Human microsomal epoxide hydrolase: genetic polymorphism and functional expression in vitro of amino acid variants
- PMID: 7516776
- PMCID: PMC4868095
- DOI: 10.1093/hmg/3.3.421
Human microsomal epoxide hydrolase: genetic polymorphism and functional expression in vitro of amino acid variants
Erratum in
- Hum Mol Genet 1994 Jul;3(7):1214
Abstract
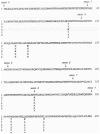
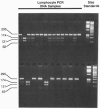
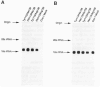
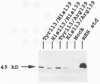
Human microsomal epoxide hydrolase (mEH) is a biotransformation enzyme that metabolizes reactive epoxide intermediates to more water-soluble trans-dihydrodiol derivatives. We compared protein-coding sequences from six full-length human mEH DNA clones and assessed potential amino acid variation at seven positions. The prevalence of these variants was assessed in at least 37 unrelated individuals using polymerase chain reaction experiments. Only Tyr/His 113 (exon 3) and His/Arg 139 (exon 4) variants were observed. The genotype frequencies determined for residue 113 alleles indicate that this locus may not be in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, whereas frequencies observed for residue 139 alleles were similar to expected values. Nucleotide sequences coding for the variant amino acids were constructed in an mEH cDNA using site-directed mutagenesis, and each was expressed in vitro by transient transfection of COS-1 cells. Epoxide hydrolase mRNA level, catalytic activity, and immunoreactive protein were evaluated for each construct. The results of these analyses demonstrated relatively uniform levels of mEH RNA expression between the constructs. mEH enzymatic activity and immunoreactive protein were strongly correlated, indicating that mEH specific activity was similar for each variant. However, marked differences were noted in the relative amounts of immunoreactive protein and enzymatic activity resulting from the amino acid substitutions. These data suggest that common human mEH amino acid polymorphisms may alter enzymatic function, possibly by modifying protein stability.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Post-transcriptional regulation of human microsomal epoxide hydrolase.Pharmacogenetics. 1998 Apr;8(2):157-67. doi: 10.1097/00008571-199804000-00008. Pharmacogenetics. 1998. PMID: 10022753
-
Variability in human sensitivity to 1,3-butadiene: Influence of the allelic variants of the microsomal epoxide hydrolase gene.Environ Mol Mutagen. 2003;41(2):140-6. doi: 10.1002/em.10142. Environ Mol Mutagen. 2003. PMID: 12605384
-
Induction of rat liver microsomal epoxide hydrolase by thiazole and pyrazine: hydrolysis of 2-cyanoethylene oxide.Carcinogenesis. 1993 Aug;14(8):1665-70. doi: 10.1093/carcin/14.8.1665. Carcinogenesis. 1993. PMID: 7689039
-
Epoxide hydrolase--polymorphism and role in toxicology.Toxicol Lett. 2000 Mar 15;112-113:365-70. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4274(99)00235-0. Toxicol Lett. 2000. PMID: 10720753 Review.
-
Microsomal epoxide hydrolase polymorphisms and lung cancer risk: a quantitative review.Biomarkers. 2002 May-Jun;7(3):230-41. doi: 10.1080/13547500210121882. Biomarkers. 2002. PMID: 12141066 Review.
Cited by
-
Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Relationship between EPHX1 Polymorphisms and the Risk of Head and Neck Cancer.PLoS One. 2015 Apr 29;10(4):e0123347. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0123347. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25923690 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association of microsomal epoxide hydrolase polymorphisms and lung cancer risk.Br J Cancer. 2003 Aug 18;89(4):702-6. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6601142. Br J Cancer. 2003. PMID: 12915882 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction of cigarette smoking and carcinogen-metabolizing polymorphisms in the risk of colorectal polyps.Carcinogenesis. 2013 Apr;34(4):779-86. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgs410. Epub 2013 Jan 8. Carcinogenesis. 2013. PMID: 23299405 Free PMC article.
-
Microsomal epoxide hydrolase gene polymorphisms and risk of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: A comprehensive meta-analysis.Oncol Lett. 2013 Mar;5(3):1022-1030. doi: 10.3892/ol.2012.1099. Epub 2012 Dec 28. Oncol Lett. 2013. PMID: 23426996 Free PMC article.
-
Carbamazepine-Mediated Adverse Drug Reactions: CBZ-10,11-epoxide but Not Carbamazepine Induces the Alteration of Peptides Presented by HLA-B∗15:02.J Immunol Res. 2018 Sep 13;2018:5086503. doi: 10.1155/2018/5086503. eCollection 2018. J Immunol Res. 2018. PMID: 30302345 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vogel-Bindel U, Bendey P, Oesch F. Eur J Biochem. 1982;126:425–431. - PubMed
-
- Guengerich FP. In: Reviews in Biochemical Toxicology. Hodgson E, Bend JR, Philpot RM, editors. Vol. 4. Elsevier Biomedical; New York: 1982. pp. 5–30.
-
- Lu AYH, Miwa GT. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1980;20:513–531. - PubMed
-
- Sims P, Grover PL, Swaisland A, Pal K, Hewer A. Nature. 1974;252:326–328. - PubMed
-
- Buehler BA, Delimont D, van Waes M, Finnell RH. N Engl J Med. 1990;322:1567–1572. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

