RAP74 induces promoter contacts by RNA polymerase II upstream and downstream of a DNA bend centered on the TATA box
- PMID: 9207059
- PMCID: PMC23774
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.94.14.7150
RAP74 induces promoter contacts by RNA polymerase II upstream and downstream of a DNA bend centered on the TATA box
Abstract
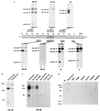
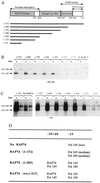
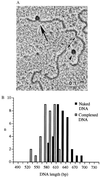
RAP74, the large subunit of transcription factor IIF, associates with a preinitiation complex containing RNA polymerase II (pol II) and other general initiation factors. We have mapped the location of RAP74 in close proximity to promoter DNA at similar distances both upstream and downstream of a DNA bend centered on the TATA box. Binding of RAP74 induces a conformational change that affects the position of pol II relative to that of the DNA. This reorganization of the preinitiation complex minimally requires the N-terminal region of RAP74 containing both its RAP30-binding domain and another region necessary for accurate transcription in vitro. We propose a role for RAP74 in controlling the topological organization of the pol II preinitiation complex.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Functions of the N- and C-terminal domains of human RAP74 in transcriptional initiation, elongation, and recycling of RNA polymerase II.Mol Cell Biol. 1998 Apr;18(4):2130-42. doi: 10.1128/MCB.18.4.2130. Mol Cell Biol. 1998. PMID: 9528785 Free PMC article.
-
A cDNA encoding RAP74, a general initiation factor for transcription by RNA polymerase II.Nature. 1992 Jan 30;355(6359):464-7. doi: 10.1038/355464a0. Nature. 1992. PMID: 1734284
-
Localization of subunits of transcription factors IIE and IIF immediately upstream of the transcriptional initiation site of the adenovirus major late promoter.J Biol Chem. 1996 Apr 12;271(15):8517-20. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.15.8517. J Biol Chem. 1996. PMID: 8621472
-
Polarity of transcription on Pol II and archaeal promoters: where is the "one-way sign" and how is it read?Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1998;63:53-61. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1998.63.53. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1998. PMID: 10384270 Review. No abstract available.
-
TATA box mimicry by TFIID: autoinhibition of pol II transcription.Cell. 1998 Sep 4;94(5):551-3. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81596-2. Cell. 1998. PMID: 9741619 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Amino acid substitutions in yeast TFIIF confer upstream shifts in transcription initiation and altered interaction with RNA polymerase II.Mol Cell Biol. 2004 Dec;24(24):10975-85. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.24.10975-10985.2004. Mol Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15572698 Free PMC article.
-
Site-specific protein-DNA photocross-linking of purified complexes: topology of the RNA polymerase II transcription initiation complex.Methods Enzymol. 2003;370:701-12. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(03)70057-3. Methods Enzymol. 2003. PMID: 14712685 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Mechanism of promoter melting by the xeroderma pigmentosum complementation group B helicase of transcription factor IIH revealed by protein-DNA photo-cross-linking.Mol Cell Biol. 2000 Nov;20(21):8168-77. doi: 10.1128/MCB.20.21.8168-8177.2000. Mol Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 11027286 Free PMC article.
-
Trajectory of DNA in the RNA polymerase II transcription preinitiation complex.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997 Nov 11;94(23):12268-73. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.23.12268. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997. PMID: 9356438 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interaction networks of the molecular machines that decode, replicate, and maintain the integrity of the human genome.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2004 Sep;3(9):851-6. doi: 10.1074/mcp.R400009-MCP200. Epub 2004 Jun 22. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2004. PMID: 15215308 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Orphanides G, Lagrange T, Reinberg D. Genes Dev. 1996;10:2657–2683. - PubMed
-
- Conaway R C, Conaway J W. Annu Rev Biochem. 1993;62:161–190. - PubMed
-
- Ranish J A, Hahn S. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1996;6:151–158. - PubMed
-
- Pugh B F. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1996;8:303–311. - PubMed
-
- Roeder R G. Trends Biochem Sci. 1996;21:327–335. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

