The alpha chain of the nascent polypeptide-associated complex functions as a transcriptional coactivator
- PMID: 9488445
- PMCID: PMC108843
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.18.3.1303
The alpha chain of the nascent polypeptide-associated complex functions as a transcriptional coactivator
Abstract
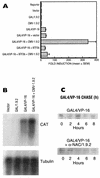
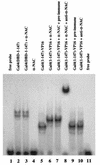
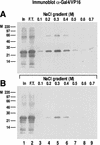
We report the characterization of clone 1.9.2, a gene expressed in mineralizing osteoblasts. Remarkably, clone 1.9.2 is the murine homolog of the alpha chain of the nascent polypeptide-associated complex (alpha-NAC). Based on sequence similarities between alpha-NAC/1.9.2 and transcriptional regulatory proteins and the fact that the heterodimerization partner of alpha-NAC was identified as the transcription factor BTF3b (B. Wiedmann, H. Sakai, T. A. Davis, and M. Wiedmann, Nature 370:434-440, 1994), we investigated a putative role for alpha-NAC/ 1.9.2 in transcriptional control. The alpha-NAC/1.9.2 protein potentiated by 10-fold the activity of the chimeric activator GAL4/VP-16 in vivo. The potentiation was shown to be mediated at the level of gene transcription, because alpha-NAC/1.9.2 increased GAL4/VP-16-mediated mRNA synthesis without affecting the half-life of the GAL4/VP-16 fusion protein. Moreover, the interaction of alpha-NAC/1.9.2 with a transcriptionally defective mutant of GAL4/VP-16 was severely compromised. Specific protein-protein interactions between alpha-NAC/1.9.2 and GAL4/VP-16 were demonstrated by gel retardation, affinity chromatography, and protein blotting assays, while interactions with TATA box-binding protein (TBP) were detected by immunoprecipitation, affinity chromatography, and protein blotting assays. Based on these interactions that define the coactivator class of proteins, we conclude that the alapha-NAC/1.9.2 gene product functions as a transcriptional coactivator.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Specific interactions with TBP and TFIIB in vitro suggest that 14-3-3 proteins may participate in the regulation of transcription when part of a DNA binding complex.Plant Cell. 1999 Aug;11(8):1591-602. doi: 10.1105/tpc.11.8.1591. Plant Cell. 1999. PMID: 10449590 Free PMC article.
-
Bone-specific expression of the alpha chain of the nascent polypeptide-associated complex, a coactivator potentiating c-Jun-mediated transcription.Mol Cell Biol. 1998 Mar;18(3):1312-21. doi: 10.1128/MCB.18.3.1312. Mol Cell Biol. 1998. PMID: 9488446 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction between acidic transcriptional activation domains of herpes simplex virus activator protein VP16 and transcriptional initiation factor IID.Methods Enzymol. 1996;274:120-33. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(96)74012-0. Methods Enzymol. 1996. PMID: 8902800 No abstract available.
-
Mechanisms of transcriptional activation and repression can both involve TFIID.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1996 Apr 29;351(1339):517-26. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1996.0050. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1996. PMID: 8735274 Review.
-
Mechanisms of viral activators.Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1998;63:243-52. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1998.63.243. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1998. PMID: 10384288 Review.
Cited by
-
Dual binding mode of the nascent polypeptide-associated complex reveals a novel universal adapter site on the ribosome.J Biol Chem. 2010 Jun 18;285(25):19679-87. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.092536. Epub 2010 Apr 21. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20410297 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying Methylation Signatures and Rules for COVID-19 With Machine Learning Methods.Front Mol Biosci. 2022 May 10;9:908080. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.908080. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 35620480 Free PMC article.
-
Lnc-GD2H Promotes Proliferation by Forming a Feedback Loop With c-Myc and Enhances Differentiation Through Interacting With NACA to Upregulate Myog in C2C12 Myoblasts.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Aug 18;9:671857. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.671857. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34490239 Free PMC article.
-
The African swine fever virus protein j4R binds to the alpha chain of nascent polypeptide-associated complex.J Virol. 2002 Oct;76(19):9991-9. doi: 10.1128/jvi.76.19.9991-9999.2002. J Virol. 2002. PMID: 12208975 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of alpha nascent polypeptide associated complex protein may induce proliferation, differentiation and enhance the cytotoxic activity of human CD8+ T cells.J Clin Immunol. 2006 Sep;26(5):457-64. doi: 10.1007/s10875-006-9041-3. Epub 2006 Sep 9. J Clin Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16964552
References
-
- Berger S L, Cress W D, Cress A, Triezenberg S J, Guarente L. Selective inhibition of activated but not basal transcription by the acidic activation domain of VP16: evidence for transcriptional adaptors. Cell. 1990;61:1199–1208. - PubMed
-
- Brownell J E, Zhou J, Ranalli T, Kobayashi R, Edmondson D G, Roth S Y, Allis C D. Tetrahymena histone acetyltransferase A: a homolog to yeast Gcn5p linking histone acetylation to gene activation. Cell. 1996;84:843–851. - PubMed
-
- Chen J-L, Attardi L D, Verrijzer C P, Yokomori K, Tjian R. Assembly of recombinant TFIID reveals differential coactivator requirements for distinct transcriptional activators. Cell. 1994;79:93–105. - PubMed
-
- Cress W D, Triezenberg S J. Critical structural elements of the VP16 transcriptional activation domain. Science. 1991;251:87–90. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
