Smad6 inhibits BMP/Smad1 signaling by specifically competing with the Smad4 tumor suppressor
- PMID: 9436979
- PMCID: PMC316444
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.12.2.186
Smad6 inhibits BMP/Smad1 signaling by specifically competing with the Smad4 tumor suppressor
Abstract
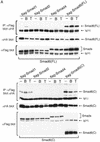
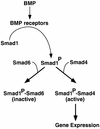
Bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) receptors signal by phosphorylating Smad1, which then associates with Smad4; this complex moves into the nucleus and activates transcription. Here we report the existence of a natural inhibitor of this process, Smad6, a longer version of the previously reported JV15-1. In Xenopus embryos and in mammalian cells, Smad6 specifically blocks signaling by the BMP/Smad1 pathway. Smad6 inhibits BMP/Smad1 signaling without interfering with receptor-mediated phosphorylation of Smad1. Smad6 specifically competes with Smad4 for binding to receptor-activated Smad1, yielding an apparently inactive Smad1-Smad6 complex. Therefore, Smad6 selectively antagonizes BMP-activated Smad1 by acting as a Smad4 decoy.
Figures

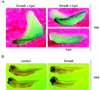


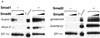
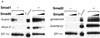
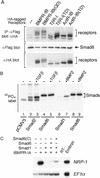






Similar articles
-
Smad6 is a Smad1/5-induced smad inhibitor. Characterization of bone morphogenetic protein-responsive element in the mouse Smad6 promoter.J Biol Chem. 2000 Mar 3;275(9):6075-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.275.9.6075. J Biol Chem. 2000. PMID: 10692396
-
Smad6 functions as an intracellular antagonist of some TGF-beta family members during Xenopus embryogenesis.Genes Cells. 1998 Jun;3(6):387-94. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2443.1998.00196.x. Genes Cells. 1998. PMID: 9734784
-
Promoting bone morphogenetic protein signaling through negative regulation of inhibitory Smads.EMBO J. 2001 Aug 1;20(15):4132-42. doi: 10.1093/emboj/20.15.4132. EMBO J. 2001. PMID: 11483516 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism for the action of bone morphogenetic proteins and regulation of their activity.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2002 Aug 15;27(16 Suppl 1):S10-5. doi: 10.1097/00007632-200208151-00004. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2002. PMID: 12205413 Review.
-
[The role of Smads and related transcription factors in the signal transduction of bone morphogenetic protein inducing bone formation].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2003 Sep;17(5):359-62. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2003. PMID: 14551929 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Transforming growth factor beta signaling and craniofacial development: modeling human diseases in zebrafish.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Feb 7;12:1338070. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1338070. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 38385025 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Loss of Neogenin alters branchial arch development and leads to craniofacial skeletal defects.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Feb 9;12:1256465. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1256465. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 38404688 Free PMC article.
-
USP15 stabilizes TGF-β receptor I and promotes oncogenesis through the activation of TGF-β signaling in glioblastoma.Nat Med. 2012 Feb 19;18(3):429-35. doi: 10.1038/nm.2619. Nat Med. 2012. PMID: 22344298
-
Repression of Inappropriate Gene Expression in the Vertebrate Embryonic Ectoderm.Genes (Basel). 2019 Nov 6;10(11):895. doi: 10.3390/genes10110895. Genes (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31698780 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genomic characterization of Wilms' tumor suppressor 1 targets in nephron progenitor cells during kidney development.Development. 2010 Apr;137(7):1189-203. doi: 10.1242/dev.045732. Development. 2010. PMID: 20215353 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Asashima M, Nakano H, Shimada K, Kinoshita K, Ishii K, Shibai H, Ueno N. Mesodermal induction in early amphibian embryos by activin A (erythroid differentiation factor) Wilhelm Roux’s Arch Dev Biol. 1990;198:330–335. - PubMed
-
- Baker J, Harland RM. A novel mesoderm inducer, mMadr-2, functions in the activin signal transduction pathway. Genes & Dev. 1996;10:1880–1889. - PubMed
-
- Chen X, Rubock MJ, Whitman M. A transcriptional partner of MAD proteins in TGF-β signalling. Nature. 1996;383:691–696. - PubMed
-
- Eppert K, Scherer SW, Ozcelik H, Pirone R, Hoodless P, Kim H, Tsui L-C, Bapat B, Gallinger S, Andrulis IL, Thomsen GH, Wrana JL, Attisano L. MADR2 maps to 18q21 and encodes a TGFβ-regulated MAD-related protein that is functionally mutated in colorectal carcinoma. Cell. 1996;86:543–552. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
