In vitro repair of oxidative DNA damage by human nucleotide excision repair system: possible explanation for neurodegeneration in xeroderma pigmentosum patients
- PMID: 9256505
- PMCID: PMC23224
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.94.17.9463
In vitro repair of oxidative DNA damage by human nucleotide excision repair system: possible explanation for neurodegeneration in xeroderma pigmentosum patients
Abstract
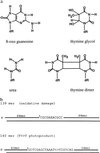
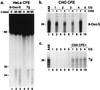
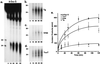
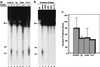
Xeroderma pigmentosum (XP) patients fail to remove pyrimidine dimers caused by sunlight and, as a consequence, develop multiple cancers in areas exposed to light. The second most common sign, present in 20-30% of XP patients, is a set of neurological abnormalities caused by neuronal death in the central and peripheral nervous systems. Neural tissue is shielded from sunlight-induced DNA damage, so the cause of neurodegeneration in XP patients remains unexplained. In this study, we show that two major oxidative DNA lesions, 8-oxoguanine and thymine glycol, are excised from DNA in vitro by the same enzyme system responsible for removing pyrimidine dimers and other bulky DNA adducts. Our results suggest that XP neurological disease may be caused by defective repair of lesions that are produced in nerve cells by reactive oxygen species generated as by-products of an active oxidative metabolism.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sunlight damage to cellular DNA: Focus on oxidatively generated lesions.Free Radic Biol Med. 2017 Jun;107:110-124. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2017.01.029. Epub 2017 Jan 18. Free Radic Biol Med. 2017. PMID: 28109890 Review.
-
Nucleotide Excision Repair: From Molecular Defects to Neurological Abnormalities.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 9;22(12):6220. doi: 10.3390/ijms22126220. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34207557 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Replication of damaged DNA: molecular defect in xeroderma pigmentosum variant cells.Mutat Res. 1999 Oct 22;435(2):111-9. doi: 10.1016/s0921-8777(99)00047-6. Mutat Res. 1999. PMID: 10556591 Review.
-
[Xeroderma pigmentosum].Nihon Rinsho. 2000 Jul;58(7):1496-500. Nihon Rinsho. 2000. PMID: 10921330 Review. Japanese.
-
The oxidative DNA lesion 8,5'-(S)-cyclo-2'-deoxyadenosine is repaired by the nucleotide excision repair pathway and blocks gene expression in mammalian cells.J Biol Chem. 2000 Jul 21;275(29):22355-62. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M002259200. J Biol Chem. 2000. PMID: 10801836
Cited by
-
The involvement of nucleotide excision repair proteins in the removal of oxidative DNA damage.Nucleic Acids Res. 2020 Nov 18;48(20):11227-11243. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa777. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020. PMID: 33010169 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deletion of XPC leads to lung tumors in mice and is associated with early events in human lung carcinogenesis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Sep 13;102(37):13200-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0503133102. Epub 2005 Sep 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 16141330 Free PMC article.
-
Monitoring repair of DNA damage in cell lines and human peripheral blood mononuclear cells.Anal Biochem. 2007 Jun 15;365(2):246-59. doi: 10.1016/j.ab.2007.03.016. Epub 2007 Mar 21. Anal Biochem. 2007. PMID: 17449003 Free PMC article.
-
The 8,5'-cyclopurine-2'-deoxynucleosides: candidate neurodegenerative DNA lesions in xeroderma pigmentosum, and unique probes of transcription and nucleotide excision repair.DNA Repair (Amst). 2008 Jul 1;7(7):1168-79. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2008.03.016. Epub 2008 May 20. DNA Repair (Amst). 2008. PMID: 18495558 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The involvement of DNA-damage and -repair defects in neurological dysfunction.Am J Hum Genet. 2008 Mar;82(3):539-66. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2008.01.009. Am J Hum Genet. 2008. PMID: 18319069 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cleaver J E, Kraemer K H. In: The Metabolic Basis of Inherited Disease. Scriver C R, Beaudet A L, Sly W S, Valle D, editors. Vol. 2. New York: McGraw–Hill; 1989. pp. 2949–2971.
-
- Friedberg E C, Walker G C, Siede W. DNA Repair and Mutagenesis. Washington, DC: Am. Soc. Microbiol.; 1995.
-
- Robbins J H. J Child Neurol. 1989;4:143–146. - PubMed
-
- Robbins J H, Brumback R A, Mendiones M, Barrett S F, Carl J R, Cho S, Denckla M B, Ganges M B, Gerber L H, Guthrie R A, Meer J, Moshell A N, Polinsky R J, Ravin P D, Sonies B C, Tarone R E. Brain. 1991;114:1335–1361. - PubMed
-
- Sancar A. Annu Rev Biochem. 1996;65:43–81. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

