Human cytomegalovirus immediate early interaction with host nuclear structures: definition of an immediate transcript environment
- PMID: 9214377
- PMCID: PMC2139949
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.138.1.5
Human cytomegalovirus immediate early interaction with host nuclear structures: definition of an immediate transcript environment
Abstract
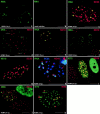
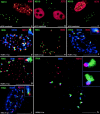
The development of an induced transcript environment was investigated at the supramolecular level through comparative localization of the human cytomegalovirus immediate early (IE) transcripts and specific nuclear domains shortly after infection. Compact aggregates of IE transcripts form only adjacent to nuclear domain 10 (ND10), and the viral protein IE86 accumulates exclusively juxtaposed to the subpopulation of ND10 with transcripts. The stream of transcripts is funneled from ND10 into the spliceosome assembly factor SC35 domain through the accumulation of IE86 protein, which recruits some components of the basal transcription machinery. Concomitantly the IE72 protein binds to ND10 and later disperses them. The domain containing the zinc finger region of IE72 is essential for this dispersal. Positional analysis of proteins IE86 and IE72, IE transcripts, ND10, the spliceosome assembly factor SC35, and basal transcription factors defines spatially and temporally an immediate transcript environment, the basic components of which exist in the cell before viral infection, providing the structural environment for the virus to usurp.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The human cytomegalovirus IE2 and UL112-113 proteins accumulate in viral DNA replication compartments that initiate from the periphery of promyelocytic leukemia protein-associated nuclear bodies (PODs or ND10).J Virol. 1999 Dec;73(12):10458-71. doi: 10.1128/JVI.73.12.10458-10471.1999. J Virol. 1999. PMID: 10559364 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription factor Sp1 mediates cell-specific trans-activation of the human cytomegalovirus DNA polymerase gene promoter by immediate-early protein IE86 in glioblastoma U373MG cells.J Virol. 1998 Jan;72(1):236-44. doi: 10.1128/JVI.72.1.236-244.1998. J Virol. 1998. PMID: 9420220 Free PMC article.
-
Disruption of PML-associated nuclear bodies by IE1 correlates with efficient early stages of viral gene expression and DNA replication in human cytomegalovirus infection.Virology. 2000 Aug 15;274(1):39-55. doi: 10.1006/viro.2000.0448. Virology. 2000. PMID: 10936087
-
The human cytomegalovirus major immediate-early gene.Intervirology. 1996;39(5-6):343-9. doi: 10.1159/000150505. Intervirology. 1996. PMID: 9130044 Review.
-
Activation and regulation of human cytomegalovirus early genes.Intervirology. 1996;39(5-6):361-77. doi: 10.1159/000150507. Intervirology. 1996. PMID: 9130046 Review.
Cited by
-
Cytomegalovirus UL91 is essential for transcription of viral true late (γ2) genes.J Virol. 2013 Aug;87(15):8651-64. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01052-13. Epub 2013 May 29. J Virol. 2013. PMID: 23720731 Free PMC article.
-
Proteasome subunits relocalize during human cytomegalovirus infection, and proteasome activity is necessary for efficient viral gene transcription.J Virol. 2010 Mar;84(6):3079-93. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02236-09. Epub 2009 Dec 30. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 20042513 Free PMC article.
-
Proteasome-independent disruption of PML oncogenic domains (PODs), but not covalent modification by SUMO-1, is required for human cytomegalovirus immediate-early protein IE1 to inhibit PML-mediated transcriptional repression.J Virol. 2001 Nov;75(22):10683-95. doi: 10.1128/JVI.75.22.10683-10695.2001. J Virol. 2001. PMID: 11602710 Free PMC article.
-
Lytic but not latent replication of epstein-barr virus is associated with PML and induces sequential release of nuclear domain 10 proteins.J Virol. 2000 Dec;74(24):11800-10. doi: 10.1128/jvi.74.24.11800-11810.2000. J Virol. 2000. PMID: 11090180 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the proximal enhancer of the major immediate-early promoter in human cytomegalovirus replication.J Virol. 2004 Dec;78(23):12788-99. doi: 10.1128/JVI.78.23.12788-12799.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 15542631 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Caswell R, Hagemeier C, Chou C-J, Hayward G, Kouzarides T, Sinclair J. The human cytomegalovirus 86K immediate early (IE) 2 protein requires the basic region of the TATA-box binding protein (TBP) for binding, and interacts with TBP and transcription factor TFIIB via regions of IE2 required for transcription regulation. J Gen Virol. 1993;74:2691–2698. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

