP3 inflammasome.PLoS One. 2013 Jun 28;8(6):e67263. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0067263. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23840644 Free PMC article.
-
Rev-Erbα and Photoreceptor Outer Segments modulate the Circadian Clock in Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells.Sci Rep. 2019 Aug 13;9(1):11790. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-48203-3. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31409842 Free PMC article.
-
The Cytoskeleton of the Retinal Pigment Epithelium: from Normal Aging to Age-Related Macular Degeneration.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jul 22;20(14):3578. doi: 10.3390/ijms20143578. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31336621 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fenofibric acid prevents retinal pigment epithelium disruption induced by interleukin-1β by suppressing AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) activation.Diabetologia. 2011 Jun;54(6):1543-53. doi: 10.1007/s00125-011-2089-5. Epub 2011 Mar 3. Diabetologia. 2011. PMID: 21369818
-
Cell models to study regulation of cell transformation in pathologies of retinal pigment epithelium.J Ophthalmol. 2014;2014:801787. doi: 10.1155/2014/801787. Epub 2014 Aug 7. J Ophthalmol. 2014. PMID: 25177495 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Zinn KM, Benjamin-Henkind JV. Anatomy of the human retinal pigment epithelium. In: Zinn KM, Marmor M, editors. The retinal pigment epithelium. Cambridge: Harvard University Press; 1979. pp. 3–31.
-
- Campochiaro PA. Cytokine production by retinal pigmented epithelial cells. Int Rev Cytol. 1993;146:75–82. - PubMed
-
- Detrick B, Newsome DA, Percopo CM, et al. Class II antigen expression and gamma interferon modulation of monocytes and retinal pigment epithelial cells from patients with retinitis pigmentosa. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1985;36:201–11. - PubMed
-
- Elner SG, Elner VM, Pavilack MA, et al. Modulation and function of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (CD54) on human retinal pigment epithelial cells. Lab Invest. 1992;66:200–11. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

