A family of human receptors structurally related to Drosophila Toll
- PMID: 9435236
- PMCID: PMC18464
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.2.588
A family of human receptors structurally related to Drosophila Toll
Abstract
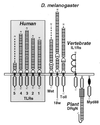
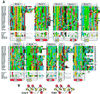
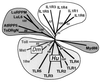
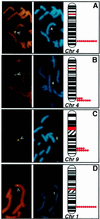
The discovery of sequence homology between the cytoplasmic domains of Drosophila Toll and human interleukin 1 receptors has sown the conviction that both molecules trigger related signaling pathways tied to the nuclear translocation of Rel-type transcription factors. This conserved signaling scheme governs an evolutionarily ancient immune response in both insects and vertebrates. We report the molecular cloning of a class of putative human receptors with a protein architecture that is similar to Drosophila Toll in both intra- and extracellular segments. Five human Toll-like receptors--named TLRs 1-5--are probably the direct homologs of the fly molecule and, as such, could constitute an important and unrecognized component of innate immunity in humans. Intriguingly, the evolutionary retention of TLRs in vertebrates may indicate another role--akin to Toll in the dorsoventralization of the Drosophila embryo--as regulators of early morphogenetic patterning. Multiple tissue mRNA blots indicate markedly different patterns of expression for the human TLRs. By using fluorescence in situ hybridization and sequence-tagged site database analyses, we also show that the cognate Tlr genes reside on chromosomes 4 (TLRs 1, 2, and 3), 9 (TLR4), and 1 (TLR5). Structure prediction of the aligned Toll-homology domains from varied insect and human TLRs, vertebrate interleukin 1 receptors and MyD88 factors, and plant disease-resistance proteins recognizes a parallel beta/alpha fold with an acidic active site; a similar structure notably recurs in a class of response regulators broadly involved in transducing sensory information in bacteria.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cloning and characterization of two Toll/Interleukin-1 receptor-like genes TIL3 and TIL4: evidence for a multi-gene receptor family in humans.Blood. 1998 Jun 1;91(11):4020-7. Blood. 1998. PMID: 9596645
-
TLR6: A novel member of an expanding toll-like receptor family.Gene. 1999 Apr 29;231(1-2):59-65. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1119(99)00098-0. Gene. 1999. PMID: 10231569
-
Structural complementarity of Toll/interleukin-1 receptor domains in Toll-like receptors and the adaptors Mal and MyD88.J Biol Chem. 2003 Oct 17;278(42):41443-51. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M301742200. Epub 2003 Jul 29. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12888566
-
The biology of Toll-like receptors.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2000 Sep;11(3):219-32. doi: 10.1016/s1359-6101(00)00006-x. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2000. PMID: 10817965 Review.
-
Evolutionary relationships, but functional differences, between the Drosophila and human Toll-like receptor families.Biochem Soc Trans. 2003 Jun;31(Pt 3):659-63. doi: 10.1042/bst0310659. Biochem Soc Trans. 2003. PMID: 12773177 Review.
Cited by
-
Suppression of TLR signaling by targeting TIR domain-containing proteins.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2012 Dec;13(8):776-88. doi: 10.2174/138920312804871148. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2012. PMID: 23305364 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A new synthetic chalcone derivative, 2-hydroxy-3',5,5'-trimethoxychalcone (DK-139), suppresses the Toll-like receptor 4-mediated inflammatory response through inhibition of the Akt/NF-κB pathway in BV2 microglial cells.Exp Mol Med. 2012 Jun 30;44(6):369-77. doi: 10.3858/emm.2012.44.6.042. Exp Mol Med. 2012. PMID: 22382990 Free PMC article.
-
Immunomodulatory effects of transforming growth factor-β in the liver.Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr. 2014 Dec;3(6):386-406. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2304-3881.2014.11.06. Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr. 2014. PMID: 25568862 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lactic Acid Bacteria and Aging: Unraveling the Interplay for Healthy Longevity.Aging Dis. 2023 Oct 10;15(4):1487-98. doi: 10.14336/AD.2023.0926. Online ahead of print. Aging Dis. 2023. PMID: 37962461 Free PMC article.
-
Cloning of Toll-like Receptor 3 Gene from Schizothorax prenanti (SpTLR3), and Expressions of Seven SpTLRs and SpMyD88 after Lipopolysaccharide Induction.Genes (Basel). 2022 Oct 15;13(10):1862. doi: 10.3390/genes13101862. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36292749 Free PMC article.
References
-
- DeRobertis E M, Sasai Y. Nature (London) 1996;380:37–40. - PubMed
-
- Arendt D, Nübler-Jung K. Mech Dev. 1997;61:7–21. - PubMed
-
- Miklos G L G, Rubin G M. Cell. 1996;86:521–529. - PubMed
-
- Chothia, C. (1994) Development Suppl. 27–33. - PubMed
-
- Banfi S, Borsani G, Rossi E, Bernard L, Guffanti A, Rubboli F, Marchitiello A, Giglio S, Coluccia E, Zollo M, Zuffardi O, Ballabio A. Nat Genet. 1996;13:167–174. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

