Unprecedented selectivity for homologous lectin targets: differential targeting of the viral receptors L-SIGN and DC-SIGN
- PMID: 39246372
- PMCID: PMC11376147
- DOI: 10.1039/d4sc02980a
Unprecedented selectivity for homologous lectin targets: differential targeting of the viral receptors L-SIGN and DC-SIGN
Abstract
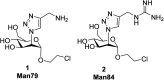
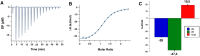
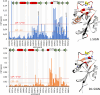
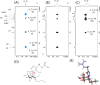
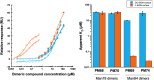
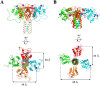
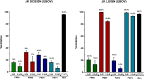
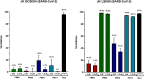
DC-SIGN (CD209) and L-SIGN (CD209L) are two C-type lectin receptors (CLRs) that facilitate SARS-CoV-2 infections as viral co-receptors. SARS-CoV-2 manipulates both DC-SIGN and L-SIGN for enhanced infection, leading to interest in developing receptor antagonists. Despite their structural similarity (82% sequence identity), they function differently. DC-SIGN, found in dendritic cells, shapes the immune response by recognizing pathogen-associated carbohydrate patterns. In contrast, L-SIGN, expressed in airway epithelial endothelial cells, is not directly involved in immunity. COVID-19's primary threat is the hyperactivation of the immune system, potentially reinforced if DC-SIGN engages with exogenous ligands. Therefore, L-SIGN, co-localized with ACE2-expressing cells in the respiratory tract, is a more suitable target for anti-adhesion therapy. However, designing a selective ligand for L-SIGN is challenging due to the high sequence identity of the Carbohydrate Recognition Domains (CRDs) of the two lectins. We here present Man84, a mannose ring modified with a methylene guanidine triazole at position 2. It binds L-SIGN with a K D of 12.7μM ± 1 μM (ITC) and is the first known L-SIGN selective ligand, showing 50-fold selectivity over DC-SIGN (SPR). The X-ray structure of the L-SIGN CRD/Man84 complex reveals the guanidinium group's role in achieving steric and electrostatic complementarity with L-SIGN. This allows us to trace the source of selectivity to a single amino acid difference between the two CRDs. NMR analysis confirms the binding mode in solution, highlighting Man84's conformational selection upon complex formation. Dimeric versions of Man84 achieve additional selectivity and avidity in the low nanomolar range. These compounds selectively inhibit L-SIGN dependent trans-infection by SARS-CoV-2 and Ebola virus. Man84 and its dimeric constructs display the best affinity and avidity reported to date for low-valency glycomimetics targeting CLRs. They are promising tools for competing with SARS-CoV-2 anchoring in the respiratory tract and have potential for other medical applications.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following competing financial interest(s): S. P., C. D., M. T., F. F., and A. B. declare the filing of a patent covering the use of glycomimetic L-SIGN ligands as antagonist, anti-viral adhesion, and for targeting human L-SIGN-expressing cells.
Figures




Similar articles
-
C-type Lectin CD209L/L-SIGN and CD209/DC-SIGN: Cell Adhesion Molecules Turned to Pathogen Recognition Receptors.Biology (Basel). 2020 Dec 22;10(1):1. doi: 10.3390/biology10010001. Biology (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33375175 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Selective targeting of dendritic cell-specific intercellular adhesion molecule-3-grabbing nonintegrin (DC-SIGN) with mannose-based glycomimetics: synthesis and interaction studies of bis(benzylamide) derivatives of a pseudomannobioside.Chemistry. 2013 Apr 8;19(15):4786-97. doi: 10.1002/chem.201202764. Epub 2013 Feb 18. Chemistry. 2013. PMID: 23417900
-
Rational-Differential Design of Highly Specific Glycomimetic Ligands: Targeting DC-SIGN and Excluding Langerin Recognition.ACS Chem Biol. 2018 Mar 16;13(3):600-608. doi: 10.1021/acschembio.7b00958. Epub 2018 Jan 8. ACS Chem Biol. 2018. PMID: 29272097
-
Sweet Drugs for Bad Bugs: A Glycomimetic Strategy against the DC-SIGN-Mediated Dissemination of SARS-CoV-2.J Am Chem Soc. 2021 Oct 27;143(42):17465-17478. doi: 10.1021/jacs.1c06778. Epub 2021 Oct 15. J Am Chem Soc. 2021. PMID: 34652144
-
From structure to function - Ligand recognition by myeloid C-type lectin receptors.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2022 Oct 20;20:5790-5812. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2022.10.019. eCollection 2022. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2022. PMID: 36382179 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

