Organization of G proteins and adenylyl cyclase at the plasma membrane
- PMID: 9398661
- PMCID: PMC25713
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.8.12.2365
Organization of G proteins and adenylyl cyclase at the plasma membrane
Abstract
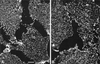
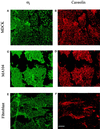
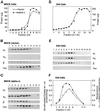
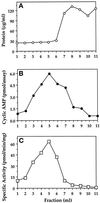
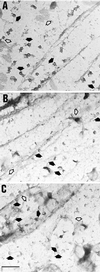
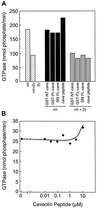
There is mounting evidence for the organization and compartmentation of signaling molecules at the plasma membrane. We find that hormone-sensitive adenylyl cyclase activity is enriched in a subset of regulatory G protein-containing fractions of the plasma membrane. These subfractions resemble, in low buoyant density, structures of the plasma membrane termed caveolae. Immunofluorescence experiments revealed a punctate pattern of G protein alpha and beta subunits, consistent with concentration of these proteins at distinct sites on the plasma membrane. Partial coincidence of localization of G protein alpha subunits with caveolin (a marker for caveolae) was observed by double immunofluorescence. Results of immunogold electron microscopy suggest that some G protein is associated with invaginated caveolae, but most of the protein resides in irregular structures of the plasma membrane that could not be identified morphologically. Because regulated adenylyl cyclase activity is present in low-density subfractions of plasma membrane from a cell type (S49 lymphoma) that does not express caveolin, this protein is not required for organization of the adenylyl cyclase system. The data suggest that hormone-sensitive adenylyl cyclase systems are localized in a specialized subdomain of the plasma membrane that may optimize the efficiency and fidelity of signal transduction.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Microtubules and actin microfilaments regulate lipid raft/caveolae localization of adenylyl cyclase signaling components.J Biol Chem. 2006 Sep 8;281(36):26391-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M602577200. Epub 2006 Jul 3. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16818493
-
Compartmentation of cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate signaling in caveolae.Mol Endocrinol. 1999 Jul;13(7):1061-70. doi: 10.1210/mend.13.7.0304. Mol Endocrinol. 1999. PMID: 10406458
-
Differential targeting of beta -adrenergic receptor subtypes and adenylyl cyclase to cardiomyocyte caveolae. A mechanism to functionally regulate the cAMP signaling pathway.J Biol Chem. 2000 Dec 29;275(52):41447-57. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M006951200. J Biol Chem. 2000. PMID: 11006286
-
Caveolin-1 and lipid microdomains regulate Gs trafficking and attenuate Gs/adenylyl cyclase signaling.Mol Pharmacol. 2009 Nov;76(5):1082-93. doi: 10.1124/mol.109.060160. Epub 2009 Aug 20. Mol Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19696145 Free PMC article.
-
Purification and characterization of smooth muscle cell caveolae.J Cell Biol. 1994 Jul;126(1):127-38. doi: 10.1083/jcb.126.1.127. J Cell Biol. 1994. PMID: 8027172 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Structural Basis of the Interaction of the G Proteins, Gαi1, Gβ1γ2 and Gαi1β1γ2, with Membrane Microdomains and Their Relationship to Cell Localization and Activity.Biomedicines. 2023 Feb 14;11(2):557. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11020557. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 36831093 Free PMC article.
-
Signaling and regulation of G protein-coupled receptors in airway smooth muscle.Respir Res. 2003;4(1):2. Epub 2003 Mar 14. Respir Res. 2003. PMID: 12648290 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Remodeling of the plasma membrane in preparation for sperm-egg recognition: roles of acrosomal proteins.Asian J Androl. 2015 Jul-Aug;17(4):574-82. doi: 10.4103/1008-682X.152817. Asian J Androl. 2015. PMID: 25994642 Free PMC article.
-
A neutral sphingomyelinase resides in sphingolipid-enriched microdomains and is inhibited by the caveolin-scaffolding domain: potential implications in tumour necrosis factor signalling.Biochem J. 2001 May 1;355(Pt 3):859-68. doi: 10.1042/bj3550859. Biochem J. 2001. PMID: 11311151 Free PMC article.
-
S1P1 receptor localization confers selectivity for Gi-mediated cAMP and contractile responses.J Biol Chem. 2008 May 2;283(18):11954-63. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M707422200. Epub 2008 Feb 24. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18296752 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anderson RGW, Kamen BA, Rothberg KG, Lacey SW. Potocytosis: sequestration and transport of small molecules by caveolae. Science. 1992;255:410–411. - PubMed
-
- Anderson, R.G.W. (1998). The caveolae membrane system. Annu. Rev. Biochem. (in press). - PubMed
-
- Brewer CB. Cytomegalovirus plasmid vectors for permanent lines of polarized epithelial cells. Methods Cell Biol. 1994;43:233–245. - PubMed
-
- Casey PJ, Fong HKW, Simon MI, Gilman AG. Gz, a guanine nucleotide-binding protein with unique biochemical properties. J Biol Chem. 1990;265:2383–2390. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

