A novel dynamin-like protein associates with cytoplasmic vesicles and tubules of the endoplasmic reticulum in mammalian cells
- PMID: 9472031
- PMCID: PMC2141745
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.140.4.779
A novel dynamin-like protein associates with cytoplasmic vesicles and tubules of the endoplasmic reticulum in mammalian cells
Abstract
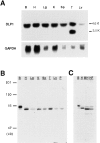
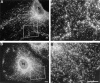
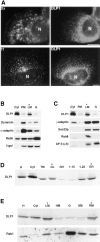
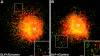
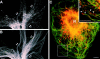
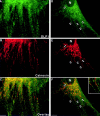
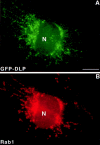
Dynamins are 100-kilodalton guanosine triphosphatases that participate in the formation of nascent vesicles during endocytosis. Here, we have tested if novel dynamin-like proteins are expressed in mammalian cells to support vesicle trafficking processes at cytoplasmic sites distinct from the plasma membrane. Immunological and molecular biological methods were used to isolate a cDNA clone encoding an 80-kilodalton novel dynamin-like protein, DLP1, that shares up to 42% homology with other dynamin-related proteins. DLP1 is expressed in all tissues examined and contains two alternatively spliced regions that are differentially expressed in a tissue-specific manner. DLP1 is enriched in subcellular membrane fractions of cytoplasmic vesicles and endoplasmic reticulum. Morphological studies of DLP1 in cultured cells using either a specific antibody or an expressed green fluorescent protein (GFP)- DLP1 fusion protein revealed that DLP1 associates with punctate cytoplasmic vesicles that do not colocalize with conventional dynamin, clathrin, or endocytic ligands. Remarkably, DLP1-positive structures coalign with microtubules and, most strikingly, with endoplasmic reticulum tubules as verified by double labeling with antibodies to calnexin and Rab1 as well as by immunoelectron microscopy. These observations provide the first evidence that a novel dynamin-like protein is expressed in mammalian cells where it associates with a secretory, rather than endocytic membrane compartment.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Mammalian dynamin-like protein DLP1 tubulates membranes.Mol Biol Cell. 2001 Sep;12(9):2894-905. doi: 10.1091/mbc.12.9.2894. Mol Biol Cell. 2001. PMID: 11553726 Free PMC article.
-
The dynamin-like protein DLP1 is essential for normal distribution and morphology of the endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria in mammalian cells.Mol Biol Cell. 1999 Dec;10(12):4403-17. doi: 10.1091/mbc.10.12.4403. Mol Biol Cell. 1999. PMID: 10588666 Free PMC article.
-
Association of a dynamin-like protein with the Golgi apparatus in mammalian cells.J Cell Biol. 1996 May;133(4):761-75. doi: 10.1083/jcb.133.4.761. J Cell Biol. 1996. PMID: 8666662 Free PMC article.
-
Participation of dynamin in the biogenesis of cytoplasmic vesicles.FASEB J. 1999 Dec;13 Suppl 2:S243-7. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.13.9002.s243. FASEB J. 1999. PMID: 10619136 Review.
-
The dynamins: redundant or distinct functions for an expanding family of related GTPases?Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997 Jan 21;94(2):377-84. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.2.377. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997. PMID: 9012790 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mammalian dynamin-like protein DLP1 tubulates membranes.Mol Biol Cell. 2001 Sep;12(9):2894-905. doi: 10.1091/mbc.12.9.2894. Mol Biol Cell. 2001. PMID: 11553726 Free PMC article.
-
Drp1 levels constitutively regulate mitochondrial dynamics and cell survival in cortical neurons.Exp Neurol. 2009 Aug;218(2):274-85. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2009.05.010. Epub 2009 May 13. Exp Neurol. 2009. PMID: 19445933 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple faces of dynamin-related protein 1 and its role in Alzheimer's disease pathogenesis.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016 Apr;1862(4):814-828. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2015.12.018. Epub 2015 Dec 17. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016. PMID: 26708942 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mitochondrial morphology in metabolic diseases.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2013 Aug 1;19(4):415-30. doi: 10.1089/ars.2012.4779. Epub 2012 Aug 27. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2013. PMID: 22793999 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plastid division control: the PDV proteins regulate DRP5B dynamin activity.Plant Mol Biol. 2013 Jun;82(3):255-66. doi: 10.1007/s11103-013-0059-7. Epub 2013 Apr 18. Plant Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23595201
References
-
- Adams, M., A. Kerlavage, R. Fleischmann, R. Fuldner, C. Bult, N. Lee, E. Kirkness, K. Weinstock, J. Gocayne, O. White, et al. 1995. Initial assessment of human gene diversity and expression patterns based upon 83 million nucleotides of cDNA sequence. Nature. 377(Suppl.):3–174. - PubMed
-
- Barlowe C, Orci L, Yeung T, Hosobuchi M, Hamamoto S, Salama N, Rexach MF, Ravazzola M, Amherdt M, Schekman R. COPII: a membrane coat formed by Sec proteins that drive vesicle budding from the endoplasmic reticulum. Cell. 1994;77:895–907. - PubMed
-
- Chomczynski P, Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987;162:156–159. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

