Inhibition of CDK activity and PCNA-dependent DNA replication by p21 is blocked by interaction with the HPV-16 E7 oncoprotein
- PMID: 9284048
- PMCID: PMC316456
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.11.16.2090
Inhibition of CDK activity and PCNA-dependent DNA replication by p21 is blocked by interaction with the HPV-16 E7 oncoprotein
Abstract
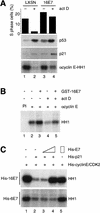
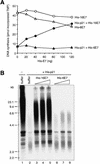
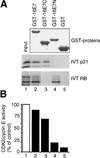
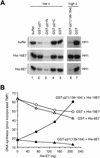
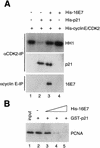
p21 inhibits cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) activity and proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA)-dependent DNA replication by binding to CDK/cyclin complexes and to PCNA through distinct domains. The human papillomavirus (HPV)-16 E7 oncoprotein (16E7) abrogated a DNA damage-induced cell cycle arrest in vivo, despite high levels of p21. Using cell lysates and purified proteins we show that 16E7 prevented p21 both from inhibiting CDK2/cyclin E activity and PCNA-dependent DNA replication, whereas the nononcogenic HPV-6 E7 had reduced effects. Inactivation of both inhibitory functions of p21 was attained through binding between 16E7 and sequences in the carboxy-terminal end of p21 that overlap with the PCNA-binding site and the second p21 cyclin-binding motif. These data imply that the carboxyl terminus of p21 simultaneously modulates both CDK activity and PCNA-dependent DNA replication and that a single protein, 16E7, can override this modulation to disrupt normal cell cycle control.
Figures
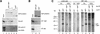



Similar articles
-
The human papillomavirus E7 oncoprotein can uncouple cellular differentiation and proliferation in human keratinocytes by abrogating p21Cip1-mediated inhibition of cdk2.Genes Dev. 1997 Aug 15;11(16):2101-11. doi: 10.1101/gad.11.16.2101. Genes Dev. 1997. PMID: 9284049 Free PMC article.
-
Initiation of DNA synthesis by human papillomavirus E7 oncoproteins is resistant to p21-mediated inhibition of cyclin E-cdk2 activity.J Virol. 1997 Jul;71(7):5570-8. doi: 10.1128/JVI.71.7.5570-5578.1997. J Virol. 1997. PMID: 9188631 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of p21Cip1/Waf1 peptide domains required for cyclin E/Cdk2 and PCNA interaction.Oncogene. 1996 Feb 1;12(3):595-607. Oncogene. 1996. PMID: 8637717
-
Growth inhibition by CDK-cyclin and PCNA binding domains of p21 occurs by distinct mechanisms and is regulated by ubiquitin-proteasome pathway.Oncogene. 1999 May 27;18(21):3290-302. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1202681. Oncogene. 1999. PMID: 10359535
-
Cell-cycle inhibition by independent CDK and PCNA binding domains in p21Cip1.Nature. 1995 May 11;375(6527):159-61. doi: 10.1038/375159a0. Nature. 1995. PMID: 7753174
Cited by
-
HIV-1 Protease Inhibitors Slow HPV16-Driven Cell Proliferation through Targeted Depletion of Viral E6 and E7 Oncoproteins.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Feb 24;13(5):949. doi: 10.3390/cancers13050949. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33668328 Free PMC article.
-
The role of cell-matrix adhesion and cell migration in breast tumor growth and progression.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Feb 5;12:1339251. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1339251. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 38374894 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic analysis of high-risk e6 in episomal maintenance of human papillomavirus genomes in primary human keratinocytes.J Virol. 2002 Nov;76(22):11359-64. doi: 10.1128/jvi.76.22.11359-11364.2002. J Virol. 2002. PMID: 12388696 Free PMC article.
-
The human papillomavirus type 16 E7 oncogene is required for the productive stage of the viral life cycle.J Virol. 2000 Jul;74(14):6622-31. doi: 10.1128/jvi.74.14.6622-6631.2000. J Virol. 2000. PMID: 10864676 Free PMC article.
-
The critical protein interactions and structures that elicit growth deregulation in cancer and viral replication.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med. 2011 Jan-Feb;3(1):48-73. doi: 10.1002/wsbm.88. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med. 2011. PMID: 21061422 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Balbín M, Hannon GJ, Pendás AM, Ferrando AA, Vizoso F, Fueyo A, López-Otín C. Functional analysis of a p21WAF1,CIP1,SDI1 mutant (Arg94 → Trp) identified in a human breast carcinoma. Evidence that the mutation impairs the ability of p21 to inhibit cyclin-dependent kinases. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:15782–15786. - PubMed
-
- Ball KL, Lain S, Fåhraeus R, Smythe C, Lane DP. Cell-cycle arrest and inhibition of cdk4 activity by small peptides basd on the carboxy-terminal domain of p21WAF1. Curr Biol. 1996;7:71–80. - PubMed
-
- Blackwood EM, Lüscher B, Eisenman RN. Myc and Max associate in vivo. Genes & Dev. 1992;6:71–80. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
