Extracellular ATP activates transcription factor NF-kappaB through the P2Z purinoreceptor by selectively targeting NF-kappaB p65
- PMID: 9412459
- PMCID: PMC2132650
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.139.7.1635
Extracellular ATP activates transcription factor NF-kappaB through the P2Z purinoreceptor by selectively targeting NF-kappaB p65
Abstract
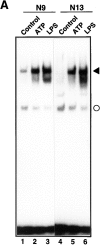
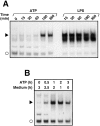
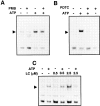
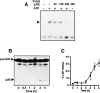
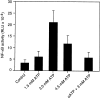
Cells of the macrophage lineage express a peculiar surface receptor for extracellular ATP, designated P2Z/P2X7 purinergic receptor, that induces pore formation and collapse of the plasma membrane potential. Although the function of the P2Z receptor is largely unknown, accumulating evidence implicates its role in cell signaling and immune reactions. Here, we investigated the effect of P2Z receptor ligation on the activation of NF-kappaB, a transcription factor controlling cytokine expression and apoptosis. Exposure of microglial cells to ATP but not other nucleotides resulted in potent NF-kappaB activation. This effect was specifically mediated by the P2Z receptor, because selective receptor antagonists prevented NF-kappaB activation. NF-kappaB activation required reactive oxygen intermediates and proteases of the caspase family, because it was abolished by antioxidants and specific protease inhibitors. The subunit composition of the ATP-induced NF- kappaB-DNA complex was rather unusual. Whereas exposure to LPS-induced prototypical NF-kappaB p50 homo- and p65 (RelA)/p50 heterodimers, ATP stimulation resulted in the sole appearance of a p65 homodimer. This is the first demonstration that a certain stimulus activates a particular NF-kappaB subunit. Because different NF-kappaB complexes exhibit distinct transcriptional and DNA-binding activities, ATP may control the expression of a subset of NF-kappaB target genes distinct from those activated by classical proinflammatory mediators.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Purinergic receptor modulation of lipopolysaccharide signaling and inducible nitric-oxide synthase expression in RAW 264.7 macrophages.J Biol Chem. 1998 Oct 16;273(42):27170-5. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.42.27170. J Biol Chem. 1998. PMID: 9765236
-
P2X7/P2Z purinoreceptor-mediated activation of transcription factor NFAT in microglial cells.J Biol Chem. 1999 May 7;274(19):13205-10. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.19.13205. J Biol Chem. 1999. PMID: 10224077
-
P2Z purinoreceptor ligation induces activation of caspases with distinct roles in apoptotic and necrotic alterations of cell death.FEBS Lett. 1999 Mar 19;447(1):71-5. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(99)00270-7. FEBS Lett. 1999. PMID: 10218585
-
Transduction mechanisms of P2Z purinoceptors.Ciba Found Symp. 1996;198:149-60; discussion 160-5. doi: 10.1002/9780470514900.ch9. Ciba Found Symp. 1996. PMID: 8879824 Review.
-
P2Z purinoceptors.Ciba Found Symp. 1996;198:71-83; discussion 83-90. doi: 10.1002/9780470514900.ch4. Ciba Found Symp. 1996. PMID: 8879819 Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibition of purinergic P2X receptor 7 (P2X7R) decreases granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) expression in U251 glioblastoma cells.Sci Rep. 2020 Sep 9;10(1):14844. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-71887-x. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32908225 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidized ATP protection against anthrax lethal toxin.Infect Immun. 2006 Jul;74(7):3707-14. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00051-06. Infect Immun. 2006. PMID: 16790743 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of P2X7 Receptor in Alzheimer's Disease.Front Mol Neurosci. 2020 Jun 3;13:94. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2020.00094. eCollection 2020. Front Mol Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32581707 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Purinergic signaling and microglia.Pflugers Arch. 2006 Aug;452(5):615-21. doi: 10.1007/s00424-006-0064-7. Epub 2006 Jun 21. Pflugers Arch. 2006. PMID: 16791619 Review.
-
Proteomic and functional evidence for a P2X7 receptor signalling complex.EMBO J. 2001 Nov 15;20(22):6347-58. doi: 10.1093/emboj/20.22.6347. EMBO J. 2001. PMID: 11707406 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baeuerle PA, Henkel T. Function and activiation of NF-κB in the immune system. Annu Rev Immunol. 1994;12:141–179. - PubMed
-
- Baeuerle PA, Baltimore D. NF-κB: ten years after. Cell. 1996;87:13–20. - PubMed
-
- Baichwal VR, Baeuerle PA. Activate NF-κB or die? . Curr Biol. 1997;7:R94–R96. - PubMed
-
- Baldwin AS. The NF-κB and IκB proteins: new discoveries and insights. Annu Rev Immunol. 1996;242:540–546. - PubMed
-
- Bauer MKA, Lieb K, Schulze-Osthoff K, Bauer J, Gebicke-Haerter PJ, Fiebich BI. Expression and regulation of cyclooxygenase-2 in rat microglia. Eur J Biochem. 1997;243:726–731. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

