Rho-stimulated contractility contributes to the fibroblastic phenotype of Ras-transformed epithelial cells
- PMID: 9362072
- PMCID: PMC25711
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.8.11.2329
Rho-stimulated contractility contributes to the fibroblastic phenotype of Ras-transformed epithelial cells
Abstract
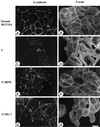
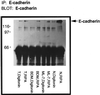
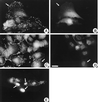
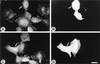
Oncogenic transformation of cells alters their morphology, cytoskeletal organization, and adhesive interactions. When the mammary epithelial cell line MCF10A is transformed by activated H-Ras, the cells display a mesenchymal/fibroblastic morphology with decreased cell-cell junctions but increased focal adhesions and stress fibers. We have investigated whether the transformed phenotype is due to Rho activation. The Ras-transformed MCF10A cells have elevated levels of myosin light chain phosphorylation and are more contractile than their normal counterparts, consistent with the activation of Rho. Furthermore, inhibitors of contractility restore a more normal epithelial phenotype to the Ras-transformed MCF10A cells. However, inhibiting Rho by microinjection of C3 exotransferase or dominant negative RhoA only partially restores the normal phenotype, in that it fails to restore normal junctional organization. This result prompted us to examine the effect that inhibiting Rho would have on the junctions of normal MCF10A cells. We have found that inhibiting Rho by C3 microinjection leads to a disruption of E-cadherin cytoskeletal links in adherens junctions and blocks the assembly of new adherens junctions. The introduction of constitutively active Rho into normal MCF10A cells did not mimic the Ras-transformed phenotype. Thus, these results lead us to conclude that some, but not all, characteristics of Ras-transformed epithelial cells are due to activated Rho. Whereas Rho is needed for the assembly of adherens junctions, high levels of activated Rho in Ras-transformed cells contribute to their altered cytoskeletal organization. However, additional events triggered by Ras must also be required for the disruption of adherens junctions and the full development of the transformed epithelial phenotype.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Tyrosine phosphorylation regulates the adhesions of ras-transformed breast epithelia.J Cell Biol. 1995 Jul;130(2):461-71. doi: 10.1083/jcb.130.2.461. J Cell Biol. 1995. PMID: 7542250 Free PMC article.
-
Rho-mediated contractility exposes a cryptic site in fibronectin and induces fibronectin matrix assembly.J Cell Biol. 1998 Apr 20;141(2):539-51. doi: 10.1083/jcb.141.2.539. J Cell Biol. 1998. PMID: 9548730 Free PMC article.
-
Restoration of E-cadherin cell-cell junctions requires both expression of E-cadherin and suppression of ERK MAP kinase activation in Ras-transformed breast epithelial cells.Neoplasia. 2008 Dec;10(12):1444-58. doi: 10.1593/neo.08968. Neoplasia. 2008. PMID: 19048123 Free PMC article.
-
Altered adhesions in ras-transformed breast epithelial cells.Biochem Soc Trans. 1995 Aug;23(3):446-50. doi: 10.1042/bst0230446. Biochem Soc Trans. 1995. PMID: 8566335 Review. No abstract available.
-
rho gene products, botulinum C3 exoenzyme and cell adhesion.Cell Signal. 1993 Jan;5(1):9-19. doi: 10.1016/0898-6568(93)90003-5. Cell Signal. 1993. PMID: 8452758 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Transformation of chicken embryo fibroblasts by v-src uncouples beta1 integrin-mediated outside-in but not inside-out signaling.Mol Cell Biol. 2001 Nov;21(21):7295-306. doi: 10.1128/MCB.21.21.7295-7306.2001. Mol Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11585912 Free PMC article.
-
Transforming growth factor-beta1 mediates epithelial to mesenchymal transdifferentiation through a RhoA-dependent mechanism.Mol Biol Cell. 2001 Jan;12(1):27-36. doi: 10.1091/mbc.12.1.27. Mol Biol Cell. 2001. PMID: 11160820 Free PMC article.
-
Generation of anisotropic strain dysregulates wild-type cell division at the interface between host and oncogenic tissue.Curr Biol. 2021 Aug 9;31(15):3409-3418.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2021.05.023. Epub 2021 Jun 9. Curr Biol. 2021. PMID: 34111402 Free PMC article.
-
Src SH3/2 domain-mediated peripheral accumulation of Src and phospho-myosin is linked to deregulation of E-cadherin and the epithelial-mesenchymal transition.Mol Biol Cell. 2004 Jun;15(6):2794-803. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e03-12-0879. Epub 2004 Apr 9. Mol Biol Cell. 2004. PMID: 15075377 Free PMC article.
-
STAT5a activation mediates the epithelial to mesenchymal transition induced by oncogenic RhoA.Mol Biol Cell. 2003 Jan;14(1):40-53. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e02-08-0454. Mol Biol Cell. 2003. PMID: 12529425 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aktories K, Hall A. Botulinum ADP-ribosyltransferase C3: a new tool to study low molecular weight GTP-binding proteins. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1989;10:415–418. - PubMed
-
- Amano M, Chihara K, Kimura K, Fukata Y, Nakamura N, Matsuura Y, Kaibuchi K. Formation of actin stress fibers and focal adhesions enhanced by Rho-kinase. Science. 1997;275:1308–1311. - PubMed
-
- Amano M, Ito M, Kimura K, Fukata Y, Chihara K, Nakano T, Matsuura Y, Kaibuchi K. Phosphorylation and activation of myosin by Rho-associated kinase (Rho-kinase) J Biol Chem. 1996;271:20246–20249. - PubMed
-
- Basolo F, Elliott J, Tait L, Chen XQ, Maloney T, Russo IH, Pauley R, Momiki S, Caamano J, Klein-Szanto AJP, Koszaika M, Russo J. Transformation of human breast epithelial cells by c-Ha-ras oncogene. Mol Carcinogen. 1991;4:25–35. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

