Randomized Clinical Trial to Evaluate the Effect of Probiotic Intake on Androgenic Alopecia
- PMID: 39275216
- PMCID: PMC11397619
- DOI: 10.3390/nu16172900
Randomized Clinical Trial to Evaluate the Effect of Probiotic Intake on Androgenic Alopecia
Abstract
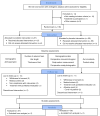
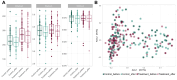
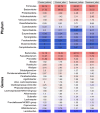
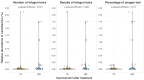
This study aimed to assess the impact of a combination of probiotic strains of Lactiplantibacillus on the treatment of androgenic alopecia (AGA). To this end, 136 individuals with AGA (62 men and 74 women) aged 18-65 years were enrolled in a double-blind, parallel-group clinical trial. A total of 115 individuals (57 in the probiotic group and 58 in the placebo group) completed this study within a 16-week intervention period. Capillary density, thickness, and length of hair were analyzed before and after the intervention using FotoFinder Trichoscale Pro. In addition, the gut microbiota was assessed by paired-end sequencing on the Illumina MiSeq platform (2 × 300 bp). At the conclusion of the treatment period, a notable decline (p < 0.05) in the number of telogen hairs was evident in the probiotic group while hair thickness decreased in the placebo group (p < 0.05). However, the remaining variables did not exhibit any statistically significant changes. In the probiotic-treated group, individuals aged less than 37.5 years exhibited a reduction in the number and density of telogen hair (p = 0.0693 and p = 0.0669, respectively) and an increase in hair length (p = 0.0871). Furthermore, a notable decline in the number and density of vellus hair (p < 0.05) was observed, and this was accompanied by no change in the hair thickness. The probiotic-treated group exhibited a significantly higher abundance of Lactobacillus (p-adjusted < 0.05, DEseq2 test) and demonstrated a notable reduction in the number and density of telogen hair, and this was accompanied by an increase in the percentage of anagen hair. The probiotic mixture was well tolerated by the participants, with a treatment adherence rate of 90%. In light of this study's limitations, it can be concluded that a mixture of three strains of Lactiplantibacillus promotes the presence of terminal follicles, preventing their gradual miniaturization, which is a characteristic of AGA.
Keywords: androgenetic alopecia; gut microbiota; probiotic; trichoscopy.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors Cristina Vilanova and Daniel Torrent were employed by the company Darwing Bioprospecting Excaellence S.L. They participated in the taxonomic analysis of the participants’ gut microbiomes. The samples analyzed were anonymized. So, the author did not know which treatment group each sample belonged to. The role of the company was to analyze the gut microbiome of the participants and the effect of probiotic/placebo supplementation on it. Authors Alejandro García-Navarro, Isabel Moles-Ugeda and Estefanía Gallego-Herrera were employed by Centro Dermatológico Estético. They participated in patient recruitment and blinded assessments, applying the study protocol. The role of the company was to conduct the study according to the approved protocol by the Ethics Committee. Author Roge Navarro-Belmonte was employed by Centro Dermatológico Estético. She participated in the management of the technical resources required to carry out the study. The role of the company was to conduct the study according to the approved protocol by the Ethics Committee. Author María Isabel Vasallo-Morillas was employed by San Antonio Technologies, S.L. She participated in the design, monitoring and management of the study. The role of the company was to manage and monitor the study according to the approved protocol by the Ethics Committee. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Finasteride increases anagen hair in men with androgenetic alopecia.Br J Dermatol. 2000 Oct;143(4):804-10. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2133.2000.03780.x. Br J Dermatol. 2000. PMID: 11069460 Clinical Trial.
-
Expression of the L-fucose moiety on infrainfundibular follicular keratinocytes of terminal follicles, its decreased expression on vellus and indeterminate follicles of androgenetic alopecia, and re-expression in drug-induced hair regrowth.J Invest Dermatol. 1992 Jan;98(1):73-8. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12495536. J Invest Dermatol. 1992. PMID: 1370232 Clinical Trial.
-
A randomized double-blind placebo-controlled pilot study to assess the efficacy of a 24-week topical treatment by latanoprost 0.1% on hair growth and pigmentation in healthy volunteers with androgenetic alopecia.J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012 May;66(5):794-800. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2011.05.026. Epub 2011 Aug 27. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012. PMID: 21875758 Clinical Trial.
-
Effectiveness and Safety of Hair Growth Formulation Containing Tectona grandis L.f (Teak) Leaf Extract: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study on Males with Androgenic Alopecia.J Evid Based Integr Med. 2024 Jan-Dec;29:2515690X241291141. doi: 10.1177/2515690X241291141. J Evid Based Integr Med. 2024. PMID: 39474646 Clinical Trial.
-
Interventions for female pattern hair loss.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 May 26;2016(5):CD007628. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007628.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27225981 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ferrando J., Grimalt R., Hausmann G., Lacueva L., Moreno G. Alopecias Guía de Diagnóstico y Tratamiento. 2000 Pulso Ediciones; Sant Cugat del Vallès, Spain: 2007.
-
- Vaño S., Jaén P. Manual Práctico de Tricología. #TricoHRC. 1st ed. Editorial Médica Panamericana; Madrid, Spain: 2019.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

