Regulated membrane localization of Tiam1, mediated by the NH2-terminal pleckstrin homology domain, is required for Rac-dependent membrane ruffling and C-Jun NH2-terminal kinase activation
- PMID: 9128250
- PMCID: PMC2139766
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.137.2.387
Regulated membrane localization of Tiam1, mediated by the NH2-terminal pleckstrin homology domain, is required for Rac-dependent membrane ruffling and C-Jun NH2-terminal kinase activation
Abstract
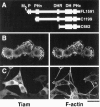
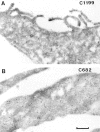
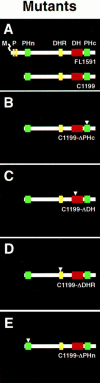
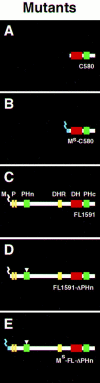
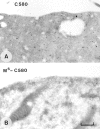
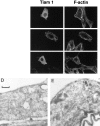
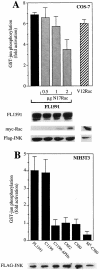
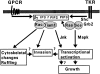
Rho-like GTPases, including Cdc42, Rac, and Rho, regulate signaling pathways that control actin cytoskeletal structures and transcriptional activation. The Tiam1 gene encodes an activator of Rac1, and similarly to constitutively activated (V12)Rac1, overexpression of Tiam1 in fibroblasts induces the formation of membrane ruffles. Tiam1 contains a Dbl homology (DH) domain and adjacent pleckstrin homology (PH) domain, hallmarks for activators of Rho-like GTPases. Unique for Tiam1 are an additional PH domain and a Discs-large homology region in the NH2-terminal part of the protein. Here we show that both in fibroblasts and COS cells, membrane localization of Tiam1 is required for the induction of membrane ruffling. A detailed mutational analysis, in combination with confocal laser scanning microscopy and immunoelectron microscopy, demonstrates that the NH2-terminal PH domain of Tiam1, but not the DH-adjacent PH domain, is essential for membrane association. This NH2-terminal PH domain of Tiam1 can be functionally replaced by the myristoylated membrane localization domain of c-Src, indicating that the primary function of this PH domain is to localize the protein at the membrane. After serum starvation, both membrane association of Tiam1 and ruffling can be induced by serum, suggesting that receptor stimulation induces membrane translocation of Tiam1. Similar to V12Rac1, Tiam1 stimulates the activity of the c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase (JNK). This Rac-dependent stimulation of JNK also requires membrane association of Tiam1. We conclude that the regulated membrane localization of Tiam1 through its NH2-terminal PH domain determines the activation of distinct Rac-mediated signaling pathways.
Figures









Similar articles
-
Targeting of Tiam1 to the plasma membrane requires the cooperative function of the N-terminal pleckstrin homology domain and an adjacent protein interaction domain.J Biol Chem. 1997 Nov 7;272(45):28447-54. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.45.28447. J Biol Chem. 1997. PMID: 9353304
-
Rac-1 dependent stimulation of the JNK/SAPK signaling pathway by Vav.Oncogene. 1996 Aug 1;13(3):455-60. Oncogene. 1996. PMID: 8760286
-
A role for Rac in Tiam1-induced membrane ruffling and invasion.Nature. 1995 May 25;375(6529):338-40. doi: 10.1038/375338a0. Nature. 1995. PMID: 7753201
-
The guanine nucleotide exchange factor Tiam1: a Janus-faced molecule in cellular signaling.Cell Signal. 2014 Mar;26(3):483-91. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.11.034. Epub 2013 Dec 2. Cell Signal. 2014. PMID: 24308970 Review.
-
Regulation of Tiam1-Rac signalling.FEBS Lett. 2003 Jul 3;546(1):11-6. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(03)00435-6. FEBS Lett. 2003. PMID: 12829230 Review.
Cited by
-
Efficient synthesis of phycocyanobilin in mammalian cells for optogenetic control of cell signaling.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Nov 7;114(45):11962-11967. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1707190114. Epub 2017 Oct 24. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017. PMID: 29078307 Free PMC article.
-
PTEN as an effector in the signaling of antimigratory G protein-coupled receptor.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Mar 22;102(12):4312-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0409784102. Epub 2005 Mar 11. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 15764699 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of the Rac1-specific exchange factor Tiam1 involves both phosphoinositide 3-kinase-dependent and -independent components.Biochem J. 2000 Oct 1;351(Pt 1):173-82. doi: 10.1042/0264-6021:3510173. Biochem J. 2000. PMID: 10998360 Free PMC article.
-
RNAi mediated Tiam1 gene knockdown inhibits invasion of retinoblastoma.PLoS One. 2013 Aug 7;8(8):e70422. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0070422. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23950931 Free PMC article.
-
The PH domain and the polybasic c domain of cytohesin-1 cooperate specifically in plasma membrane association and cellular function.Mol Biol Cell. 1998 Aug;9(8):1981-94. doi: 10.1091/mbc.9.8.1981. Mol Biol Cell. 1998. PMID: 9693361 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boguski MS, McCormick F. Proteins regulating Ras and its relatives. Nature (Lond) 1993;366:643–654. - PubMed
-
- Bokoch GM. Regulation of the human neutrophil NADPH oxidase by the Rac GTP-binding proteins. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1994;6:212–218. - PubMed
-
- Cerione RA, Zheng Y. The Dbl family of oncogenes. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1996;8:216–222. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

