Suppression of tumor necrosis factor-induced cell death by inhibitor of apoptosis c-IAP2 is under NF-kappaB control
- PMID: 9294162
- PMCID: PMC23303
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.94.19.10057
Suppression of tumor necrosis factor-induced cell death by inhibitor of apoptosis c-IAP2 is under NF-kappaB control
Abstract
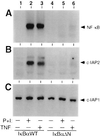
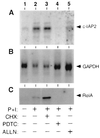
Members of the NF-kappaB/Rel and inhibitor of apoptosis (IAP) protein families have been implicated in signal transduction programs that prevent cell death elicited by the cytokine tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF). Although NF-kappaB appears to stimulate the expression of specific protective genes, neither the identities of these genes nor the precise role of IAP proteins in this anti-apoptotic process are known. We demonstrate here that NF-kappaB is required for TNF-mediated induction of the gene encoding human c-IAP2. When overexpressed in mammalian cells, c-IAP2 activates NF-kappaB and suppresses TNF cytotoxicity. Both of these c-IAP2 activities are blocked in vivo by coexpressing a dominant form of IkappaB that is resistant to TNF-induced degradation. In contrast to wild-type c-IAP2, a mutant lacking the C-terminal RING domain inhibits NF-kappaB induction by TNF and enhances TNF killing. These findings suggest that c-IAP2 is critically involved in TNF signaling and exerts positive feedback control on NF-kappaB via an IkappaB targeting mechanism. Functional coupling of NF-kappaB and c-IAP2 during the TNF response may provide a signal amplification loop that promotes cell survival rather than death.
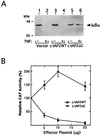
Figures
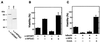
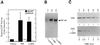
Similar articles
-
MAP kinase-dependent, NF-kappaB-independent regulation of inhibitor of apoptosis protein genes by TNF-alpha.J Cell Physiol. 2007 Mar;210(3):703-10. doi: 10.1002/jcp.20881. J Cell Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17133355
-
Dexamethasone and tumor necrosis factor-alpha act together to induce the cellular inhibitor of apoptosis-2 gene and prevent apoptosis in a variety of cell types.Endocrinology. 2002 Oct;143(10):3866-74. doi: 10.1210/en.2002-220188. Endocrinology. 2002. PMID: 12239098
-
Differential roles of RelA (p65) and c-Rel subunits of nuclear factor kappa B in tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand signaling.Cancer Res. 2003 Mar 1;63(5):1059-66. Cancer Res. 2003. PMID: 12615723
-
(Un)expected roles of c-IAPs in apoptotic and NFkappaB signaling pathways.Cell Cycle. 2008 Jun 1;7(11):1511-21. doi: 10.4161/cc.7.11.5959. Epub 2008 Mar 16. Cell Cycle. 2008. PMID: 18469528 Review.
-
Cracking the NF-κB code.Sci Signal. 2014 Feb 18;7(313):pe5. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2005108. Sci Signal. 2014. PMID: 24550540 Review.
Cited by
-
Discovery of a potent small-molecule antagonist of inhibitor of apoptosis (IAP) proteins and clinical candidate for the treatment of cancer (GDC-0152).J Med Chem. 2012 May 10;55(9):4101-13. doi: 10.1021/jm300060k. Epub 2012 Mar 28. J Med Chem. 2012. PMID: 22413863 Free PMC article.
-
Reciprocal inhibition of p53 and nuclear factor-kappaB transcriptional activities determines cell survival or death in neurons.J Neurosci. 2003 Sep 17;23(24):8586-95. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-24-08586.2003. J Neurosci. 2003. PMID: 13679428 Free PMC article.
-
Genetically engineered T cells for cancer immunotherapy.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2019 Sep 20;4:35. doi: 10.1038/s41392-019-0070-9. eCollection 2019. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2019. PMID: 31637014 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fusobacterium nucleatum promotes chemoresistance to 5-fluorouracil by upregulation of BIRC3 expression in colorectal cancer.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019 Jan 10;38(1):14. doi: 10.1186/s13046-018-0985-y. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 30630498 Free PMC article.
-
Secreted Mycobacterium tuberculosis Rv3654c and Rv3655c proteins participate in the suppression of macrophage apoptosis.PLoS One. 2010 May 4;5(5):e10474. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0010474. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20454556 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Smith C A, Farrah T, Goodwin R G. Cell. 1994;76:959–962. - PubMed
-
- Vandenabeele P, Declercq W, Beyaert R, Fiers W. Trends Cell Biol. 1995;5:392–399. - PubMed
-
- Tartaglia L A, Rothe M, Hu Y-F, Goeddel D V. Cell. 1993;73:213–216. - PubMed
-
- Tartaglia L A, Ayres T M, Wong G H W, Goeddel D V. Cell. 1993;74:845–853. - PubMed
-
- Kruppa G, Thoma B, Machleidt T, Wiegmann K, Krönke M. J Immunol. 1992;148:3152–3157. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

