DSIF, a novel transcription elongation factor that regulates RNA polymerase II processivity, is composed of human Spt4 and Spt5 homologs
- PMID: 9450929
- PMCID: PMC316480
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.12.3.343
DSIF, a novel transcription elongation factor that regulates RNA polymerase II processivity, is composed of human Spt4 and Spt5 homologs
Abstract
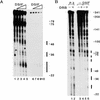
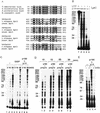
We report the identification of a transcription elongation factor from HeLa cell nuclear extracts that causes pausing of RNA polymerase II (Pol II) in conjunction with the transcription inhibitor 5,6-dichloro-1-beta-D-ribofuranosylbenzimidazole (DRB). This factor, termed DRB sensitivity-inducing factor (DSIF), is also required for transcription inhibition by H8. DSIF has been purified and is composed of 160-kD (p160) and 14-kD (p14) subunits. Isolation of a cDNA encoding DSIF p160 shows it to be a homolog of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae transcription factor Spt5. Recombinant Supt4h protein, the human homolog of yeast Spt4, is functionally equivalent to DSIF p14, indicating that DSIF is composed of the human homologs of Spt4 and Spt5. In addition to its negative role in elongation, DSIF is able to stimulate the rate of elongation by RNA Pol II in a reaction containing limiting concentrations of ribonucleoside triphosphates. A role for DSIF in transcription elongation is further supported by the fact that p160 has a region homologous to the bacterial elongation factor NusG. The combination of biochemical studies on DSIF and genetic analysis of Spt4 and Spt5 in yeast, also in this issue, indicates that DSIF associates with RNA Pol II and regulates its processivity in vitro and in vivo.
Figures


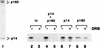



Similar articles
-
Structure and function of the human transcription elongation factor DSIF.J Biol Chem. 1999 Mar 19;274(12):8085-92. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.12.8085. J Biol Chem. 1999. PMID: 10075709
-
Domains in the SPT5 protein that modulate its transcriptional regulatory properties.Mol Cell Biol. 2000 May;20(9):2970-83. doi: 10.1128/MCB.20.9.2970-2983.2000. Mol Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 10757782 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence that Spt4, Spt5, and Spt6 control transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Genes Dev. 1998 Feb 1;12(3):357-69. doi: 10.1101/gad.12.3.357. Genes Dev. 1998. PMID: 9450930 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of Transcription Elongation Factor DSIF (Spt4-Spt5).J Mol Biol. 2021 Jul 9;433(14):166657. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2020.09.016. Epub 2020 Sep 25. J Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 32987031 Review.
-
The pleiotropic roles of SPT5 in transcription.Transcription. 2022 Feb-Jun;13(1-3):53-69. doi: 10.1080/21541264.2022.2103366. Epub 2022 Jul 25. Transcription. 2022. PMID: 35876486 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
NELF-A controls Drosophila healthspan by regulating heat-shock protein-mediated cellular protection and heterochromatin maintenance.Aging Cell. 2021 May;20(5):e13348. doi: 10.1111/acel.13348. Epub 2021 Mar 31. Aging Cell. 2021. PMID: 33788376 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription elongation control by the 7SK snRNP complex: Releasing the pause.Cell Cycle. 2016 Aug 17;15(16):2115-2123. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2016.1181241. Epub 2016 May 6. Cell Cycle. 2016. PMID: 27152730 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High-Resolution Mapping of RNA Polymerases Identifies Mechanisms of Sensitivity and Resistance to BET Inhibitors in t(8;21) AML.Cell Rep. 2016 Aug 16;16(7):2003-16. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2016.07.032. Epub 2016 Aug 4. Cell Rep. 2016. PMID: 27498870 Free PMC article.
-
Extensive polymerase pausing during Drosophila axis patterning enables high-level and pliable transcription.Genes Dev. 2013 May 15;27(10):1146-58. doi: 10.1101/gad.215459.113. Genes Dev. 2013. PMID: 23699410 Free PMC article.
-
Presenilin-based genetic screens in Drosophila melanogaster identify novel notch pathway modifiers.Genetics. 2006 Apr;172(4):2309-24. doi: 10.1534/genetics.104.035170. Epub 2006 Jan 16. Genetics. 2006. PMID: 16415372 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akoulitchev S, Makela TP, Weinberg RA, Reinberg D. Requirement for TFIIH kinase activity in transcription by RNA polymerase II. Nature. 1995;377:557–560. - PubMed
-
- Aso T, Lane WS, Conaway JW, Conaway RC. Elongin (SIII): A multisubunit regulator of elongation by RNA polymerase II. Science. 1995;269:1439–1443. - PubMed
-
- Bortvin A, Winston F. Evidence that Spt6p controls chromatin structure by a direct interaction with histones. Science. 1996;272:1473–1476. - PubMed
-
- Bradsher JN, Jackson KW, Conaway RC, Conaway JW. RNA polymerase II transcription factor SIII. I. Identification, purification, and properties. J Biol Chem. 1993a;268:25587–25593. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
