Integrins, oncogenes, and anchorage independence
- PMID: 9348275
- PMCID: PMC2141711
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.139.3.575
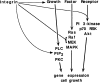
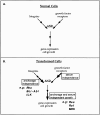
Integrins, oncogenes, and anchorage independence
Figures
Similar articles
-
Signaling by integrins: implications for tumorigenesis.Cancer Res. 1993 Apr 1;53(7):1503-6. Cancer Res. 1993. PMID: 8453614 No abstract available.
-
Toward a genetic analysis of cell-matrix adhesion.Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1992;57:249-58. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1992.057.01.030. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1992. PMID: 1339663 Review. No abstract available.
-
Extracellular matrix, integrins and focal adhesions.Curr Top Pathol. 1999;93:75-85. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-58456-5_8. Curr Top Pathol. 1999. PMID: 10339900 Review. No abstract available.
-
Adhesion and matrix in vertebrate development.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1994 Oct;6(5):747-51. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(94)90103-1. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1994. PMID: 7833054 Review.
-
Integrins in development: moving on, responding to, and sticking to the extracellular matrix.Dev Cell. 2002 Sep;3(3):311-21. doi: 10.1016/s1534-5807(02)00265-4. Dev Cell. 2002. PMID: 12361595 Review.
Cited by
-
Oncogenic Ras blocks anoikis by activation of a novel effector pathway independent of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase.Mol Cell Biol. 2001 Aug;21(16):5488-99. doi: 10.1128/MCB.21.16.5488-5499.2001. Mol Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11463831 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation of tyrosine residues 31 and 118 on paxillin regulates cell migration through an association with CRK in NBT-II cells.J Cell Biol. 2000 Mar 6;148(5):957-70. doi: 10.1083/jcb.148.5.957. J Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 10704446 Free PMC article.
-
Adhesion to the extracellular matrix regulates the coupling of the small GTPase Rac to its effector PAK.EMBO J. 2000 May 2;19(9):2008-14. doi: 10.1093/emboj/19.9.2008. EMBO J. 2000. PMID: 10790367 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of Integrin-HER2 signaling by Cucurbitacin B leads to in vitro and in vivo breast tumor growth suppression.Oncotarget. 2014 Apr 15;5(7):1812-28. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.1743. Oncotarget. 2014. PMID: 24729020 Free PMC article.
-
Transformation of MCF-10A cells by random mutagenesis with frameshift mutagen ICR191: a model for identifying candidate breast-tumor suppressors.Mol Cancer. 2008 Jun 5;7:51. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-7-51. Mol Cancer. 2008. PMID: 18534021 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams JC, Watt FM. Regulation of development and differentiation by the extracellular matrix. Development. 1993;117:1183–1198. - PubMed
-
- Anderson D, Koch CA, Grey L, Ellis C, Moran MF, Pawson T. Binding of SH2 domains of phospholipase Cγ1, GAP and src to activated growth factor receptors. Science (Wash DC) 1990;250:979–981. - PubMed
-
- Barry ST, Flinn HM, Humphries MJ, Critchley DR, Ridley AJ. Requirement for Rho in integrin signalling. Cell Adhes Commun. 1997;4:387–398. - PubMed
-
- Bejcek BE, Li DY, Deuel TF. Transformation by v-sis occurs by an internal autoactivation mechanism. Science (Wash DC) 1989;245:1496–1499. - PubMed

