The leaving or Q fraction of the murine cerebral proliferative epithelium: a general model of neocortical neuronogenesis
- PMID: 8815900
- PMCID: PMC6579174
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.16-19-06183.1996
The leaving or Q fraction of the murine cerebral proliferative epithelium: a general model of neocortical neuronogenesis
Abstract
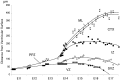
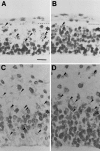
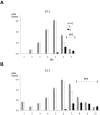
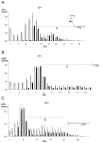
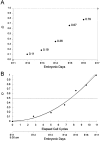
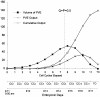
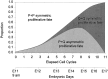
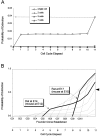
Neurons of neocortical layers II-VI in the dorsomedial cortex of the mouse arise in the pseudostratified ventricular epithelium (PVE) through 11 cell cycles over the six embryonic days 11-17 (E11-E17). The present experiments measure the proportion of daughter cells that leave the cycle (quiescent or Q fraction or Q) during a single cell cycle and the complementary proportion that continues to proliferate (proliferative or P fraction or P; P = 1 - Q). Q and P for the PVE become 0.5 in the course of the eighth cycle, occurring on E14, and Q rises to approximately 0.8 (and P falls to approximately 0.2) in the course of the 10th cycle occurring on E16. This indicates that early in neuronogenesis, neurons are produced relatively slowly and the PVE expands rapidly but that the reverse happens in the final phase of neuronogenesis. The present analysis completes a cycle of analyses that have determined the four fundamental parameters of cell proliferation: growth fraction, lengths of cell cycle, and phases Q and P. These parameters are the basis of a coherent neuronogenetic model that characterizes patterns of growth of the PVE and mathematically relates the size of the initial proliferative population to the neuronal population of the adult neocortex.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The mathematics of neocortical neuronogenesis.Dev Neurosci. 1997;19(1):17-22. doi: 10.1159/000111179. Dev Neurosci. 1997. PMID: 9078427
-
Population dynamics during cell proliferation and neuronogenesis in the developing murine neocortex.Results Probl Cell Differ. 2002;39:1-25. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-46006-0_1. Results Probl Cell Differ. 2002. PMID: 12353465 Review.
-
The cell cycle of the pseudostratified ventricular epithelium of the embryonic murine cerebral wall.J Neurosci. 1995 Sep;15(9):6046-57. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.15-09-06046.1995. J Neurosci. 1995. PMID: 7666188 Free PMC article.
-
A gradient in the duration of the G1 phase in the murine neocortical proliferative epithelium.Cereb Cortex. 1997 Oct-Nov;7(7):678-89. doi: 10.1093/cercor/7.7.678. Cereb Cortex. 1997. PMID: 9373022
-
Proliferative events in the cerebral ventricular zone.Brain Dev. 1995 May-Jun;17(3):159-63. doi: 10.1016/0387-7604(95)00029-b. Brain Dev. 1995. PMID: 7573753 Review.
Cited by
-
Nuclear receptor TLX regulates cell cycle progression in neural stem cells of the developing brain.Mol Endocrinol. 2008 Jan;22(1):56-64. doi: 10.1210/me.2007-0290. Epub 2007 Sep 27. Mol Endocrinol. 2008. PMID: 17901127 Free PMC article.
-
The RNA-binding protein HuD regulates neuronal cell identity and maturation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Mar 22;102(12):4625-30. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0407523102. Epub 2005 Mar 11. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 15764704 Free PMC article.
-
Role of founder cell deficit and delayed neuronogenesis in microencephaly of the trisomy 16 mouse.J Neurosci. 2000 Jun 1;20(11):4156-64. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-11-04156.2000. J Neurosci. 2000. PMID: 10818151 Free PMC article.
-
Basic fibroblast growth factor (Fgf2) is necessary for cell proliferation and neurogenesis in the developing cerebral cortex.J Neurosci. 2000 Jul 1;20(13):5012-23. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-13-05012.2000. J Neurosci. 2000. PMID: 10864959 Free PMC article.
-
Infantile neurodegenerative disorder associated with mutations in TBCD, an essential gene in the tubulin heterodimer assembly pathway.Hum Mol Genet. 2016 Nov 1;25(21):4635-4648. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddw292. Hum Mol Genet. 2016. PMID: 28158450 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Austin CP, Cepko CL. Cellular migration patterns in the developing mouse cerebral cortex. Development. 1990;110:713–732. - PubMed
-
- Bayer SA, Altman J. Raven; New York: 1991. Neocortical development. .
-
- Blaschke A, Staley K, Chun J. Widespread programmed cell death in proliferative and postmitotic regions of the fetal cerebral cortex. Development. 1996;122:1165–1174. - PubMed
-
- Caviness VS., Jr Neocortical histogenesis in normal and reeler mice: a developmental study based upon [3H]thymidine autoradiography. Dev Brain Res. 1982;4:293–302. - PubMed
-
- Caviness VS, Jr, Takahashi T, Nowakowski RS. Numbers, time and neocortical neuronogeneis: a general developmental and evolutionary model. Trends Neurosci. 1995;18:379–383. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
