A broad range of chemokine receptors are used by primary isolates of human immunodeficiency virus type 2 as coreceptors with CD4
- PMID: 9557695
- PMCID: PMC109635
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.72.5.4065-4071.1998
A broad range of chemokine receptors are used by primary isolates of human immunodeficiency virus type 2 as coreceptors with CD4
Abstract
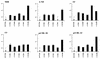
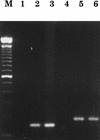
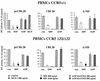
Like human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) and simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV), HIV-2 requires a coreceptor in addition to CD4 for entry into cells. HIV and SIV coreceptor molecules belong to a family of seven-transmembrane-domain G-protein-coupled receptors. Here we show that primary HIV-2 isolates can use a broad range of coreceptor molecules, including CCR1, CCR2b, CCR3, CCR4, CCR5, and CXCR4. Despite broad coreceptor use, the chemokine ligand SDF-1 substantially blocked HIV-2 infectivity of peripheral blood mononuclear cells, indicating that its receptor, CXCR4, was the predominant coreceptor for infection of these cells. However, expression of CXCR4 together with CD4 on some cell types did not confer susceptibility to infection by all CXCR4-using virus isolates. These data therefore indicate that another factor(s) influences the ability of HIV-2 to replicate in human cell types that express the appropriate receptors for virus entry.
Figures
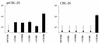
Similar articles
-
Use of inhibitors to evaluate coreceptor usage by simian and simian/human immunodeficiency viruses and human immunodeficiency virus type 2 in primary cells.J Virol. 2000 Aug;74(15):6893-910. doi: 10.1128/jvi.74.15.6893-6910.2000. J Virol. 2000. PMID: 10888629 Free PMC article.
-
Nonproductive human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection of human fetal astrocytes: independence from CD4 and major chemokine receptors.Virology. 1999 Nov 25;264(2):370-84. doi: 10.1006/viro.1999.9998. Virology. 1999. PMID: 10562499
-
Primary human immunodeficiency virus type 2 (HIV-2) isolates infect CD4-negative cells via CCR5 and CXCR4: comparison with HIV-1 and simian immunodeficiency virus and relevance to cell tropism in vivo.J Virol. 1999 Sep;73(9):7795-804. doi: 10.1128/JVI.73.9.7795-7804.1999. J Virol. 1999. PMID: 10438870 Free PMC article.
-
Synthetic peptides for study of human immunodeficiency virus infection.Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2002 Jul-Dec;102-103(1-6):41-7. doi: 10.1385/abab:102-103:1-6:041. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2002. PMID: 12396109 Review.
-
Chemokine receptors and virus entry in the central nervous system.J Neurovirol. 1999 Dec;5(6):643-58. doi: 10.3109/13550289909021293. J Neurovirol. 1999. PMID: 10602405 Review.
Cited by
-
The promiscuous CC chemokine receptor D6 is a functional coreceptor for primary isolates of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) and HIV-2 on astrocytes.J Virol. 2005 Aug;79(15):9618-24. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.15.9618-9624.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 16014924 Free PMC article.
-
CCR5, GPR15, and CXCR6 are major coreceptors of human immunodeficiency virus type 2 variants isolated from individuals with and without plasma viremia.J Virol. 2005 Feb;79(3):1686-700. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.3.1686-1700.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 15650194 Free PMC article.
-
Simian immunodeficiency viruses of diverse origin can use CXCR4 as a coreceptor for entry into human cells.J Virol. 2000 Jun;74(12):5702-8. doi: 10.1128/jvi.74.12.5702-5708.2000. J Virol. 2000. PMID: 10823878 Free PMC article.
-
HIV-2 interaction with cell coreceptors: amino acids within the V1/V2 region of viral envelope are determinant for CCR8, CCR5 and CXCR4 usage.Retrovirology. 2014 Nov 25;11:99. doi: 10.1186/s12977-014-0099-3. Retrovirology. 2014. PMID: 25421818 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of a late entry event in the replication cycle of human immunodeficiency virus type 2.J Virol. 2001 Aug;75(15):6914-22. doi: 10.1128/JVI.75.15.6914-6922.2001. J Virol. 2001. PMID: 11435571 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Albert J, Stalhandske P, Marquina S, Karis J, Fouchier R A, Norrby E, Chiodi F. Biological phenotype of HIV type 2 isolates correlates with V3 genotype. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1996;12:821–828. - PubMed
-
- Alkhatib G, Combadiere C, Broder C C, Feng Y, Kennedy P E, Murphy P M, Berger E A. CC CKR5: a RANTES, MIP-1alpha, MIP-1beta receptor as a fusion cofactor for macrophage-tropic HIV-1. Science. 1996;272:1955–1958. - PubMed
-
- Alkhatib G, Liao F, Berger E A, Farber J M, Peden K W. A new SIV co-receptor, STRL33. Nature. 1997;388:238. - PubMed
-
- Bleul C C, Farzan M, Choe H, Parolin C, Clark Lewis I, Sodroski J, Springer T A. The lymphocyte chemoattractant SDF-1 is a ligand for LESTR/fusin and blocks HIV-1 entry. Nature. 1996;382:829–833. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

