Segregation of viral plasmids depends on tethering to chromosomes and is regulated by phosphorylation
- PMID: 9539738
- PMCID: PMC22490
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.8.4338
Segregation of viral plasmids depends on tethering to chromosomes and is regulated by phosphorylation
Abstract
Eukaryotic viruses can maintain latency in dividing cells as extrachromosomal nuclear plasmids. Segregation and nuclear retention of DNA is, therefore, a key issue in retaining copy number. The E2 enhancer protein of the papillomaviruses is required for viral DNA replication and transcription. Viral mutants that prevent phosphorylation of the bovine papillomavirus type 1 (BPV) E2 protein are transformation-defective, despite normal viral gene expression and replication function. Cell colonies harboring such mutants show sectoring of viral DNA and are unable to maintain the episome. We find that transforming viral DNA attaches to mitotic chromosomes, in contrast to the mutant genome encoding the E2 phosphorylation mutant. Second-site suppressor mutations were uncovered in both E1 and E2 genes that allow for transformation, maintenance, and chromosomal attachment. E2 protein was also found to colocalize to mitotic chromosomes, whereas the mutant did not, suggesting a direct role for E2 in viral attachment to chromosomes. Such viral hitch-hiking onto cellular chromosomes is likely to provide a general mechanism for maintaining nuclear plasmids.
Figures
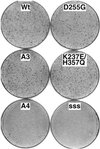
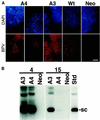
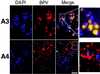


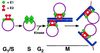
Comment in
-
Stability without a centromere.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998 Apr 14;95(8):4084-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.8.4084. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998. PMID: 9539691 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
E1 protein of bovine papillomavirus type 1 interferes with E2 protein-mediated tethering of the viral DNA to mitotic chromosomes.J Virol. 2002 Apr;76(7):3440-51. doi: 10.1128/jvi.76.7.3440-3451.2002. J Virol. 2002. PMID: 11884568 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation of the Bovine Papillomavirus E2 Protein on Tyrosine Regulates Its Transcription and Replication Functions.J Virol. 2017 Jan 3;91(2):e01854-16. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01854-16. Print 2017 Jan 15. J Virol. 2017. PMID: 27807239 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of the hinge region and the DNA binding domain of the bovine papillomavirus type 1 E2 protein in initiation of DNA replication.Virus Res. 2001 Jun;75(2):95-106. doi: 10.1016/s0168-1702(01)00219-2. Virus Res. 2001. PMID: 11325464
-
Partitioning viral genomes in mitosis: same idea, different targets.Cell Cycle. 2006 Jul;5(14):1499-502. doi: 10.4161/cc.5.14.3094. Epub 2006 Jul 17. Cell Cycle. 2006. PMID: 16861919 Review.
-
Targeting mitotic chromosomes: a conserved mechanism to ensure viral genome persistence.Proc Biol Sci. 2009 May 7;276(1662):1535-44. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2008.1642. Epub 2009 Jan 20. Proc Biol Sci. 2009. PMID: 19203914 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The papillomavirus E2 proteins.Virology. 2013 Oct;445(1-2):57-79. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2013.06.006. Epub 2013 Jul 10. Virology. 2013. PMID: 23849793 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mitotic kinesin-like protein 2 binds and colocalizes with papillomavirus E2 during mitosis.J Virol. 2007 Feb;81(4):1736-45. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01638-06. Epub 2006 Nov 29. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17135315 Free PMC article.
-
A transactivator function of cottontail rabbit papillomavirus e2 is essential for tumor induction in rabbits.J Virol. 2002 Nov;76(22):11209-15. doi: 10.1128/jvi.76.22.11209-11215.2002. J Virol. 2002. PMID: 12388680 Free PMC article.
-
Brd4 links chromatin targeting to HPV transcriptional silencing.Genes Dev. 2006 Sep 1;20(17):2383-96. doi: 10.1101/gad.1448206. Epub 2006 Aug 18. Genes Dev. 2006. PMID: 16921027 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of the papillomavirus E2 and bromodomain protein Brd4 interaction using bimolecular fluorescence complementation.PLoS One. 2013 Oct 25;8(10):e77994. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0077994. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24205059 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nordstrom K, Austin S. Annu Rev Genet. 1989;23:37–69. - PubMed
-
- Niki H, Hiraga S. Cell. 1997;90:951–957. - PubMed
-
- Mohl D A, Gober J W. Cell. 1997;88:675–684. - PubMed
-
- Webb C D, Teleman A, Gordon S, Straight A, Belmont A, Lin D C, Grossman A D, Wright A, Losick R. Cell. 1997;88:667–674. - PubMed
-
- Zur Hausen H. Virology. 1991;184:9–13. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

