Spatial organization of large-scale chromatin domains in the nucleus: a magnified view of single chromosome territories
- PMID: 9412456
- PMCID: PMC2132633
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.139.7.1597
Spatial organization of large-scale chromatin domains in the nucleus: a magnified view of single chromosome territories
Abstract
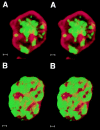
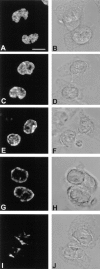
We have analyzed the spatial organization of large scale chromatin domains in chinese hamster fibroblast, human lymphoid (IM-9), and marsupial kidney epithelial (PtK) cells by labeling DNA at defined stages of S phase via pulsed incorporation of halogenated deoxynucleosides. Most, if not all, chromosomes contribute multiple chromatin domains to both peripheral and internal nucleoplasmic compartments. The peripheral compartment contains predominantly late replicating G/Q bands, whereas early replicating R bands preferentially localize to the internal nucleoplasmic compartment. During mitosis, the labeled chromatin domains that were separated in interphase form a pattern of intercalated bands along the length of each metaphase chromosome. The transition from a banded (mitotic) to a compartmentalized (interphasic) organization of chromatin domains occurs during the late telophase/early G1 stage and is independent of transcriptional activation of the genome. Interestingly, generation of micronuclei with a few chromosomes showed that the spatial separation of early and late replicating chromatin compartments is recapitulated independently of chromosome number, even in micronuclei containing only a single chromosome. Our data strongly support the notion that the compartmentalization of large-scale (band size) chromatin domains seen in the intact nucleus is a magnified image of a similar compartmentalization occurring in individual chromosome territories.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Chromosome territories, interchromatin domain compartment, and nuclear matrix: an integrated view of the functional nuclear architecture.Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2000;10(2):179-212. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2000. PMID: 11186332 Review.
-
Nuclear organization of mammalian genomes. Polar chromosome territories build up functionally distinct higher order compartments.J Cell Biol. 1999 Sep 20;146(6):1211-26. doi: 10.1083/jcb.146.6.1211. J Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 10491386 Free PMC article.
-
Specific staining of human chromosomes in Chinese hamster x man hybrid cell lines demonstrates interphase chromosome territories.Hum Genet. 1985;71(4):281-7. doi: 10.1007/BF00388452. Hum Genet. 1985. PMID: 2416668
-
Spatial distributions of early and late replicating chromatin in interphase chromosome territories.Exp Cell Res. 1998 Sep 15;243(2):398-407. doi: 10.1006/excr.1998.4144. Exp Cell Res. 1998. PMID: 9743599
-
[Topology of chromosomes in somatic cells. Part 1].Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2006;60:331-42. Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2006. PMID: 16819432 Review. Polish.
Cited by
-
Plant nucleolar DNA: Green light shed on the role of Nucleolin in genome organization.Nucleus. 2017 Jan 2;8(1):11-16. doi: 10.1080/19491034.2016.1236167. Epub 2016 Sep 20. Nucleus. 2017. PMID: 27644794 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IMACULAT - an open access package for the quantitative analysis of chromosome localization in the nucleus.PLoS One. 2013;8(4):e61386. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0061386. Epub 2013 Apr 8. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23577217 Free PMC article.
-
Interphase chromosome positioning in in vitro porcine cells and ex vivo porcine tissues.BMC Cell Biol. 2012 Nov 15;13:30. doi: 10.1186/1471-2121-13-30. BMC Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 23151271 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative analysis of the functional genome architecture of animal and plant cell nuclei.Chromosome Res. 2003;11(5):471-84. doi: 10.1023/a:1024978711705. Chromosome Res. 2003. PMID: 12971723
-
Spatial and temporal dynamics of DNA replication sites in mammalian cells.J Cell Biol. 1998 Dec 14;143(6):1415-25. doi: 10.1083/jcb.143.6.1415. J Cell Biol. 1998. PMID: 9852140 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agard DA, Sedat JW. Three-dimensional architecture of a polytene nucleus. Nature. 1983;302:676–681. - PubMed
-
- Aten JA, Stap J, Hoebe R, Bakker PJM. Application and detection of IdUrd and CldUrd as two independent cell-cycle markers. Methods Cell Biol. 1994;41:317–326. - PubMed
-
- Belmont AS, Braunfeld MB, Sedat JW, Agard DA. Large-scale chromatin structural domains within mitotic and interphase chromosomes in vivo and in vitro. Chromosoma. 1989;98:129–143. - PubMed

