A genome-wide investigation into the underlying genetic architecture of personality traits and overlap with psychopathology
- PMID: 39134740
- PMCID: PMC11576509
- DOI: 10.1038/s41562-024-01951-3
A genome-wide investigation into the underlying genetic architecture of personality traits and overlap with psychopathology
Abstract
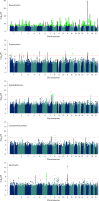
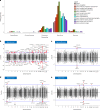
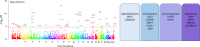
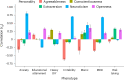
Personality is influenced by both genetic and environmental factors and is associated with other psychiatric traits such as anxiety and depression. The 'big five' personality traits, which include neuroticism, extraversion, agreeableness, conscientiousness and openness, are a widely accepted and influential framework for understanding and describing human personality. Of the big five personality traits, neuroticism has most often been the focus of genetic studies and is linked to various mental illnesses, including depression, anxiety and schizophrenia. Our knowledge of the genetic architecture of the other four personality traits is more limited. Here, utilizing the Million Veteran Program cohort, we conducted a genome-wide association study in individuals of European and African ancestry. Adding other published data, we performed genome-wide association study meta-analysis for each of the five personality traits with sample sizes ranging from 237,390 to 682,688. We identified 208, 14, 3, 2 and 7 independent genome-wide significant loci associated with neuroticism, extraversion, agreeableness, conscientiousness and openness, respectively. These findings represent 62 novel loci for neuroticism, as well as the first genome-wide significant loci discovered for agreeableness. Gene-based association testing revealed 254 genes showing significant association with at least one of the five personality traits. Transcriptome-wide and proteome-wide analysis identified altered expression of genes and proteins such as CRHR1, SLC12A5, MAPT and STX4. Pathway enrichment and drug perturbation analyses identified complex biology underlying human personality traits. We also studied the inter-relationship of personality traits with 1,437 other traits in a phenome-wide genetic correlation analysis, identifying new associations. Mendelian randomization showed positive bidirectional effects between neuroticism and depression and anxiety, while a negative bidirectional effect was observed for agreeableness and these psychiatric traits. This study improves our comprehensive understanding of the genetic architecture underlying personality traits and their relationship to other complex human traits.
© 2024. This is a U.S. Government work and not under copyright protection in the US; foreign copyright protection may apply.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Update of
-
A genome-wide investigation into the underlying genetic architecture of personality traits and overlap with psychopathology.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jan 17:2024.01.17.24301428. doi: 10.1101/2024.01.17.24301428. medRxiv. 2024. Update in: Nat Hum Behav. 2024 Nov;8(11):2235-2249. doi: 10.1038/s41562-024-01951-3. PMID: 38293137 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
Similar articles
-
Haplotype function score improves biological interpretation and cross-ancestry polygenic prediction of human complex traits.Elife. 2024 Apr 19;12:RP92574. doi: 10.7554/eLife.92574. Elife. 2024. PMID: 38639992 Free PMC article.
-
Depressing time: Waiting, melancholia, and the psychoanalytic practice of care.In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. PMID: 36137063 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
A genome-wide investigation into the underlying genetic architecture of personality traits and overlap with psychopathology.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jan 17:2024.01.17.24301428. doi: 10.1101/2024.01.17.24301428. medRxiv. 2024. Update in: Nat Hum Behav. 2024 Nov;8(11):2235-2249. doi: 10.1038/s41562-024-01951-3. PMID: 38293137 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Dynamic Field Theory of Executive Function: Identifying Early Neurocognitive Markers.Monogr Soc Res Child Dev. 2024 Dec;89(3):7-109. doi: 10.1111/mono.12478. Monogr Soc Res Child Dev. 2024. PMID: 39628288 Free PMC article.
-
Trends in Surgical and Nonsurgical Aesthetic Procedures: A 14-Year Analysis of the International Society of Aesthetic Plastic Surgery-ISAPS.Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2024 Oct;48(20):4217-4227. doi: 10.1007/s00266-024-04260-2. Epub 2024 Aug 5. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2024. PMID: 39103642 Review.
References
-
- John, O. P. & Srivastava, S. in Handbook of Personality: Theory and Research (eds Pervin, L. A. and John, O. P.) (Guilford Press, 1999).
-
- McCrae, R. R. & Costa, P. T. Personality in Adulthood: A Five-factor Theory Perspective (Guilford Press, 2003).
-
- Kendler, K. S. & Myers, J. The genetic and environmental relationship between major depression and the five-factor model of personality. Psychol. Med.40, 801–806 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Hettema, J. M. et al. A population-based twin study of the relationship between neuroticism and internalizing disorders. Am. J. Psychiatry163, 857–864 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Hettema, J. M., Prescott, C. A. & Kendler, K. S. Genetic and environmental sources of covariation between generalized anxiety disorder and neuroticism. Am. J. Psychiatry161, 1581–1587 (2004). - PubMed

