Calcium-dependent regulation of rab3 in short-term plasticity
- PMID: 9547223
- PMCID: PMC6792638
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-09-03147.1998
Calcium-dependent regulation of rab3 in short-term plasticity
Abstract
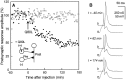
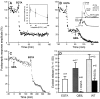
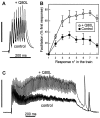
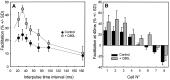
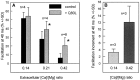
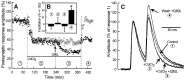
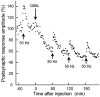
The Rab3 proteins are monomeric GTP-binding proteins associated with secretory vesicles. In their active GTP-bound state, Rab3 proteins are involved in the regulation of hormone secretion and neurotransmitter release. This action is thought to involve specific effectors, including two Ca2+-binding proteins, Rabphilin and Rim. Rab3 acts late in the exocytotic process, in a cell domain in which the intracellular Ca2+ concentration is susceptible to rapid changes. Therefore, we examined the possible Ca2+-dependency of the regulatory action of GTP-bound Rab3 and wild-type Rab3 on neuroexocytosis at identified cholinergic synapses in Aplysia californica. The effects of recombinant GTPase-deficient Aplysia-Rab3 (apRab3-Q80L) or wild-type apRab3 were studied on evoked acetylcholine release. Intraneuronal application of apRab3-Q80L in identified neurons of the buccal ganglion of Aplysia led to inhibition of neurotransmission; wild-type apRab3 was less effective. Intracellular chelation of Ca2+ ions by EGTA greatly potentiated the inhibitory action of apRab3-Q80L. Train and paired-pulse facilitation, two Ca2+-dependent forms of short-term plasticity induced by a rise in intraterminal Ca2+ concentration, were increased after injection of apRab3-Q80L. This result suggests that the inhibition exerted by GTP-bound Rab3 on neuroexocytosis is reduced during transient augmentations of intracellular Ca2+ concentration. Therefore, a Ca2+-dependent modulation of GTP-bound Rab3 function may contribute to short-term plasticity.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Suppression of long-term facilitation by Rab3-effector protein interaction.Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 2005 Sep 13;139(1):13-22. doi: 10.1016/j.molbrainres.2005.05.004. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 2005. PMID: 15936113
-
Evidence for a functional link between Rab3 and the SNARE complex.J Cell Sci. 1996 Dec;109 ( Pt 12):2875-84. doi: 10.1242/jcs.109.12.2875. J Cell Sci. 1996. PMID: 9013335
-
Rabphilin knock-out mice reveal that rabphilin is not required for rab3 function in regulating neurotransmitter release.J Neurosci. 1999 Jul 15;19(14):5834-46. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-14-05834.1999. J Neurosci. 1999. PMID: 10407024 Free PMC article.
-
Rab3 proteins: key players in the control of exocytosis.Trends Neurosci. 1994 Oct;17(10):426-32. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(94)90017-5. Trends Neurosci. 1994. PMID: 7530881 Review.
-
RAB3 and synaptotagmin: the yin and yang of synaptic membrane fusion.Annu Rev Neurosci. 1998;21:75-95. doi: 10.1146/annurev.neuro.21.1.75. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1998. PMID: 9530492 Review.
Cited by
-
A role for phospholipase D1 in neurotransmitter release.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001 Dec 18;98(26):15300-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.261358698. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001. PMID: 11752468 Free PMC article.
-
Inositol Pyrophosphate Metabolism Regulates Presynaptic Vesicle Cycling at Central Synapses.iScience. 2020 Apr 24;23(4):101000. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2020.101000. Epub 2020 Mar 22. iScience. 2020. PMID: 32252022 Free PMC article.
-
Rab3a is critical for trapping alpha-MSH granules in the high Ca²⁺-affinity pool by preventing constitutive exocytosis.PLoS One. 2013 Oct 21;8(10):e78883. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0078883. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24205339 Free PMC article.
-
Rab3A negatively regulates activity-dependent modulation of exocytosis in bovine adrenal chromaffin cells.J Physiol. 2004 Mar 1;555(Pt 2):439-57. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2003.056333. Epub 2003 Dec 23. J Physiol. 2004. PMID: 14694148 Free PMC article.
-
Real-time imaging of Rab3a and Rab5a reveals differential roles in presynaptic function.J Physiol. 2005 Nov 15;569(Pt 1):103-17. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2005.092528. Epub 2005 Sep 1. J Physiol. 2005. PMID: 16141272 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bao J-X, Kandel ER, Hawkins RD. Involvement of pre- and postsynaptic mechanisms in posttetanic potentiation at Aplysia synapses. Science. 1997;275:969–973. - PubMed
-
- Bean AJ, Scheller RH. Better late than never: a role for Rabs late in exocytosis. Neuron. 1997;19:751–754. - PubMed
-
- Bittner MA, Holz RW. Kinetic analysis of secretion from permeabilized adrenal chromaffin cells reveals distinct components. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:16219–16225. - PubMed
-
- Borst JGG, Sakmann B. Calcium influx and transmitter release at fast CNS synapse. Nature. 1996;383:431–434. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
