Disruption of cholesterol 7alpha-hydroxylase gene in mice. II. Bile acid deficiency is overcome by induction of oxysterol 7alpha-hydroxylase
- PMID: 8663430
- PMCID: PMC4451191
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.271.30.18024
Disruption of cholesterol 7alpha-hydroxylase gene in mice. II. Bile acid deficiency is overcome by induction of oxysterol 7alpha-hydroxylase
Abstract
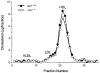
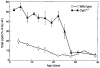
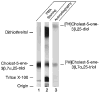
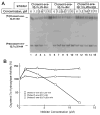
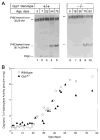
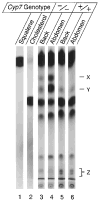
Past experiments and current paradigms of cholesterol homeostasis suggest that cholesterol 7alpha-hydroxylase plays a crucial role in sterol metabolism by controlling the conversion of cholesterol into bile acids. Consistent with this conclusion, we show in the accompanying paper that mice deficient in cholesterol 7alpha-hydroxylase (Cyp7-/- mice) exhibit a complex phenotype consisting of abnormal lipid excretion, skin pathologies, and behavioral irregularities (Ishibashi, S., Schwarz, M., Frykman, P. K. , Herz, J., and Russell, D. W.(1996) J. Biol. Chem. 261, 18017-18023). Aspects of lipid metabolism in the Cyp7-/- mice are characterized here to deduce the physiological basis of this phenotype. Serum lipid, cholesterol, and lipoprotein contents are indistinguishable between wild-type and Cyp7-/- mice. Vitamin D3 and E levels are low to undetectable in knockout animals. Stool fat content is significantly elevated in newborn Cyp7-/- mice and gradually declines to wild-type levels at 28 days of age. Several species of 7alpha-hydroxylated bile acids are detected in the bile and stool of adult Cyp7-/- animals. A hepatic oxysterol 7alpha-hydroxylase enzyme activity that may account for the 7alpha-hydroxylated bile acids is induced between days 21 and 30 in both wild-type and deficient mice. An anomalous oily coat in the Cyp7-/- animals is due to the presence of excess monoglyceride esters in the fur. These data show that 7alpha-hydroxylase and the pathway of bile acid synthesis initiated by this enzyme are essential for proper absorption of dietary lipids and fat-soluble vitamins in newborn mice, but not for the maintenance of serum cholesterol and lipid levels. In older animals, an alternate pathway of bile acid synthesis involving an inducible oxysterol 7alpha-hydroxylase plays a crucial role in lipid and bile acid metabolism.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Disruption of cholesterol 7alpha-hydroxylase gene in mice. I. Postnatal lethality reversed by bile acid and vitamin supplementation.J Biol Chem. 1996 Jul 26;271(30):18017-23. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.30.18017. J Biol Chem. 1996. PMID: 8663429
-
Alternate pathways of bile acid synthesis in the cholesterol 7alpha-hydroxylase knockout mouse are not upregulated by either cholesterol or cholestyramine feeding.J Lipid Res. 2001 Oct;42(10):1594-603. J Lipid Res. 2001. PMID: 11590215
-
Identification and characterization of a mouse oxysterol 7alpha-hydroxylase cDNA.J Biol Chem. 1997 Sep 19;272(38):23995-4001. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.38.23995. J Biol Chem. 1997. PMID: 9295351
-
Regulation of bile acid synthesis.Front Biosci. 1998 Feb 15;3:d176-93. doi: 10.2741/a273. Front Biosci. 1998. PMID: 9450986 Review.
-
Cytochrome P450s in the synthesis of cholesterol and bile acids--from mouse models to human diseases.FEBS J. 2012 May;279(9):1516-33. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2011.08432.x. Epub 2011 Dec 22. FEBS J. 2012. PMID: 22111624 Review.
Cited by
-
Delineation of biochemical, molecular, and physiological changes accompanying bile acid pool size restoration in Cyp7a1(-/-) mice fed low levels of cholic acid.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2012 Jul 15;303(2):G263-74. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00111.2012. Epub 2012 May 24. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22628034 Free PMC article.
-
Intestinal caveolin-1 is important for dietary fatty acid absorption.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Aug;1831(8):1311-21. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2013.05.001. Epub 2013 May 7. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23665238 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of HSD3B7 knockout mice reveals that a 3alpha-hydroxyl stereochemistry is required for bile acid function.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Jul 10;104(28):11526-33. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0705089104. Epub 2007 Jun 29. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 17601774 Free PMC article.
-
Mice deficient in group VIB phospholipase A2 (iPLA2gamma) exhibit relative resistance to obesity and metabolic abnormalities induced by a Western diet.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2010 Jun;298(6):E1097-114. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00780.2009. Epub 2010 Feb 23. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2010. PMID: 20179248 Free PMC article.
-
The bile acid synthetic gene 3beta-hydroxy-Delta(5)-C(27)-steroid oxidoreductase is mutated in progressive intrahepatic cholestasis.J Clin Invest. 2000 Nov;106(9):1175-84. doi: 10.1172/JCI10902. J Clin Invest. 2000. PMID: 11067870 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Russell DW, Setchell KDR. Biochemistry. 1992;31:4737–4749. - PubMed
-
- Axelson M, Sjövall J. J Steroid Biochem. 1990;36:631–640. - PubMed
-
- Björkhem I. J Lipid Res. 1992;33:455–471. - PubMed
-
- Toll A, Wikvall K, Sudjana-Sugiaman E, Kondo K, Björkhem I. Eur J Biochem. 1994;224:309–316. - PubMed
-
- Axelson M, Shoda J, Sjövall J, Toll A, Wikvall K. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:1701–1704. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

