Characterization of a 34-kDa soybean binding protein for the syringolide elicitors
- PMID: 9501258
- PMCID: PMC19737
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.6.3306
Characterization of a 34-kDa soybean binding protein for the syringolide elicitors
Abstract
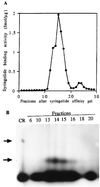
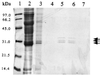
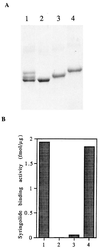
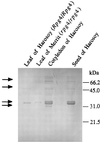
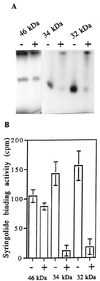
Syringolides are water-soluble, low-molecular-weight elicitors that trigger defense responses in soybean cultivars carrying the Rpg4 disease-resistance gene but not in rpg4 cultivars. 125I-syringolide 1 previously was shown to bind to a soluble protein(s) in extracts from soybean leaves. A 34-kDa protein that accounted for 125I-syringolide 1 binding activity was isolated with a syringolide affinity-gel column. Partial sequences of internal peptides of the 34-kDa protein were identical to P34, a previously described soybean seed allergen. In soybean seeds, P34 is processed from a 46-kDa precursor protein and was shown to have homology with thiol proteases. P34 is a moderately abundant protein in soybean seeds and cotyledons but its level in leaves is low. cDNAs encoding 46-, 34-, and 32-kDa forms of the soybean protein were cloned into the baculovirus vector, pVL1392, and expressed in insect cells. The resulting 32- and 34-kDa proteins, but not the 46-kDa protein, exhibited ligand-specific 125I-syringolide binding activity. These results suggest that P34 may be the receptor that mediates syringolide signaling.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cloning of soybean genes induced during hypersensitive cell death caused by syringolide elicitor.Planta. 2004 Feb;218(4):606-14. doi: 10.1007/s00425-003-1136-y. Epub 2003 Oct 30. Planta. 2004. PMID: 14586656
-
The P34 syringolide elicitor receptor interacts with a soybean photorespiration enzyme, NADH-dependent hydroxypyruvate reductase.Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2002 Dec;15(12):1213-8. doi: 10.1094/MPMI.2002.15.12.1213. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2002. PMID: 12481993
-
Specific Binding of the Syringolide Elicitors to a Soluble Protein Fraction from Soybean Leaves.Plant Cell. 1997 Aug;9(8):1425-1433. doi: 10.1105/tpc.9.8.1425. Plant Cell. 1997. PMID: 12237390 Free PMC article.
-
Allergenic proteins in soybean: processing and reduction of P34 allergenicity.Nutr Rev. 2005 Feb;63(2):47-58. doi: 10.1111/j.1753-4887.2005.tb00121.x. Nutr Rev. 2005. PMID: 15762088 Review.
-
Characterization of hepta-beta-glucoside elicitor-binding protein(s) in soybean.Biochem Soc Trans. 1994 May;22(2):408-14. doi: 10.1042/bst0220408. Biochem Soc Trans. 1994. PMID: 7958335 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Cloning of soybean genes induced during hypersensitive cell death caused by syringolide elicitor.Planta. 2004 Feb;218(4):606-14. doi: 10.1007/s00425-003-1136-y. Epub 2003 Oct 30. Planta. 2004. PMID: 14586656
-
Genetic complexity of pathogen perception by plants: the example of Rcr3, a tomato gene required specifically by Cf-2.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000 Aug 1;97(16):8807-14. doi: 10.1073/pnas.97.16.8807. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000. PMID: 10922039 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pto mutants differentially activate Prf-dependent, avrPto-independent resistance and gene-for-gene resistance.Plant Physiol. 2003 Mar;131(3):1239-49. doi: 10.1104/pp.016113. Plant Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12644674 Free PMC article.
-
Cosuppression of the alpha subunits of beta-conglycinin in transgenic soybean seeds induces the formation of endoplasmic reticulum-derived protein bodies.Plant Cell. 2001 May;13(5):1165-78. doi: 10.1105/tpc.13.5.1165. Plant Cell. 2001. PMID: 11340189 Free PMC article.
-
Cross-reactivity between the soybean protein p34 and bovine caseins.Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2015 Jan;7(1):60-8. doi: 10.4168/aair.2015.7.1.60. Epub 2014 Sep 11. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2015. PMID: 25553264 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

