Diabetes, defective pancreatic morphogenesis, and abnormal enteroendocrine differentiation in BETA2/neuroD-deficient mice
- PMID: 9308961
- PMCID: PMC316513
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.11.18.2323
Diabetes, defective pancreatic morphogenesis, and abnormal enteroendocrine differentiation in BETA2/neuroD-deficient mice
Abstract
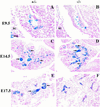
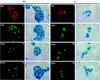
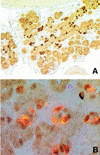
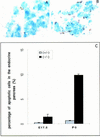
Candidate transcription factors involved in pancreatic endocrine development have been isolated using insulin gene regulation as a paradigm. The cell-type restricted basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) gene, BETA2/NeuroD, expressed in pancreatic endocrine cells, the intestine, and the brain, activates insulin gene transcription and can induce neurons to differentiate. To understand the importance of BETA2 in pancreatic endocrine cell differentiation, mice lacking a functional BETA2 gene were generated by gene targeting experiments. Mice carrying a targeted disruption of the BETA2 gene developed severe diabetes and died perinatally. Homozygous BETA2 null mice had a striking reduction in the number of insulin-producing beta cells and failed to develop mature islets. Islet morphogenesis appeared to be arrested between E14.5 and E17.5, a period characterized by major expansion of the beta cell population. The presence of severe diabetes in these mice suggests that proper islet structure plays an important role in blood glucose homeostasis. In addition, secretin- and cholecystokinin-producing enteroendocrine cells failed to develop in the absence of BETA2. The absence of these two pancreatic secretagogs may explain the abnormal cellular polarity and inability to secrete zymogen granules in pancreatic acinar exocrine cells. The nervous system appeared to develop normally, despite abundant expression of BETA2 in differentiating neurons. Thus, BETA2 is critical for the normal development of several specialized cell types arising from the gut endoderm.
Figures



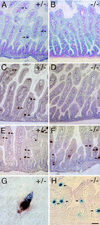
Similar articles
-
Neogenesis of beta-cells in adult BETA2/NeuroD-deficient mice.Mol Endocrinol. 2002 Mar;16(3):541-51. doi: 10.1210/mend.16.3.0784. Mol Endocrinol. 2002. PMID: 11875114
-
Cre/loxP-mediated inactivation of the bHLH transcription factor gene NeuroD/BETA2.Genesis. 2005 Aug;42(4):247-52. doi: 10.1002/gene.20138. Genesis. 2005. PMID: 16028233
-
Targeted ablation of secretin-producing cells in transgenic mice reveals a common differentiation pathway with multiple enteroendocrine cell lineages in the small intestine.Development. 1999 Sep;126(18):4149-56. doi: 10.1242/dev.126.18.4149. Development. 1999. PMID: 10457023
-
BETA2 and pancreatic islet development.Recent Prog Horm Res. 2001;56:23-46. doi: 10.1210/rp.56.1.23. Recent Prog Horm Res. 2001. PMID: 11237215 Review.
-
Gene therapy for diabetes: reinventing the islet.Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2006 Apr;17(3):92-100. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2006.02.002. Epub 2006 Feb 28. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2006. PMID: 16504534 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of Neurod1 contributes to the lineage potential of Neurogenin3+ endocrine precursor cells in the pancreas.PLoS Genet. 2013;9(2):e1003278. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003278. Epub 2013 Feb 7. PLoS Genet. 2013. PMID: 23408910 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of variant A45T in NEUROD1/BETA2 for its association with type 2 diabetes mellitus.Endocrine. 2013 Aug;44(1):99-106. doi: 10.1007/s12020-012-9844-3. Epub 2012 Dec 1. Endocrine. 2013. PMID: 23203005
-
Chromatin Dynamics in Intestinal Epithelial Homeostasis: A Paradigm of Cell Fate Determination versus Cell Plasticity.Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2020 Dec;16(6):1062-1080. doi: 10.1007/s12015-020-10055-0. Epub 2020 Oct 13. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2020. PMID: 33051755 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Different levels of Notch signaling regulate quiescence, renewal and differentiation in pancreatic endocrine progenitors.Development. 2012 May;139(9):1557-67. doi: 10.1242/dev.076000. Development. 2012. PMID: 22492351 Free PMC article.
-
Dual regulatory role for phosphatase and tensin homolog in specification of intestinal endocrine cell subtypes.World J Gastroenterol. 2012 Apr 14;18(14):1579-89. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i14.1579. World J Gastroenterol. 2012. PMID: 22529686 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahlgren U, Pfaff SL, Jessell TM, Edlund T, Edlund H. Independent requirement for ISL1 in formation of pancreatic mesenchyme and islet cells. Nature. 1997;385:257–260. - PubMed
-
- Alpert S, Hanahan D, Teitelman G. Hybrid insulin genes reveal a developmental lineage for pancreatic endocrine cell and imply a relationship with neurons. Cell. 1988;53:295–308. - PubMed
-
- Bain G, Maandag ECR, Izon DJ, Amsen D, Kruisbeek AM, Weintraub BC, Krop I, Schlissel MS, Feenyey AJ, Roon MV. E2A proteins are required for proper B cell development and initiation of immunoglobulin gene rearrangements. Cell. 1994;79:885–892. - PubMed
-
- Bartholoma A, Nave K A. NEX-1: A novel brain specific helix loop helix protein with autoregulation and sustained expression in mature cortical neurons. Mech Dev. 1994;48:217–228. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
