Distinct roles of type I bone morphogenetic protein receptors in the formation and differentiation of cartilage
- PMID: 9303535
- PMCID: PMC275391
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.11.17.2191
Distinct roles of type I bone morphogenetic protein receptors in the formation and differentiation of cartilage
Abstract
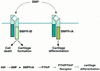
The bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs), TGF beta superfamily members, play diverse roles in embryogenesis, but how the BMPs exert their action is unclear and how different BMP receptors (BMPRs) contribute to this process is not known. Here we demonstrate that the two type I BMPRs, BMPR-IA and BMPR-IB, regulate distinct processes during chick limb development. BmpR-IB expression in the embryonic limb prefigures the future cartilage primordium, and its activity is necessary for the initial steps of chondrogenesis. During later chondrogenesis, BmpR-IA is specifically expressed in prehypertrophic chondrocytes. BMPR-IA regulates chondrocyte differentiation, serving as a downstream mediator of Indian Hedgehog (IHH) function in both a local signaling loop and a longer-range relay system to PTHrP. BMPR-IB also regulates apoptosis: Expression of activated BMPR-IB results in increased cell death, and we showed previously that dominant-negative BMPR-IB inhibits apoptosis. Our studies indicate that in TGF beta signaling systems, different type I receptor isoforms are dedicated to specific functions during embryogenesis.
Figures


Similar articles
-
ALK2 functions as a BMP type I receptor and induces Indian hedgehog in chondrocytes during skeletal development.J Bone Miner Res. 2003 Sep;18(9):1593-604. doi: 10.1359/jbmr.2003.18.9.1593. J Bone Miner Res. 2003. PMID: 12968668
-
BMP signaling stimulates chondrocyte maturation and the expression of Indian hedgehog.J Orthop Res. 2001 Jan;19(1):18-25. doi: 10.1016/S0736-0266(00)00017-6. J Orthop Res. 2001. PMID: 11332615
-
Utilization of bone morphogenetic protein receptors during chondrocyte maturation.J Bone Miner Res. 2000 Aug;15(8):1630-9. doi: 10.1359/jbmr.2000.15.8.1630. J Bone Miner Res. 2000. PMID: 10934663
-
Bone morphogenetic proteins.Growth Factors. 2004 Dec;22(4):233-41. doi: 10.1080/08977190412331279890. Growth Factors. 2004. PMID: 15621726 Review.
-
The crystal structure of the BMP-2:BMPR-IA complex and the generation of BMP-2 antagonists.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2001;83-A Suppl 1(Pt 1):S7-14. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2001. PMID: 11263668 Review.
Cited by
-
Heparan sulfate in skeletal development, growth, and pathology: the case of hereditary multiple exostoses.Dev Dyn. 2013 Sep;242(9):1021-32. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.24010. Epub 2013 Jul 29. Dev Dyn. 2013. PMID: 23821404 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enhanced BMP signaling prevents degeneration and leads to endochondral ossification of Meckel's cartilage in mice.Dev Biol. 2013 Sep 15;381(2):301-11. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2013.07.016. Epub 2013 Jul 23. Dev Biol. 2013. PMID: 23891934 Free PMC article.
-
Functional conservation of the human EXT1 tumor suppressor gene and its Drosophila homolog tout velu.Dev Genes Evol. 2007 Aug;217(8):555-61. doi: 10.1007/s00427-007-0163-2. Epub 2007 Jul 4. Dev Genes Evol. 2007. PMID: 17610078
-
Sox5 and Sox6 are needed to develop and maintain source, columnar, and hypertrophic chondrocytes in the cartilage growth plate.J Cell Biol. 2004 Mar 1;164(5):747-58. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200312045. J Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 14993235 Free PMC article.
-
BMP action in skeletogenesis involves attenuation of retinoid signaling.J Cell Biol. 2006 Jul 3;174(1):101-13. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200604150. J Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16818722 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahrens PB, Solursh M, Reiter RS. Stage-related capacity for limb chondrogenesis in cell culture. Dev Biol. 1977;60:69–82. - PubMed
-
- Blair SS. Compartments and appendage development in Drosophila. BioEssays. 1995;17:299–309. - PubMed
-
- Brummel TJ, Twombly V, Marqués G, Wrana JL, Newfeld SJ, O’Connor MB, Gelbart WM. Characterization and relationship of Dpp receptors encoded by the saxophone and thick veins genes in Drosophila. Cell. 1994;78:251–261. - PubMed
-
- Chang SC, Hoang B, Thomas JT, Vukicevi S, Luyten FP, Ryba NJP, Kazak CA, Reddi AH, Moos M. Cartilage-derived morphogenetic proteins. New members of the transforming growth factor-beta superfamily predominantly expressed in long bones during human embryonic development. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:28227–28234. - PubMed
-
- Dewulf N, Verschueren K, Lonnoy O, Morén A, Grimsby S, Vande Spiegle K, Miyazono K, Huylebroeck D, ten Dijke P. Distinct spatial and temporal expression patterns of two type I receptors for Bone Morphogenetic Proteins during mouse embryogenesis. Endocrinology. 1995;136:2652–2663. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
