Evidence for phosphorylation and oligomeric assembly of presenilin 1
- PMID: 9144195
- PMCID: PMC24636
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.94.10.5090
Evidence for phosphorylation and oligomeric assembly of presenilin 1
Abstract
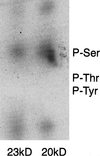
Pathogenic mutations in presenilin 1 (PS1) are associated with approximately 50% of early-onset familial Alzheimer disease. PS1 is endoproteolytically cleaved to yield a 30-kDa N-terminal fragment (NTF) and an 18-kDa C-terminal fragment (CTF). Using COS7 cells transfected with human PS1, we have found that phorbol 12, 13-dibutyrate and forskolin increase the state of phosphorylation of serine residues of the human CTF. Phosphorylation of the human CTF resulted in a shift in electrophoretic mobility from a single major species of 18 kDa to a doublet of 20-23 kDa. This mobility shift was also observed with human PS1 that had been transfected into mouse neuroblastoma (N2a) cells. Treatment of the phosphorylated CTF doublet with phage lambda protein phosphatase eliminated the 20- to 23-kDa doublet while enhancing the 18-kDa species, consistent with the interpretation that the electrophoretic mobility shift was due to the addition of phosphate to the 18-kDa species. The NTF and CTF eluted from a gel filtration column at an estimated mass of over 100 kDa, suggesting that these fragments exist as an oligomerized species. Upon phosphorylation of the PS1 CTF, the apparent mass of the NTF- or CTF-containing oligomers was unchanged. Thus, the association of PS1 fragments may be maintained during cycles of phosphorylation/dephosphorylation of the PS1 CTF.
Figures
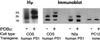
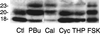

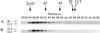

Similar articles
-
Abrogation of the presenilin 1/beta-catenin interaction and preservation of the heterodimeric presenilin 1 complex following caspase activation.J Biol Chem. 1998 Dec 18;273(51):33909-14. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.51.33909. J Biol Chem. 1998. PMID: 9852041
-
Determination of a cleavage site of presenilin 2 protein in stably transfected SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cell lines.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1997 Nov 26;240(3):728-31. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1997.7730. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1997. PMID: 9398634
-
Glycogen synthase kinase-3beta regulates presenilin 1 C-terminal fragment levels.J Biol Chem. 2001 Aug 17;276(33):30701-7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M102849200. Epub 2001 Jun 11. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11402035
-
C-terminal maturation fragments of presenilin 1 and 2 control secretion of APP alpha and A beta by human cells and are degraded by proteasome.Mol Med. 1999 Mar;5(3):160-8. Mol Med. 1999. PMID: 10404513 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolism of presenilin 1: influence of presenilin 1 on amyloid precursor protein processing.Neurobiol Aging. 1998 Jan-Feb;19(1 Suppl):S15-8. doi: 10.1016/s0197-4580(98)00026-8. Neurobiol Aging. 1998. PMID: 9562461 Review.
Cited by
-
Phosphorylation of presenilin-2 regulates its cleavage by caspases and retards progression of apoptosis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999 Feb 16;96(4):1391-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.4.1391. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999. PMID: 9990034 Free PMC article.
-
Twenty Years of Presenilins--Important Proteins in Health and Disease.Mol Med. 2015 Oct 27;21 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S41-8. doi: 10.2119/molmed.2015.00163. Mol Med. 2015. PMID: 26605647 Free PMC article.
-
Flavonoid-mediated presenilin-1 phosphorylation reduces Alzheimer's disease beta-amyloid production.J Cell Mol Med. 2009 Mar;13(3):574-88. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2008.00344.x. Epub 2008 Apr 9. J Cell Mol Med. 2009. PMID: 18410522 Free PMC article.
-
Proteasome inhibitors prevent the degradation of familial Alzheimer's disease-linked presenilin 1 and potentiate A beta 42 recovery from human cells.Mol Med. 1998 Mar;4(3):147-57. Mol Med. 1998. PMID: 9562973 Free PMC article.
-
Protein kinase C and rho activated coiled coil protein kinase 2 (ROCK2) modulate Alzheimer's APP metabolism and phosphorylation of the Vps10-domain protein, SorL1.Mol Neurodegener. 2010 Dec 30;5:62. doi: 10.1186/1750-1326-5-62. Mol Neurodegener. 2010. PMID: 21192821 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tanzi R E, Kovacs D M, Kim T-W, Moir R D, Guenette S Y, Wasco W. Neurobiol Dis. 1996;3:159–168. - PubMed
-
- Goate A, Chartier-Harlin M-C, Mullan M, Brown J, Crawford F, Fidani L, Giuffra L, Haynes A, Irving N, James L, Mant R, Newton P, Rooke K, Roques P, Talbot C, Pericak-Vance M, Roses A, Williamson R, Rossor M, Owen M, Hardy J. Nature (London) 1991;349:704–706. - PubMed
-
- Chartier-Harlin M-C, Crawford F, Houlden H, Warrem A, Hughes D, Fidani L, Goate A, Rossor M, Roques P, Hardy J, Mullan M. Nature (London) 1991;353:844–846. - PubMed
-
- Naruse S, Igarashi S, Kobayashi H, Aoki K, Inuzuka T, Kaneko K, Shimizu T, Ihara K, Kojima T, Miyatake T, Tsuji S. Lancet. 1991;337:978–979. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

