Cockayne syndrome group B protein enhances elongation by RNA polymerase II
- PMID: 9326587
- PMCID: PMC23417
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.94.21.11205
Cockayne syndrome group B protein enhances elongation by RNA polymerase II
Abstract
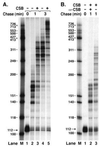
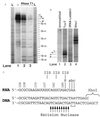
Cockayne syndrome (CS) is characterized by impaired physical and mental development. Two complementation groups, CSA and CSB, have been identified. Here we report that the CSB gene product enhances elongation by RNA polymerase II. CSB stimulated the rate of elongation on an undamaged template by a factor of about 3. A thymine-thymine cyclobutane dimer located in the template strand is known to be a strong block to transcription. Addition of CSB to the blocked polymerase resulted in addition of one nucleotide to the nascent transcript. Finally, addition of transcription factor IIS is known to cause polymerase blocked at a thymine-thymine cyclobutane dimer to digest its nascent transcript, and CSB counteracted this transcript shortening action of transcription factor IIS. Thus a deficiency in transcription elongation may contribute to the CS phenotype.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Recruitment of the putative transcription-repair coupling factor CSB/ERCC6 to RNA polymerase II elongation complexes.Mol Cell Biol. 1997 Dec;17(12):6803-14. doi: 10.1128/MCB.17.12.6803. Mol Cell Biol. 1997. PMID: 9372911 Free PMC article.
-
Human transcription release factor 2 dissociates RNA polymerases I and II stalled at a cyclobutane thymine dimer.J Biol Chem. 1999 Aug 27;274(35):24779-86. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.35.24779. J Biol Chem. 1999. PMID: 10455150
-
The Cockayne syndrome B protein, involved in transcription-coupled DNA repair, resides in an RNA polymerase II-containing complex.EMBO J. 1997 Oct 1;16(19):5955-65. doi: 10.1093/emboj/16.19.5955. EMBO J. 1997. PMID: 9312053 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription-coupled homologous recombination after oxidative damage.DNA Repair (Amst). 2016 Aug;44:76-80. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2016.05.009. Epub 2016 May 16. DNA Repair (Amst). 2016. PMID: 27233112 Review.
-
The role of Cockayne syndrome group A (CSA) protein in transcription-coupled nucleotide excision repair.Mech Ageing Dev. 2013 May-Jun;134(5-6):196-201. doi: 10.1016/j.mad.2013.03.008. Epub 2013 Apr 6. Mech Ageing Dev. 2013. PMID: 23571135 Review.
Cited by
-
The chromatin remodeling factor CSB recruits histone acetyltransferase PCAF to rRNA gene promoters in active state for transcription initiation.PLoS One. 2013 May 7;8(5):e62668. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0062668. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23667505 Free PMC article.
-
The Winged Helix Domain of CSB Regulates RNAPII Occupancy at Promoter Proximal Pause Sites.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 25;22(7):3379. doi: 10.3390/ijms22073379. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33806087 Free PMC article.
-
Neil2-null Mice Accumulate Oxidized DNA Bases in the Transcriptionally Active Sequences of the Genome and Are Susceptible to Innate Inflammation.J Biol Chem. 2015 Oct 9;290(41):24636-48. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.658146. Epub 2015 Aug 5. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 26245904 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of Rad26- and Rpb9-mediated DNA repair by different promoter elements.J Biol Chem. 2006 Dec 1;281(48):36643-51. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M604885200. Epub 2006 Oct 5. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 17023424 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional bypass of bulky DNA lesions causes new mutant RNA transcripts in human cells.EMBO Rep. 2007 Apr;8(4):388-93. doi: 10.1038/sj.embor.7400932. Epub 2007 Mar 16. EMBO Rep. 2007. PMID: 17363972 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nance M A, Berry S A. Am J Med Genet. 1992;42:68–84. - PubMed
-
- Friedberg E C, Walker G C, Siede W. DNA Repair Mechanisms. Washington, DC: Am. Soc. Microbiol.; 1995.
-
- Mayne L V, Lehmann A R. Cancer Res. 1982;42:1473–1478. - PubMed
-
- Bohr V A, Smith C A, Okumoto D S, Hanawalt P C. Cell. 1985;40:359–369. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

