Syk tyrosine kinase is required for the positive selection of immature B cells into the recirculating B cell pool
- PMID: 9396770
- PMCID: PMC2199169
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.186.12.2013
Syk tyrosine kinase is required for the positive selection of immature B cells into the recirculating B cell pool
Abstract
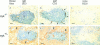
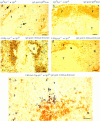
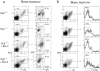
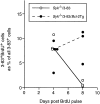
The tyrosine kinase Syk has been implicated as a key signal transducer from the B cell antigen receptor (BCR). We show here that mutation of the Syk gene completely blocks the maturation of immature B cells into recirculating cells and stops their entry into B cell follicles. Furthermore, using radiation chimeras we demonstrate that this developmental block is due to the absence of Syk in the B cells themselves. Syk-deficient B cells are shown to have the life span of normal immature B cells. If this is extended by over-expression of Bcl-2, they accumulate in the T zone and red pulp of the spleen in increased numbers, but still fail to mature to become recirculating follicular B cells. Despite this defect in maturation, Syk-deficient B cells were seen to give rise to switched as well as nonswitched splenic plasma cells. Normally only a proportion of immature B cells is recruited into the recirculating pool. Our results suggest that Syk transduces a BCR signal that is absolutely required for the positive selection of immature B cells into the recirculating B cell pool.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The tyrosine kinase Syk is required for light chain isotype exclusion but dispensable for the negative selection of B cells.Eur J Immunol. 2004 Apr;34(4):1102-10. doi: 10.1002/eji.200324309. Eur J Immunol. 2004. PMID: 15048721
-
Syk tyrosine kinase required for mouse viability and B-cell development.Nature. 1995 Nov 16;378(6554):303-6. doi: 10.1038/378303a0. Nature. 1995. PMID: 7477353
-
Cbl-b negatively regulates B cell antigen receptor signaling in mature B cells through ubiquitination of the tyrosine kinase Syk.J Exp Med. 2003 Jun 2;197(11):1511-24. doi: 10.1084/jem.20021686. Epub 2003 May 27. J Exp Med. 2003. PMID: 12771181 Free PMC article.
-
Autoinhibition and adapter function of Syk.Immunol Rev. 2009 Nov;232(1):286-99. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2009.00837.x. Immunol Rev. 2009. PMID: 19909371 Review.
-
Role of protein-tyrosine kinase syk in oxidative stress signaling in B cells.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2002 Jun;4(3):533-41. doi: 10.1089/15230860260196335. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2002. PMID: 12215221 Review.
Cited by
-
CD19 and BAFF-R can signal to promote B-cell survival in the absence of Syk.EMBO J. 2015 Apr 1;34(7):925-39. doi: 10.15252/embj.201489732. Epub 2015 Jan 28. EMBO J. 2015. PMID: 25630702 Free PMC article.
-
Hantavirus pulmonary syndrome-associated hantaviruses contain conserved and functional ITAM signaling elements.J Virol. 2003 Jan;77(2):1638-43. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.2.1638-1643.2003. J Virol. 2003. PMID: 12502882 Free PMC article.
-
B cell-specific S1PR1 deficiency blocks prion dissemination between secondary lymphoid organs.J Immunol. 2012 May 15;188(10):5032-40. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1200349. Epub 2012 Apr 13. J Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22504650 Free PMC article.
-
Syk inhibition with fostamatinib leads to transitional B lymphocyte depletion.Clin Immunol. 2012 Mar;142(3):237-42. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2011.12.012. Epub 2012 Jan 5. Clin Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22284392 Free PMC article.
-
Low-Level Expression of CD138 Marks Naturally Arising Anergic B Cells.Immune Netw. 2022 Oct 24;22(6):e50. doi: 10.4110/in.2022.22.e50. eCollection 2022 Dec. Immune Netw. 2022. PMID: 36627940 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rajewsky K. Clonal selection and learning in the antibody system. Nature. 1996;381:751–758. - PubMed
-
- Lortan JE, Roobottom CA, Oldfield S, MacLennan ICM. Newly produced virgin B-cells migrate to secondary lymphoid organs but their capacity to enter follicles is restricted. Eur J Immunol. 1987;17:1311–1316. - PubMed
-
- Chan EY-T, MacLennan ICM. Only a small proportion of splenic B cells in adults are short-lived virgin cells. Eur J Immunol. 1993;23:357–363. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

