Sequestration of the delta opioid receptor. Role of the C terminus in agonist-mediated internalization
- PMID: 8910588
- PMCID: PMC3856721
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.271.46.29279
Sequestration of the delta opioid receptor. Role of the C terminus in agonist-mediated internalization
Abstract
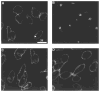
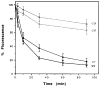
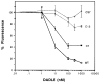
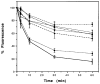
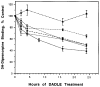
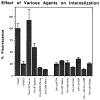
The primary structure of the opioid receptors have revealed that many of the structural features that are conserved in other G protein-coupled receptors are also conserved in the opioid receptors. Upon exposure to agonists, some G protein-coupled receptors internalize rapidly, whereas other structurally homologous G protein-coupled receptors do not. It is not known whether opioid receptors are regulated by rapid endocytosis. In transfected Chinese hamster ovary cells expressing the epitope-tagged wild type delta opioid receptor, exposure to 100 nM [D-Ala2,D-Leu5]enkephalin causes internalization of the receptor within 30 min as determined by confocal microscopy. The rate of internalization of the wild type receptor is rapid with a half-maximal reduction by about 10 min, as determined by the reduction in mean surface receptor fluorescence intensity measured using flow cytometry. In contrast, the cells expressing receptors lacking the C-terminal 15 or 37 amino acids exhibit a substantially slower rate of internalization. Furthermore, the cells expressing receptors with point mutations of any of the Ser/Thr between Ser344 and Ser363 in the C-terminal tail exhibit a significant reduction in the rate of receptor internalization. These results suggest that a portion of the C-terminal tail is involved in receptor internalization. Agents that block the formation of clathrin-coated pits considerably reduce the extent of agonist-mediated internalization of the wild type receptor. Taken together, these results suggest that the wild type opioid receptor undergoes rapid agonist-mediated internalization via a classic endocytic pathway and that a portion of the C-terminal tail plays an important role in this internalization process.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Role for C-tail residues in delta opioid receptor downregulation.DNA Cell Biol. 2000 Feb;19(2):93-101. doi: 10.1089/104454900314609. DNA Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 10701775
-
Thr353, located within the COOH-terminal tail of the delta opiate receptor, is involved in receptor down-regulation.J Biol Chem. 1996 Feb 23;271(8):4073-6. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.8.4073. J Biol Chem. 1996. PMID: 8626742
-
Recycling and resensitization of delta opioid receptors.DNA Cell Biol. 2000 Apr;19(4):195-204. doi: 10.1089/104454900314465. DNA Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 10798443 Free PMC article.
-
The molecular mechanisms of cellular tolerance to delta-opioid agonists. A minireview.Acta Biol Hung. 2003;54(2):203-18. doi: 10.1556/ABiol.54.2003.2.9. Acta Biol Hung. 2003. PMID: 14535626 Review.
-
Mechanism and consequences of delta-opioid receptor internalization.Crit Rev Neurobiol. 2005;17(1):1-26. doi: 10.1615/critrevneurobiol.v17.i1.10. Crit Rev Neurobiol. 2005. PMID: 16307525 Review.
Cited by
-
Oligomerization of opioid receptors with beta 2-adrenergic receptors: a role in trafficking and mitogen-activated protein kinase activation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001 Jan 2;98(1):343-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.98.1.343. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001. PMID: 11134510 Free PMC article.
-
Interplay between the Endogenous Opioid System and Proteasome Complex: Beyond Signaling.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Mar 21;20(6):1441. doi: 10.3390/ijms20061441. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30901925 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ligand-directed trafficking of the δ-opioid receptor in vivo: two paths toward analgesic tolerance.J Neurosci. 2010 Dec 8;30(49):16459-68. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3748-10.2010. J Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 21147985 Free PMC article.
-
Requirement of receptor internalization for opioid stimulation of mitogen-activated protein kinase: biochemical and immunofluorescence confocal microscopic evidence.J Neurosci. 1999 Jan 1;19(1):56-63. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-01-00056.1999. J Neurosci. 1999. PMID: 9870938 Free PMC article.
-
Stimulus-dependent translocation of kappa opioid receptors to the plasma membrane.J Neurosci. 1999 Apr 1;19(7):2658-64. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-07-02658.1999. J Neurosci. 1999. PMID: 10087079 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Herz A. Opioids. Vol. 1. Springer-Verlag; Berlin, FRG: 1993.
-
- Dohlman HG, Thorner J, Caron MG, Lefkowitz RJ. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:653–688. - PubMed
-
- Benovic JL, Bouvier M, Caron MG, Lefkowitz RJ. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1988;4:405–428. - PubMed
-
- Evans CJ, Keith DE, Morrison H, Magendzo K, Edwards RH. Science. 1992;258:1952–1955. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

