p53 expression induces apoptosis in hippocampal pyramidal neuron cultures
- PMID: 9006981
- PMCID: PMC6793734
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.17-04-01397.1997
p53 expression induces apoptosis in hippocampal pyramidal neuron cultures
Abstract
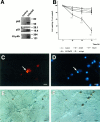
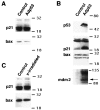
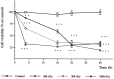
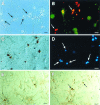
The tumor suppressor gene p53 has been implicated in the induction of apoptosis in dividing cells. We now show that overexpression of p53 using an adenoviral vector in cultured rat hippocampal pyramidal neurons causes widespread neuronal death with features typical of apoptosis. p53 overexpression did not induce p21, bax, or mdm2 in neurons. X-irradiation of hippocampal neurons induced p53 immunoreactivity and cell death associated with features typical of apoptosis. Overexpression of a constitutively active nonphosphorylatable form of the retinoblastoma gene product blocked x-irradiation-induced neuronal death. However, overexpression of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21 did not. Treatment of neurons with transforming growth factor-beta1 protected them from x-irradiation. These results are consistent with a role for p53 in nerve cell death that is distinct from its actions relating to cell cycle arrest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evidence for involvement of Bax and p53, but not caspases, in radiation-induced cell death of cultured postnatal hippocampal neurons.J Neurosci Res. 1998 Dec 15;54(6):721-33. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-4547(19981215)54:6<721::AID-JNR1>3.0.CO;2-1. J Neurosci Res. 1998. PMID: 9856857
-
The maintenance of hippocampal pyramidal neuron populations is dependent on the modulation of specific cell cycle regulators by thyroid hormones.Brain Res. 2009 May 19;1271:27-35. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2009.02.043. Epub 2009 Mar 6. Brain Res. 2009. PMID: 19269280
-
Role and regulation of p53 in depolarization-induced neuronal death.Neuroscience. 2003;122(3):707-15. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2003.08.030. Neuroscience. 2003. PMID: 14622914
-
Subtype-selective induction of wild-type p53 and apoptosis, but not cell cycle arrest, by human somatostatin receptor 3.Mol Endocrinol. 1996 Dec;10(12):1688-96. doi: 10.1210/mend.10.12.8961277. Mol Endocrinol. 1996. PMID: 8961277
-
Down-regulation of cyclin-dependent kinase 5 attenuates p53-dependent apoptosis of hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons following transient cerebral ischemia.Sci Rep. 2019 Sep 10;9(1):13032. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-49623-x. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31506563 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Mitochondrial translocation of p53 mediates release of cytochrome c and hippocampal CA1 neuronal death after transient global cerebral ischemia in rats.J Neurosci. 2006 Jul 26;26(30):7974-83. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0897-06.2006. J Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 16870742 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of docosahexaenoic acid on retinal development: cellular and molecular aspects.Lipids. 2001 Sep;36(9):927-35. doi: 10.1007/s11745-001-0803-8. Lipids. 2001. PMID: 11724465
-
Response of cell cycle proteins to neurotrophic factor and chemokine stimulation in human neuroglia.Exp Neurol. 2001 Feb;167(2):205-14. doi: 10.1006/exnr.2000.7594. Exp Neurol. 2001. PMID: 11161609 Free PMC article.
-
Complex regulation of p73 isoforms after alteration of amyloid precursor polypeptide (APP) function and DNA damage in neurons.J Biol Chem. 2011 Dec 16;286(50):43013-25. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.261271. Epub 2011 Oct 14. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 22002055 Free PMC article.
-
Synaptic activity-mediated suppression of p53 and induction of nuclear calcium-regulated neuroprotective genes promote survival through inhibition of mitochondrial permeability transition.J Neurosci. 2009 Apr 8;29(14):4420-9. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0802-09.2009. J Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19357269 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barr E, Carrol J, Tripathy S, Korzarsky K, Wilson J, Leiden JM. Efficient catheter mediated gene transfer into heart using replication defective adenovirus. Gene Ther. 1994;1:51–58. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
