Evidence for a mediator cycle at the initiation of transcription
- PMID: 9177171
- PMCID: PMC21003
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.94.12.6075
Evidence for a mediator cycle at the initiation of transcription
Abstract
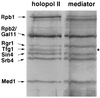
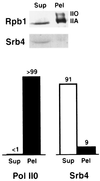
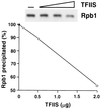
Free and elongating (DNA-bound) forms of RNA polymerase II were separated from yeast. Most cellular polymerase II was found in the elongating fraction, which contained all enzyme phosphorylated on the C-terminal domain and none of the 15-subunit mediator of transcriptional regulation. These and other findings suggest that mediator enters and leaves initiation complexes during every round of transcription, in a process that may be coupled to C-terminal domain phosphorylation.
Figures

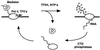
Similar articles
-
Transcription elongation through DNA arrest sites. A multistep process involving both RNA polymerase II subunit RPB9 and TFIIS.J Biol Chem. 1997 Jun 6;272(23):14747-54. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.23.14747. J Biol Chem. 1997. PMID: 9169440
-
Elongator, a multisubunit component of a novel RNA polymerase II holoenzyme for transcriptional elongation.Mol Cell. 1999 Jan;3(1):109-18. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(00)80179-3. Mol Cell. 1999. PMID: 10024884
-
Transcription elongation factor Spt4 mediates loss of phosphorylated RNA polymerase II transcription in response to DNA damage.Nucleic Acids Res. 2002 Aug 15;30(16):3532-9. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkf475. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002. PMID: 12177294 Free PMC article.
-
The RNA polymerase II general elongation factors.Trends Biochem Sci. 1996 Sep;21(9):351-5. Trends Biochem Sci. 1996. PMID: 8870500 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Purification of yeast RNA polymerase II holoenzymes.Methods Enzymol. 1996;273:176-84. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(96)73018-5. Methods Enzymol. 1996. PMID: 8791611 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Mediator and p300/CBP-steroid receptor coactivator complexes have distinct roles, but function synergistically, during estrogen receptor alpha-dependent transcription with chromatin templates.Mol Cell Biol. 2003 Jan;23(1):335-48. doi: 10.1128/MCB.23.1.335-348.2003. Mol Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 12482985 Free PMC article.
-
Protein characterization of Saccharomyces cerevisiae RNA polymerase II after in vivo cross-linking.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Dec 11;104(50):19948-53. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0710179104. Epub 2007 Dec 5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 18077427 Free PMC article.
-
The role of mediator complex subunit 19 in human diseases.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2021 Aug;246(15):1681-1687. doi: 10.1177/15353702211011701. Epub 2021 May 26. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2021. PMID: 34038190 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phosphorylation by Cak1 regulates the C-terminal domain kinase Ctk1 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Mol Cell Biol. 2005 May;25(10):3906-13. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.10.3906-3913.2005. Mol Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 15870265 Free PMC article.
-
The essential and multifunctional TFIIH complex.Protein Sci. 2018 Jun;27(6):1018-1037. doi: 10.1002/pro.3424. Epub 2018 Apr 27. Protein Sci. 2018. PMID: 29664212 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kelleher R J, III, Flanagan P M, Kornberg R D. Cell. 1990;61:1209–1215. - PubMed
-
- Flanagan P M, Kelleher R J, III, Sayre M H, Tschochner H, Kornberg R D. Nature (London) 1991;350:436–438. - PubMed
-
- Kim Y J, Bjorklund S, Li Y, Sayre M H, Kornberg R D. Cell. 1994;77:599–608. - PubMed
-
- Thompson C M, Koleske A J, Chao D M, Young R A. Cell. 1993;73:1361–1375. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

